|
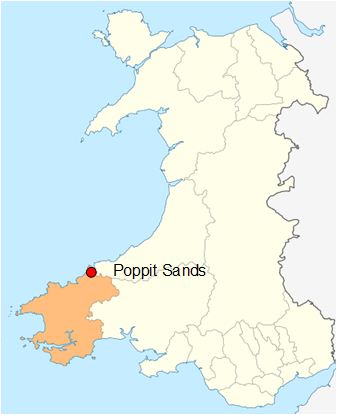
Poppit Sign
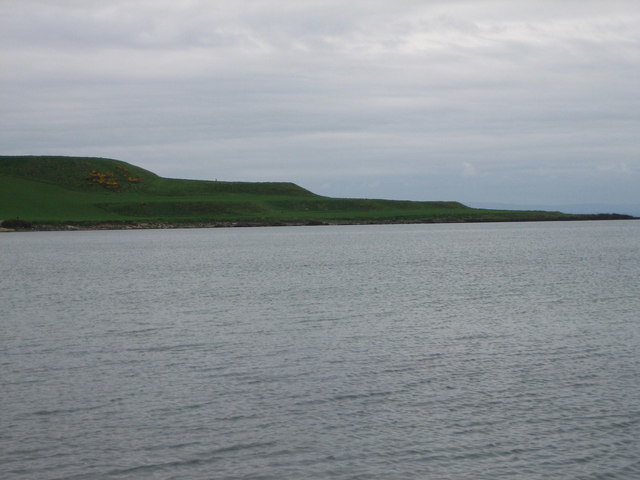
Poppit (), is a small, dispersed settlement which lies on the southern side of the estuary of the River Teifi, near Cardigan, in northern Pembrokeshire, Wales. It is primarily known for its popular sandy beach, called Poppit Sands () which adjoins St Dogmaels beach at its eastern estuary end. The beach offers views across the estuary and bay towards Gwbert and Cardigan Island, and the nearest village is St Dogmaels, 1½ miles away. The beach has Blue Flag status and lifeboat and lifeguard cover. Geography Features Backed by low dunes, the top of the beach comprises about 80m of dry, very loose sand, making it very popular with families. Lower down it is hard-packed. The beach slopes gently, and therefore the sea is shallow for quite a long way out. Even at high tide there is plenty of soft sand exposed. On the eastern side of the dunes, erosion has formed sand cliffs over 4 metres (13 feet) high. New dunes are now building up close to the access boardwalk. When the tid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poppit Sign
Poppit (), is a small, dispersed settlement which lies on the southern side of the estuary of the River Teifi, near Cardigan, in northern Pembrokeshire, Wales. It is primarily known for its popular sandy beach, called Poppit Sands () which adjoins St Dogmaels beach at its eastern estuary end. The beach offers views across the estuary and bay towards Gwbert and Cardigan Island, and the nearest village is St Dogmaels, 1½ miles away. The beach has Blue Flag status and lifeboat and lifeguard cover. Geography Features Backed by low dunes, the top of the beach comprises about 80m of dry, very loose sand, making it very popular with families. Lower down it is hard-packed. The beach slopes gently, and therefore the sea is shallow for quite a long way out. Even at high tide there is plenty of soft sand exposed. On the eastern side of the dunes, erosion has formed sand cliffs over 4 metres (13 feet) high. New dunes are now building up close to the access boardwalk. When the tid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bottlenose Dolphin
Bottlenose dolphins are aquatic mammals in the genus ''Tursiops.'' They are common, cosmopolitan members of the family Delphinidae, the family of oceanic dolphins. Molecular studies show the genus definitively contains two species: the common bottlenose dolphin (''Tursiops truncatus'') and the Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphin (''Tursiops aduncus''). Others, like the Burrunan dolphin (''Tursiops (aduncus) australis''), may be alternately considered their own species or be subspecies of ''T. aduncus''. Bottlenose dolphins inhabit warm and temperate seas worldwide, being found everywhere except for the Arctic and Antarctic Circle regions. Their name derives from the Latin ''tursio'' (dolphin) and ''truncatus'' for their characteristic truncated teeth. Numerous investigations of bottlenose dolphin intelligence have been conducted, examining mimicry, use of artificial language, object categorization, and self-recognition. They can use tools (sponging; using marine sponges to forage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Station
