|
Pot De Fer
The ''pot-de-fer'' was a primitive cannon made of iron. It was used by France in the Middle Ages, the French in the Hundred Years' War. The name means "iron pot" in French language, French. In Italy, ''pots-de-fer'' were known as ''vasi'' or ''vasii'', meaning "pot" or "vase". Description Though occasionally made with casting, cast bronze, the ''pot-de-fer'' was essentially an iron bottle with a narrow neck. It was loaded with gunpowder, powder and an iron arrow-like Crossbow bolt, bolt, fletching, feathered with iron. It is believed that the middle of the bolt was likely wrapped in leather for a snug fit, necessary to enhance the thrust from the gaseous pressure within the cannon. However, this feature is not shown in illuminated manuscript, manuscript illuminations. The cannon was set off through a small-diameter touchhole, where a red-hot wire could be thrust to set off an explosion and fire the cannon.Manucy, Albert, ''Artillery through the Ages: A Short Illustrated History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illuminated Manuscript
An illuminated manuscript is a formally prepared document where the text is often supplemented with flourishes such as borders and miniature illustrations. Often used in the Roman Catholic Church for prayers, liturgical services and psalms, the practice continued into secular texts from the 13th century onward and typically include proclamations, enrolled bills, laws, charters, inventories and deeds. While Islamic manuscripts can also be called illuminated, and use essentially the same techniques, comparable Far Eastern and Mesoamerican works are described as ''painted''. The earliest illuminated manuscripts in existence come from the Kingdom of the Ostrogoths and the Eastern Roman Empire and date from between 400 and 600 CE. Examples include the Codex Argenteus and the Rossano Gospels, both of which are from the 6th century. The majority of extant manuscripts are from the Middle Ages, although many survive from the Renaissance, along with a very limited number from Late Antiqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Quesnoy
Le Quesnoy (; pcd, L' Kénoé) is a commune and small town in the east of the Nord department of northern France. It was part of the historical province of French Hainaut. It had a keynote industry in shoemaking before the late 1940s, followed by a chemical factory and dairy, giving way to its weekly market, tourism, local commuting to elsewhere such as Valenciennes and local shops. Le Quesnoy's inhabitants are known as ''Quercitains''. Economy The town of Le Quesnoy has somehow missed much of the Industrial Revolution. Unlike the neighboring towns of Valenciennes or Maubeuge, iron/steel works did not take hold. The lack of wealth underground and of a major transportation route partly explains this. The authorities, however, took note of this weakness and proposed the Ecaillon canal from Sambre to Scheldt; considered but abandoned because of low water yield in the forest of Mormal. Shoemaking was a major local industry until at least 1945, when a hundred shoemakers were s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
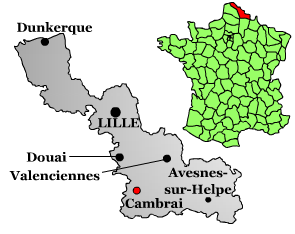
Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; pcd, Kimbré; nl, Kamerijk), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord (French department), Nord Departments of France, department and in the Hauts-de-France Regions of France, region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the Escaut river. A Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture of the department, Cambrai is a town which had 32,501 inhabitants in 2018. It is in the heart of the urban unit of Cambrai with 46,772 inhabitants. Its functional area (France), functional area, a more extensive range, included 94,576 inhabitants in 2018.Comparateur de territoire: Aire d'attraction des villes 2020 de Cambra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Périgord
Périgord ( , ; ; oc, Peiregòrd / ) is a natural region and former province of France, which corresponds roughly to the current Dordogne department, now forming the northern part of the administrative region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine. It is divided into four areas called the Périgord Noir (Black), named so for the truffles that can be found there, the Périgord Blanc (White), for chalk cliffs and quarries, the Périgord Vert (Green), for forests and forestry and the Périgord Pourpre (Purple), for wine and viticulture . The geography and natural resources of Périgord make it a region rich in history and wildlife, and the newly created Parc Naturel Régional Périgord-Limousin aims to conserve it as such. Périgord is noted for its cuisine, especially its duck and goose products, such as ''confit de canard'' and ''foie gras''. It is known as a centre for truffles in France. Périgourdine wines include Bergerac (red and white) and Monbazillac. Geography Périgord surrounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southampton
Southampton () is a port city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. It is located approximately south-west of London and west of Portsmouth. The city forms part of the South Hampshire built-up area, which also covers Portsmouth and the towns of Havant, Waterlooville, Eastleigh, Fareham and Gosport. A major port, and close to the New Forest, it lies at the northernmost point of Southampton Water, at the confluence of the River Test and Itchen, with the River Hamble joining to the south. Southampton is classified as a Medium-Port City . Southampton was the departure point for the and home to 500 of the people who perished on board. The Spitfire was built in the city and Southampton has a strong association with the ''Mayflower'', being the departure point before the vessel was forced to return to Plymouth. In the past century, the city was one of Europe's main ports for ocean liners and more recently, Southampton is known as the home port of some of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muzzle (firearm)
