|
Ports Collection
Ports collections (or ''ports trees'', or just ''ports'') are the sets of makefiles and patches provided by the BSD-based operating systems, FreeBSD, NetBSD, and OpenBSD, as a simple method of installing software or creating binary packages. They are usually the base of a package management system, with ports handling package creation and additional tools managing package removal, upgrade, and other tasks. In addition to the BSDs, a few Linux distributions have implemented similar infrastructure, including Gentoo's Portage, Arch's Arch Build System (ABS), CRUX's Ports and Void Linux's Templates. The main advantage of the ports system when compared with a binary distribution model is that the installation can be tuned and optimized according to available resources. For example, the system administrator can easily install a 32 bit version of a package if the 64 bit version is not available or is not optimized for that machine. Conversely, the main disadvantage is compilation time, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FreeBSD Ports
The FreeBSD Ports collection is a package management system for the FreeBSD operating system, providing an easy and consistent way of installing software packages. As of February 2020, there are over 38,487 ports available in the collection. It has also been adopted by NetBSD as the basis of its pkgsrc system. Installing from source The ports collection uses Makefiles arranged in a directory hierarchy so that software can be built, installed and uninstalled with the make command. When installing an application, very little (if any) user intervention is required after issuing a beginning command such as make install or make install clean in the ports directory of the desired application. In most cases the software is automatically downloaded from the Internet, patched and configured if necessary, then compiled, installed and registered in the package database. If the new port has needed dependencies on other applications or libraries, these are installed beforehand automatica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makefile
In software development, Make is a build automation tool that automatically builds executable programs and libraries from source code by reading files called ''Makefiles'' which specify how to derive the target program. Though integrated development environments and language-specific compiler features can also be used to manage a build process, Make remains widely used, especially in Unix and Unix-like operating systems. Besides building programs, Make can be used to manage any project where some files must be updated automatically from others whenever the others change. Origin There are now a number of dependency-tracking build utilities, but Make is one of the most widespread, primarily due to its inclusion in Unix, starting with the PWB/UNIX 1.0, which featured a variety of tools targeting software development tasks. It was originally created by Stuart Feldman in April 1976 at Bell Labs. Feldman received the 2003 ACM Software System Award for the authoring of this widesprea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illumos
Illumos (stylized as illumos) is a partly free and open-source Unix operating system. It is based on OpenSolaris, which was based on System V Release 4 (SVR4) and the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). Illumos comprises a kernel, device drivers, system libraries, and utility software for system administration. This core is now the base for many different open-sourced illumos distributions, in a similar way in which the Linux kernel is used in different Linux distributions. The maintainers write ''illumos'' in lowercase since some computer fonts do not clearly distinguish a lowercase ''L'' from an uppercase ''i'': ''Il'' (see homoglyph). The project name is a combination of words ''illuminare'' from Latin for ''to light'' and ''OS'' for ''Operating System''. Overview Illumos was announced via webinar on Thursday, 3 August 2010, as a community effort of some core Solaris engineers to create a truly open source Solaris by swapping closed source bits of OpenSolaris wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
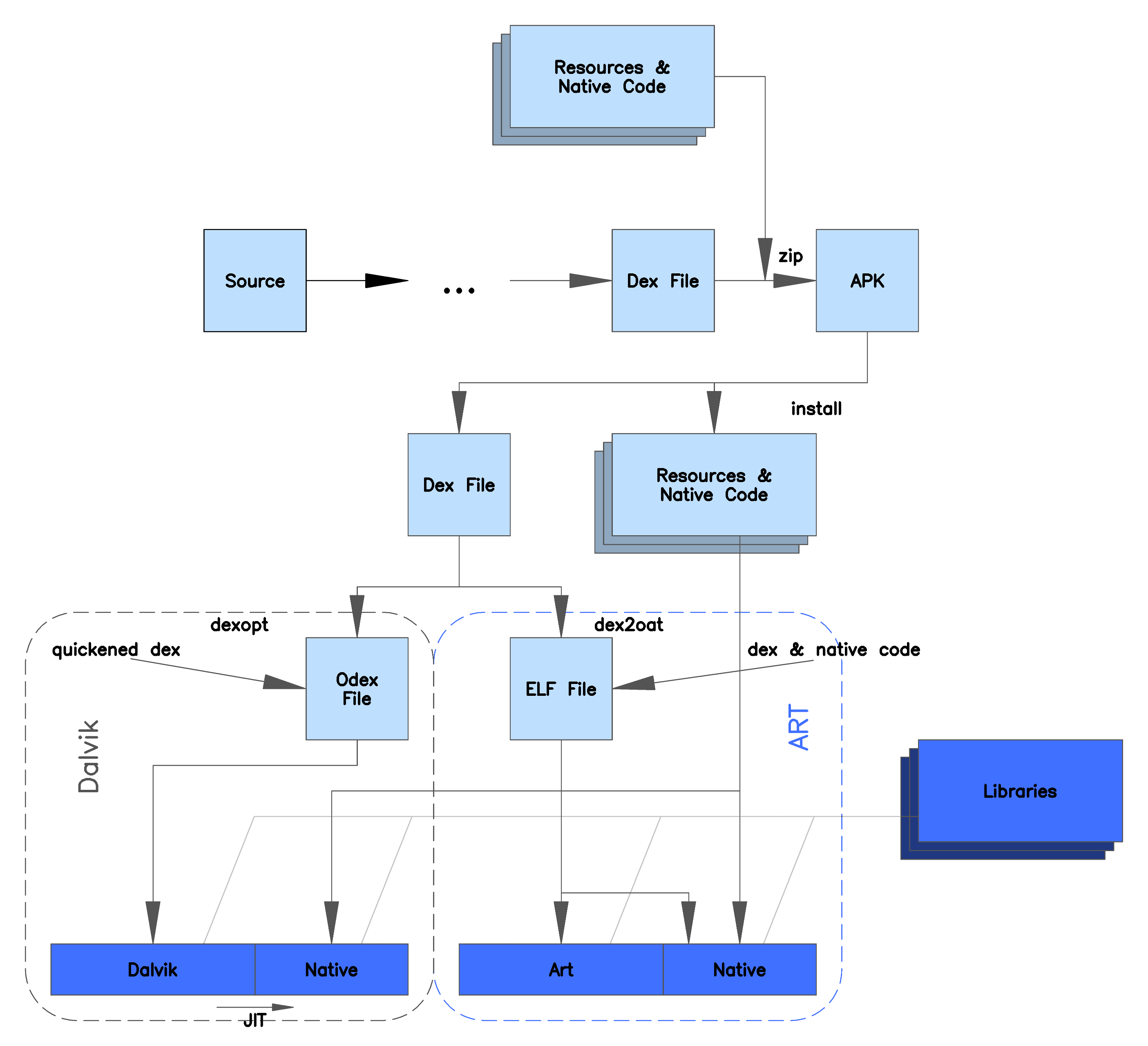
Ahead-of-time Compilation