A weather station is a facility, either on land or sea, with instruments and equipment for measuring atmospheric conditions to provide information for weather forecasts and to study the weather and climate. The measurements taken include temperature, atmospheric pressure, humidity, wind speed, wind direction, and precipitation amounts. Wind measurements are taken with as few other obstructions as possible, while temperature and humidity measurements are kept free from direct solar radiation, or insolation. Manual observations are taken at least once daily, while automated measurements are taken at least once an hour. Weather conditions out at sea are taken by ships and buoys, which measure slightly different meteorological quantities such as sea surface temperature (SST), wave height, and wave period. Drifting weather buoys outnumber their moored versions by a significant amount. Weather instruments Typical weather stations have the following instruments: * Thermometer for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Met Office
The Meteorological Office, abbreviated as the Met Office, is the United Kingdom's national weather service. It is an executive agency and trading fund of the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy and is led by CEO Penelope Endersby, who took on the role as Chief Executive in December 2018 and is the first woman to do so. The Met Office makes meteorological predictions across all timescales from weather forecasts to climate change. History The Met Office was established on 1 August 1854 as a small department within the Board of Trade under Vice Admiral (Royal Navy), Vice Admiral Robert FitzRoy as a service to sailor, mariners. The loss of the passenger vessel, the Royal Charter (ship), ''Royal Charter'', and 459 lives off the coast of Anglesey in a violent storm in October 1859 led to the first gale warning service. FitzRoy established a network of 15 coastal stations from which visual gale warnings could be provided for ships at sea. The new electric tele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters (for their latitude), with a relatively narrow annual temperature range and few extremes of temperature. Oceanic climates can be found in both hemispheres generally between 45 and 63 latitude, most notably in northwestern Europe, northwestern America, as well as New Zealand. Precipitation Locations with oceanic climates tend to feature frequent cloudy conditions with precipitation, low hanging clouds, and frequent fronts and storms. Thunderstorms are normally few, since strong daytime heating and hot and cold air masses meet infrequently in the region. In most areas with an oceanic climate, precipitation comes in the form of rain for the majority of the year. However, some areas with this climate see some snowfall annually during winter. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, and over six thousand smaller islands."British Isles", ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. They have a total area of and a combined population of almost 72 million, and include two sovereign states, the Republic of Ireland (which covers roughly five-sixths of Ireland), and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. The Channel Islands, off the north coast of France, are normally taken to be part of the British Isles, even though they do not form part of the archipelago. The oldest rocks are 2.7 billion years old and are found in Ireland, Wales and the northwest of Scotland. During the Silurian period, the north-western regions collided with the south-east, which had been part of a separate continental landmass. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raised Beach
A raised beach, coastal terrace,Pinter, N (2010): 'Coastal Terraces, Sealevel, and Active Tectonics' (educational exercise), from 2/04/2011/ref> or perched coastline is a relatively flat, horizontal or gently inclined surface of marine origin,Pirazzoli, PA (2005a): 'Marine Terraces', in Schwartz, ML (ed) ''Encyclopedia of Coastal Science.'' Springer, Dordrecht, pp. 632–633 mostly an old abrasion platform which has been lifted out of the sphere of wave activity (sometimes called "tread"). Thus, it lies above or under the current sea level, depending on the time of its formation.Strahler AH; Strahler AN (2005): ''Physische Geographie.'' Ulmer, Stuttgart, 686 p.Leser, H (ed)(2005): ‚''Wörterbuch Allgemeine Geographie.'' Westermann&Deutscher Taschenbuch Verlag, Braunschweig, 1119 p. It is bounded by a steeper ascending slope on the landward side and a steeper descending slope on the seaward side (sometimes called "riser"). Due to its generally flat shape, it is often used for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
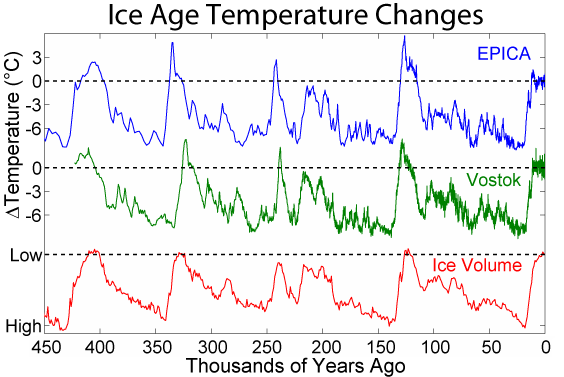
Interglacial Period
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene interglacial began at the end of the Pleistocene, about 11,700 years ago. Pleistocene During the 2.5 million years of the Pleistocene, numerous glacials, or significant advances of continental ice sheets, in North America and Europe, occurred at intervals of approximately 40,000 to 100,000 years. The long glacial periods were separated by more temperate and shorter interglacials. During interglacials, such as the present one, the climate warms and the tundra recedes polewards following the ice sheets. Forests return to areas that once supported tundra vegetation. Interglacials are identified on land or in shallow epicontinental seas by their paleontology. Floral and faunal remains of species pointing to temperate climate and indicating a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
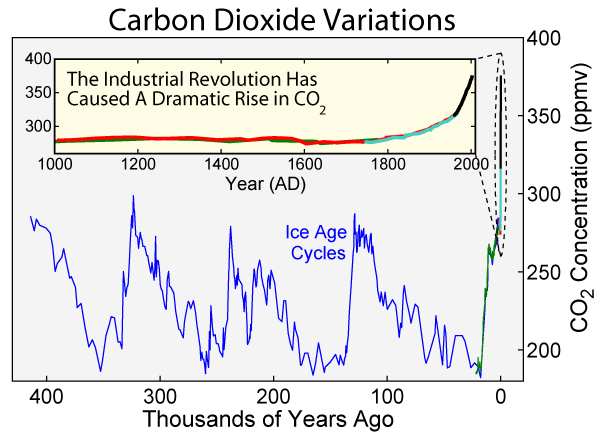
Eemian
The Eemian (also called the last interglacial, Sangamonian, Sangamonian Stage, Ipswichian, Mikulin, Kaydaky, penultimate,NOAA - Penultimate Interglacial Period http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/global-warming/penultimate-interglacial-period Valdivia or Riss-Würm) was the interglacial period which began about 130,000 years ago at the end of the Penultimate Glacial Period and ended about 115,000 years ago at the beginning of the Last Glacial Period. It corresponds to Marine Isotope Stage 5e. Although sometimes referred to as the "last interglacial" (in the "most recent previous" sense of "last"), it was the second-to-latest interglacial period of the current Ice Age, the most recent being the Holocene which extends to the present day (having followed the last glacial period). The prevailing Eemian climate was, on average, around 1 to 2 degrees Celsius (1.8 to 3.6 Fahrenheit) warmer than that of the Holocene. During the Eemian, the proportion of in the atmosphere was about 280 parts per mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
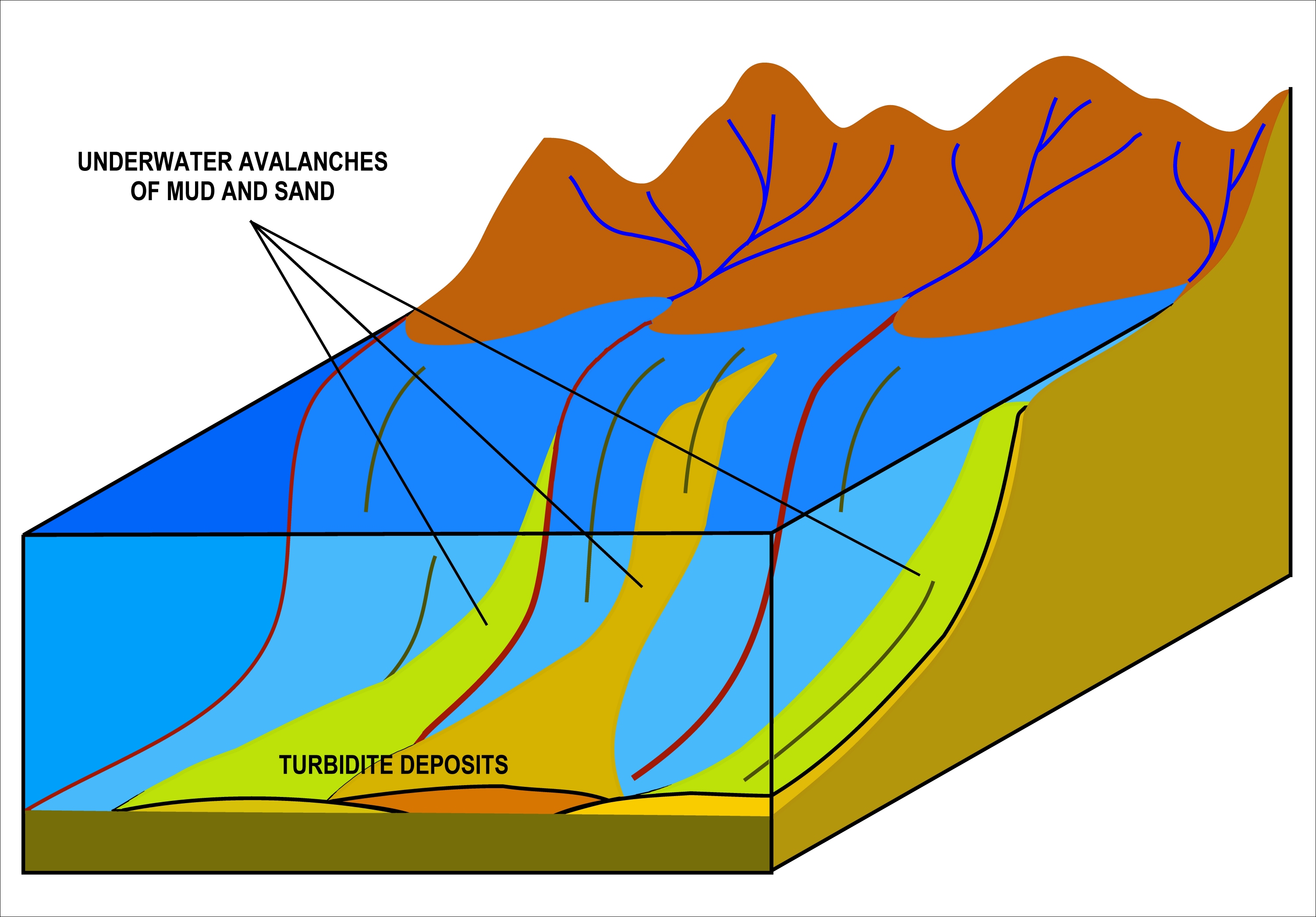
Turbidites
A turbidite is the geologic deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of amalgamation of fluidal and sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean. Sequencing Turbidites were first properly described by Arnold H. Bouma (1962), who studied deepwater sediments and recognized particular "fining-up intervals" within deep water, fine-grained shales, which were anomalous because they started at pebble conglomerates and terminated in shales. This was anomalous because within the deep ocean it had historically been assumed that there was no mechanism by which tractional flow could carry and deposit coarse-grained sediments into the abyssal depths. Bouma cycles begin with an erosional contact of a coarse lower bed of pebble to granule conglomerate in a sandy matrix, and grade up through coarse then medium plane parallel sandstone; through cross-bedded sandstone; rippled cross-bedded sand/silty sand, and finally lamina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) because they are the most resistant minerals to weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be any color due to impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Since sandstone beds often form highly visible cliffs and other topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have been strongly identified with certain regions. Rock formations that are primarily composed of sandstone usually allow the percolation of water and other fluids and are porous enough to store large quantities, making them valuable aquifers and petroleum reservoirs. Quartz-bearing sandstone can be changed into quartzite through metamorphism, usually related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mudstone
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from '' shale'' by its lack of fissility (parallel layering).Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology.'' New York, New York, W. H. Freeman, 2nd ed, 529 pp. The term ''mudstone'' is also used to describe carbonate rocks (limestone or dolomite) that are composed predominantly of carbonate mud. However, in most contexts, the term refers to siliciclastic mudstone, composed mostly of silicate minerals. The NASA Curiosity rover has found deposits of mudstone on Mars that contain organic substances such as propane, benzene and toluene. Definition There is not a single definition of mudstone that has gained general acceptance,Boggs 2006, p.143 though there is wide agreement that mudstones are fine-grained sedimentary rocks, composed mostly of silicate grains with a grain size less than . Individual grains this size are too small to be disting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





Saunders_Quarry-1.jpg)