A gun barrel is a crucial part of gun-type weapons such as small firearms, artillery pieces, and air guns. It is the straight shooting tube, usually made of rigid high-strength metal, through which a contained rapid expansion of high-pressure gas(es) is used to propel a projectile out of the front end ( muzzle) at a high velocity. The hollow interior of the barrel is called the bore, and the diameter of the bore is called its caliber, usually measured in inches or millimetres. The first firearms were made at a time when metallurgy was not advanced enough to cast tubes capable of withstanding the explosive forces of early cannons, so the pipe (often built from staves of metal) needed to be braced periodically along its length for structural reinforcement, producing an appearance somewhat reminiscent of storage barrels being stacked together, hence the English name.''A History of Warfare'' - Keegan, John, Vintage 1993. History Gun barrels are usually metal. However, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linstock
A linstock (also called a lintstock) is a staff with a fork at one end to hold a lighted slow match. The name was adapted from the Dutch ''lontstok'', "match stick". Linstocks were used for discharging cannons in the early days of artillery; the linstock allowed the gunner to stand farther from the cannon as it was dangerous applying the lighted match to the touch hole at the breech of the gun: not only could the charge flash back, but the recoil of the cannon might send the carriage toward the gunner. Design Linstocks had serpentine jaws to grip the slow match and a sharp point at the base to stick in the ground. In emergencies gunners could use the spear blade as a weapon to defend the cannon. Like much early modern military equipment the linstock could have an additional function; 16th century examples had measurements in inches and a protractor engraved on the blade to allow the gun captain to check the angle. Obsolescence By the 18th century artillery pieces were bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armor
Armour (British English) or armor (American English; see spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, especially direct contact weapons or projectiles during combat, or from a potentially dangerous environment or activity (e.g. cycling, construction sites, etc.). Personal armour is used to protect soldiers and war animals. Vehicle armour is used on warships, armoured fighting vehicles, and some mostly ground attack combat aircraft. A second use of the term ''armour'' describes armoured forces, armoured weapons, and their role in combat. After the development of armoured warfare, tanks and mechanised infantry and their combat formations came to be referred to collectively as "armour". Etymology The word "armour" began to appear in the Middle Ages as a derivative of Old French. It is dated from 1297 as a "mail, defensive covering worn in combat". The word originates from the Old French , itself derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of England
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign reigns as the head of state of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies (the Bailiwick of Guernsey, the Bailiwick of Jersey and the Isle of Man) and the British Overseas Territories. The current monarch is King Charles III, who ascended the throne on 8 September 2022, upon the death of his mother, Queen Elizabeth II. The monarch and their immediate family undertake various official, ceremonial, diplomatic and representational duties. As the monarchy is constitutional, the monarch is limited to functions such as bestowing honours and appointing the prime minister, which are performed in a non-partisan manner. The sovereign is also able to comment on draft laws which directly affect the monarchy. The monarch is also Head of the British Armed Forces. Though the ultimate executive authority over the government is still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring royal authority after the disastrous and unorthodox reign of his father, Edward II. EdwardIII transformed the Kingdom of England into one of the most formidable military powers in Europe. His fifty-year reign was one of the longest in English history, and saw vital developments in legislation and government, in particular the evolution of the English Parliament, as well as the ravages of the Black Death. He outlived his eldest son, Edward the Black Prince, and the throne passed to his grandson, Richard II. Edward was crowned at age fourteen after his father was deposed by his mother, Isabella of France, and her lover Roger Mortimer. At age seventeen he led a successful coup d'état against Mortimer, the ''de facto'' ruler of the cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter De Millimete
Walter de Milemete was an English scholar who in his early twenties was commissioned by Queen Isabella of France to write a treatise on kingship for her son, the young prince Edward, later king Edward III of England called ''De nobilitatibus, sapientiis, et prudentiis regum'' in 1326. The Treatise includes images of siege weapons and what is probably the first illustration of a firearm: a ''pot-de-fer''. One of the marginal border illustrations in the Milemete Treatise shows a soldier firing a large vase-shaped cannon, the arrow-shaped projectile is seen projecting from the cannon which is pointed at a fortification. In the 1331 siege of Cividale, German knights used guns which were probably very similar to Milemete weapons. The treatise includes an illustration of St. George giving Prince Edward a shield decorated with coat of arms. The manuscript, in a red velvet binding, is now held by the library of Christ Church, Oxford. The treatise also depicts a group of knights flying a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.jpg)