In computer science, ahead-of-time compilation (AOT compilation) is the act of compiling an (often) higher-level programming language into an (often) lower-level language before execution of a program, usually at build-time, to reduce the amount of work needed to be performed at run time. Most often, It is associated with the act of compiling a higher-level programming language such as C or C++, or an intermediate representation such as Java bytecode or .NET Framework Common Intermediate Language (CIL) code, into a native (system-dependent) machine code so that the resulting binary file can execute natively, just like a ''standard'' native compiler. When being used in this specific context, it's often seen as an opposite of just-in-time (JIT) compiling. Speaking more generally, the target languages of an AOT compilation are not necessarily specific to native machine code but are defined rather arbitrarily. Some academic papers use this word to mean the act of compiling the Java ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Android Runtime
Android Runtime (ART) is an application runtime environment used by the Android operating system. Replacing Dalvik, the process virtual machine originally used by Android, ART performs the translation of the application's bytecode into native instructions that are later executed by the device's runtime environment. Overview Android 2.2 "Froyo" brought trace-based just-in-time (JIT) compilation into Dalvik, optimizing the execution of applications by continually profiling applications each time they run and dynamically compiling frequently executed short segments of their bytecode into native machine code. While Dalvik interprets the rest of application's bytecode, native execution of those short bytecode segments, called "traces", provides significant performance improvements. Unlike Dalvik, ART introduces the use of ahead-of-time (AOT) compilation by compiling entire applications into native machine code upon their installation. By eliminating Dalvik's interpretation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GitHub
GitHub, Inc. () is an Internet hosting service for software development and version control using Git. It provides the distributed version control of Git plus access control, bug tracking, software feature requests, task management, continuous integration, and wikis for every project. Headquartered in California, it has been a subsidiary of Microsoft since 2018. It is commonly used to host open source software development projects. As of June 2022, GitHub reported having over 83 million developers and more than 200 million repositories, including at least 28 million public repositories. It is the largest source code host . History GitHub.com Development of the GitHub.com platform began on October 19, 2007. The site was launched in April 2008 by Tom Preston-Werner, Chris Wanstrath, P. J. Hyett and Scott Chacon after it had been made available for a few months prior as a beta release. GitHub has an annual keynote called GitHub Universe. Organizational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Source Code
In computing, source code, or simply code, is any collection of code, with or without comments, written using a human-readable programming language, usually as plain text. The source code of a program is specially designed to facilitate the work of computer programmers, who specify the actions to be performed by a computer mostly by writing source code. The source code is often transformed by an assembler or compiler into binary machine code that can be executed by the computer. The machine code is then available for execution at a later time. Most application software is distributed in a form that includes only executable files. If the source code were included it would be useful to a user, programmer or a system administrator, any of whom might wish to study or modify the program. Alternatively, depending on the technology being used, source code may be interpreted and executed directly. Definitions Richard Stallman's definition, formulated in his 1989 seminal li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Text File
