|
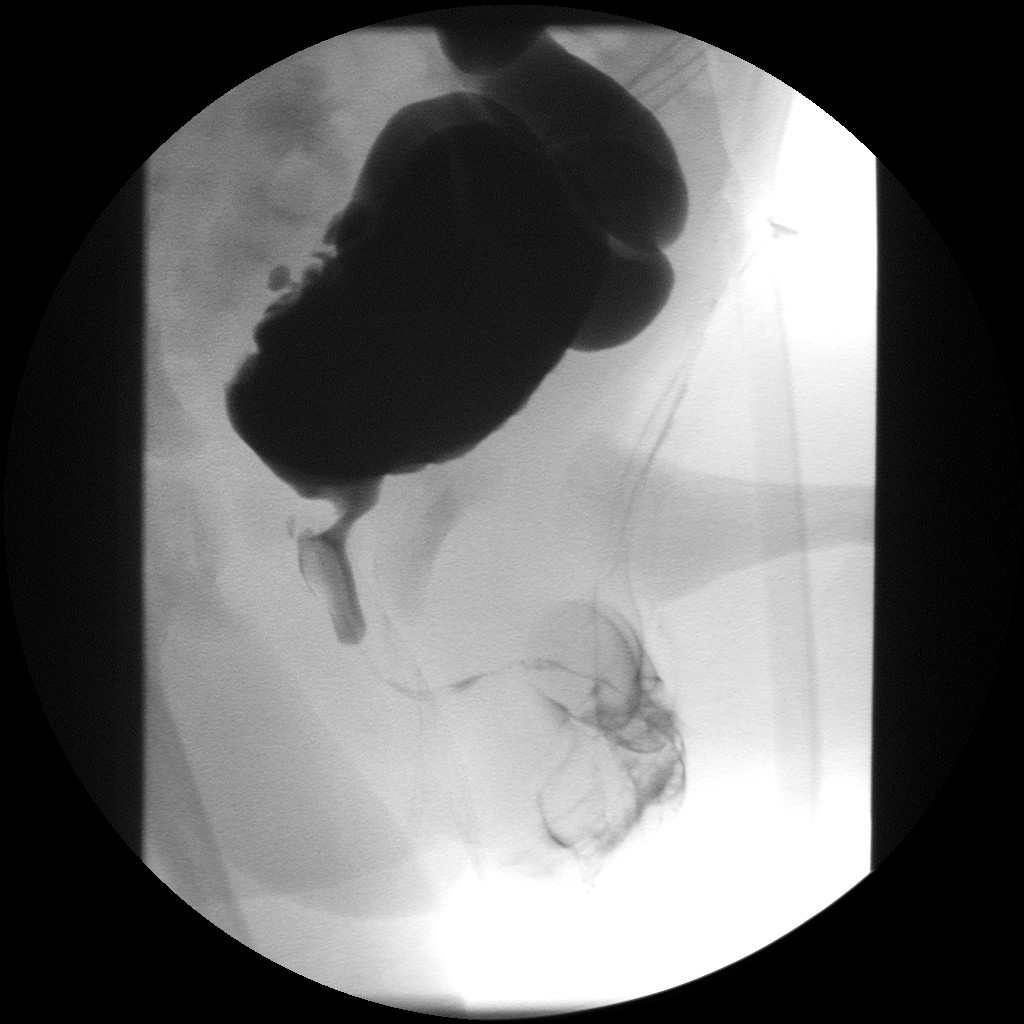
Posterior Urethral Valve
Posterior urethral valve (PUV) disorder is an obstructive developmental anomaly in the urethra and genitourinary system of male newborns. A posterior urethral valve is an obstructing membrane in the posterior male urethra as a result of abnormal ''in utero'' development. It is the most common cause of bladder outlet obstruction in male newborns. The disorder varies in degree, with mild cases presenting late due to milder symptoms. More severe cases can have renal and respiratory failure from lung underdevelopment as result of low amniotic fluid volumes, requiring intensive care and close monitoring. It occurs in about one in 8,000 babies. Presentation PUV can be diagnosed before birth, or even at birth when the ultrasound shows that the male baby has a hydronephrosis. Some babies may also have oligohydramnios due to the urinary obstruction. The later presentation can be a urinary tract infection, diurnal enuresis, or voiding pain. Complications * Incontinence * Urinary tract i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus. Females use their urethra only for urinating, but males use their urethra for both urination and ejaculation. The external urethral sphincter is a striated muscle that allows voluntary control over urination. The internal sphincter, formed by the involuntary smooth muscles lining the bladder neck and urethra, receives its nerve supply by the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. The internal sphincter is present both in males and females. Structure The urethra is a fibrous and muscular tube which connects the urinary bladder to the external urethral meatus. Its length differs between the sexes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diverticula
In medicine or biology, a diverticulum is an outpouching of a hollow (or a fluid-filled) structure in the body. Depending upon which layers of the structure are involved, diverticula are described as being either true or false. In medicine, the term usually implies the structure is not normally present, but in embryology, the term is used for some normal structures arising from others, as for instance the thyroid diverticulum, which arises from the tongue. The word comes from Latin ''dīverticulum'', "bypath" or "byway". Classification Diverticula are described as being true or false depending upon the layers involved: *False diverticula (also known as "pseudodiverticula") do not involve muscular layers or adventitia. False diverticula, in the gastrointestinal tract for instance, involve only the submucosa and mucosa. *True diverticula involve all layers of the structure, including muscularis propria and adventitia, such as Meckel's diverticulum. Embryology *The kidneys are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonologists
Pulmonology (, , from Latin ''pulmō, -ōnis'' "lung" and the Greek suffix "study of"), pneumology (, built on Greek πνεύμων "lung") or pneumonology () is a medical specialty that deals with diseases involving the respiratory tract.ACP: Pulmonology: Internal Medicine Subspecialty . Acponline.org. Retrieved on 2011-09-30. It is also known as respirology, respiratory medicine, or chest medicine in some countries and areas. Pulmonology is considered a branch of internal medicine, and is related to |
Paediatric Surgeons/ Paediatric Urologists
Pediatrics ( also spelled ''paediatrics'' or ''pædiatrics'') is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, paediatrics covers many of their youth until the age of 18. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends people seek pediatric care through the age of 21, but some pediatric subspecialists continue to care for adults up to 25. Worldwide age limits of pediatrics have been trending upward year after year. A medical doctor who specializes in this area is known as a pediatrician, or paediatrician. The word ''pediatrics'' and its cognates mean "healer of children," derived from the two Greek words: (''pais'' "child") and (''iatros'' "doctor, healer"). Pediatricians work in clinics, research centers, universities, general hospitals and children's hospitals, including those who practice pediatric subspecialties (e.g. neonatology requires resources available in a NICU). History The earlies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Bladder
The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10.14 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico -'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad , a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed forward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoma
In botany, a stoma (from Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth", plural "stomata"), also called a stomate (plural "stomates"), is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exchange. The pore is bordered by a pair of specialized parenchyma cells known as guard cells that are responsible for regulating the size of the stomatal opening. The term is usually used collectively to refer to the entire stomatal complex, consisting of the paired guard cells and the pore itself, which is referred to as the stomatal aperture. Air, containing oxygen, which is used in respiration, and carbon dioxide, which is used in photosynthesis, passes through stomata by gaseous diffusion. Water vapour diffuses through the stomata into the atmosphere in a process called transpiration. Stomata are present in the sporophyte generation of all land plant groups except liverworts. In vascular plants the number, size and distribution of stomata varies widely. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amniotic Fluid