A text file (sometimes spelled textfile; an old alternative name is flatfile) is a kind of computer file that is structured as a sequence of lines of electronic text. A text file exists stored as data within a computer file system. In operating systems such as CP/M and MS-DOS, where the operating system does not keep track of the file size in bytes, the end of a text file is denoted by placing one or more special characters, known as an end-of-file marker, as padding after the last line in a text file. On modern operating systems such as Microsoft Windows and Unix-like systems, text files do not contain any special EOF character, because file systems on those operating systems keep track of the file size in bytes. Most text files need to have end-of-line delimiters, which are done in a few different ways depending on operating system. Some operating systems with record-orientated file systems may not use new line delimiters and will primarily store text files with lines separat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Package (installation)
A package manager or package-management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer in a consistent manner. A package manager deals with ''packages'', distributions of software and data in archive files. Packages contain metadata, such as the software's name, description of its purpose, version number, vendor, checksum (preferably a cryptographic hash function), and a list of dependencies necessary for the software to run properly. Upon installation, metadata is stored in a local package database. Package managers typically maintain a database of software dependencies and version information to prevent software mismatches and missing prerequisites. They work closely with software repositories, binary repository managers, and app stores. Package managers are designed to eliminate the need for manual installs and updates. This can be particularly useful for large enterp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DragonFly BSD
DragonFly BSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system forked from FreeBSD 4.8. Matthew Dillon, an Amiga developer in the late 1980s and early 1990s and FreeBSD developer between 1994 and 2003, began working on DragonFly BSD in June 2003 and announced it on the FreeBSD mailing lists on 16 July 2003. Dillon started DragonFly in the belief that the techniques adopted for threading and symmetric multiprocessing in FreeBSD 5 would lead to poor performance and maintenance problems. He sought to correct these anticipated problems within the FreeBSD project. Due to conflicts with other FreeBSD developers over the implementation of his ideas, his ability to directly change the codebase was eventually revoked. Despite this, the DragonFly BSD and FreeBSD projects still work together, sharing bug fixes, driver updates, and other improvements. Intended as the logical continuation of the FreeBSD 4.x series, DragonFly has diverged significantly from FreeBSD, implementing lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unix-like
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X or *nix) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Unix-like application is one that behaves like the corresponding Unix command or shell. Although there are general philosophies for Unix design, there is no technical standard defining the term, and opinions can differ about the degree to which a particular operating system or application is Unix-like. Some well-known examples of Unix-like operating systems include Linux and BSD. These systems are often used on servers, as well as on personal computers and other devices. Many popular applications, such as the Apache web server and the Bash shell, are also designed to be used on Unix-like systems. One of the key features of Unix-like systems is their ability to support multiple users and processes simultaneously. This allows users to run multipl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy. Popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, and Ubuntu, the latter of which itself consists of many different distributions and modifications, including Lubuntu and Xubuntu. Commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux and SUSE Linux Enterprise. Desktop Linux distributions include a windowing system such as X11 or Wayland, and a desktop environment such as GNOME or KDE Plasma. Distributions intended for ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)