The amniotic fluid is the protective liquid contained by the amniotic sac of a gravid amniote. This fluid serves as a cushion for the growing fetus, but also serves to facilitate the exchange of nutrients, water, and biochemical products between mother and fetus. For humans, the amniotic fluid is commonly called water or waters (Latin liquor amnii). Development Amniotic fluid is present from the formation of the gestational sac. Amniotic fluid is in the amniotic sac. It is generated from maternal plasma, and passes through the fetal membranes by osmotic and hydrostatic forces. When fetal kidneys begin to function around week 16, fetal urine also contributes to the fluid. In earlier times, it was believed that the amniotic fluid was composed entirely of fetal urine. The fluid is absorbed through the fetal tissue and skin. After 22 to 25 week of pregnancy, keratinization of an embryo's skin occurs. When this process completes around the 25th week, the fluid is primarily absor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eponymous
An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''. Usage of the word The term ''eponym'' functions in multiple related ways, all based on an explicit relationship between two named things. A person, place, or thing named after a particular person share an eponymous relationship. In this way, Elizabeth I of England is the eponym of the Elizabethan era. When Henry Ford is referred to as "the ''eponymous'' founder of the Ford Motor Company", his surname "Ford" serves as the eponym. The term also refers to the title character of a fictional work (such as Rocky Balboa of the ''Rocky'' film series), as well as to ''self-titled'' works named after their creators (such as the album ''The Doors'' by the band the Doors). Walt Disney created the eponymous Walt Disney Company, with his name similarly extended to theme parks such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostate
The prostate is both an Male accessory gland, accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found only in some mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physiologically. Anatomically, the prostate is found below the Urinary bladder, bladder, with the urethra passing through it. It is described in gross anatomy as consisting of lobes and in microanatomy by zone. It is surrounded by an elastic, fibromuscular capsule and contains glandular tissue as well as connective tissue. The prostate glands produce and contain fluid that forms part of semen, the substance emitted during ejaculation as part of the male Human sexual response cycle, sexual response. This prostatic fluid is slightly alkaline, milky or white in appearance. The alkalinity of semen helps neutralize the acidity of the vagina, vaginal tract, prolonging the lifespan of sperm. The prostatic fluid is expelled in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verumontanum
The seminal colliculus (Latin ''colliculus seminalis''), or verumontanum, of the prostatic urethra is a landmark distal to the entrance of the ejaculatory ducts (on both sides, corresponding vas deferens and seminal vesicle feed into corresponding ejaculatory duct). ''Verumontanum'' is translated from Latin to mean 'mountain ridge', a reference to the distinctive median elevation of urothelium that characterizes the landmark on magnified views. Embryologically, it is derived from the uterovaginal primordium. The landmark is important in classification of several urethral developmental disorders. The margins of seminal colliculus are the following: * the orifices of the prostatic utricle * the slit-like openings of the ejaculatory ducts. * the openings of the prostatic ducts Posterior urethral valves The verumontanum is an important anatomic landmark for pathology in a congenital anomaly known as posterior urethral valves, in which there is a developmental obstruction of the ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emedicine
eMedicine is an online clinical medical knowledge base founded in 1996 by doctors Scott Plantz and Jonathan Adler, and computer engineer Jeffrey Berezin. The eMedicine website consists of approximately 6,800 medical topic review articles, each of which is associated with a clinical subspecialty "textbook". The knowledge base includes over 25,000 clinically multimedia files. Each article is authored by board certified specialists in the subspecialty to which the article belongs and undergoes three levels of physician peer-review, plus review by a Doctor of Pharmacy. The article's authors are identified with their current faculty appointments. Each article is updated yearly, or more frequently as changes in practice occur, and the date is published on the article. eMedicine.com was sold to WebMD in January, 2006 and is available as the Medscape Reference. History Plantz, Adler and Berezin evolved the concept for eMedicine.com in 1996 and deployed the initial site via Boston Med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |