|
Pope Nicholas II
Pope Nicholas II ( la, Nicholaus II; c. 990/995 – 27 July 1061), otherwise known as Gerard of Burgundy, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 24 January 1059 until his death in 27 July 1061. At the time of his election, he was bishop of Florence. During his Papacy, Nicholas II successfully expanded the influence of the papacy in Milan and southern Italy. He was also responsible for passing papal election reforms which resulted in greater papal influence in electing new Popes. Early life Gerard of Burgundy was born in Chevron, in what is now Savoy. He was canon at Liège. In 1046 he became bishop of Florence, where he restored the canonical life among the clergy of numerous churches.Weber, Nicholas. "Pope Nicholas II." The Catholic Encyclopedia Vol. 11. New Yo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Rome
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is called episcopacy. Organizationally, several Christian denominations utilize ecclesiastical structures that call for the position of bishops, while other denominations have dispensed with this office, seeing it as a symbol of power. Bishops have also exercised political authority. Traditionally, bishops claim apostolic succession, a direct historical lineage dating back to the original Twelve Apostles or Saint Paul. The bishops are by doctrine understood as those who possess the full priesthood given by Jesus Christ, and therefore may ordain other clergy, including other bishops. A person ordained as a deacon, priest (i.e. presbyter), and then bishop is understood to hold the fullness of the ministerial priesthood, given responsibi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
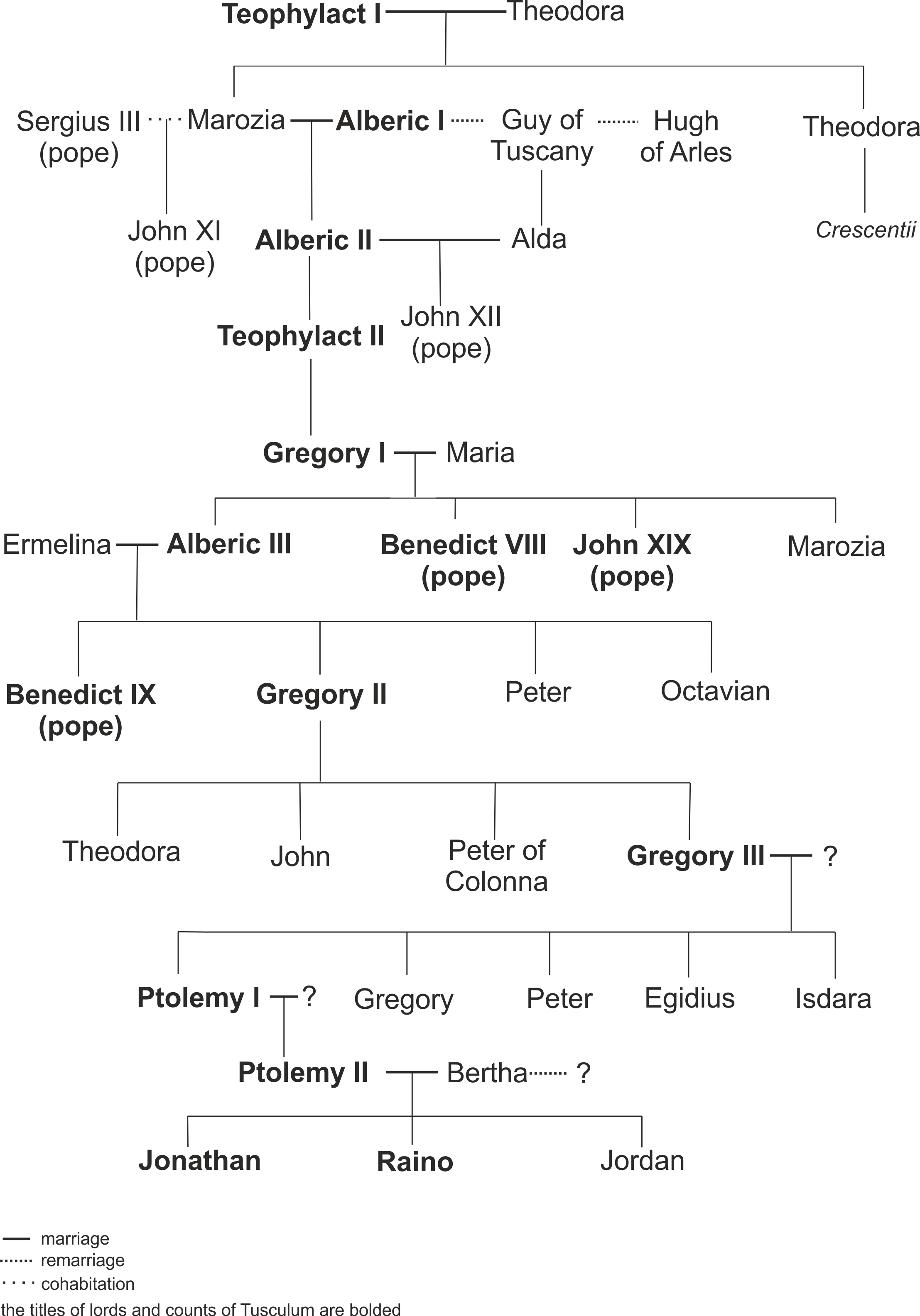
Count Of Tusculum
The counts of Tusculum, also known as the Theophylacti, were a family of secular noblemen from Latium that maintained a powerful position in Rome between the 10th and 12th centuries. Several popes and an antipope during the 11th century came from their ranks. They created and perfected the political formula of noble-papacy, wherein the pope was arranged to be elected only from the ranks of the Roman nobles. The Pornocracy, the period of influence by powerful female courtesans of the family, also influenced papal history. The counts of Tusculum remained arbiters of Roman politics and religion for more than a century. In addition to the papal influence, they held lay power through consulships and senatorial membership. Traditionally they were pro-Byzantine and anti-Germanic in their political affiliation. After 1049, the Tusculan Papacy came to an end with the appointment of Pope Leo IX. In fact, the Tusculan papacy was largely responsible for the reaction known as the Gregorian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humbert
Humbert, Umbert or Humberto (Latinized ''Humbertus'') is a Germanic given name, from ''hun'' "warrior" and ''beraht'' "bright". It also came into use as a surname. Given name ;Royalty and Middle Ages * Emebert (died 710) * Humbert of Maroilles (before 652 – 680) * Humbert (bishop of Würzburg) (died 842) * Humbert I, Count of Savoy (980 – 1047 or 1048) * Humbert II, Count of Savoy (1065–1103) * Humbert III, Count of Savoy (1135–1189) * Humbert, bastard of Savoy (c.1318–1374), soldier * Humbert V de Beaujeu (1198–1250) * Humbert I of Viennois (1240–1307), Dauphin of the Viennois * Humbert II of Viennois (1312–1355), Dauphin of the Viennois * Humbert I of Italy (1844–1900) * Humbert II of Italy (1904–1983) * Humbert of Silva Candida (1015–1061), Roman Catholic cardinal and Benedictine oblate * Humbert of Romans (died 1277), master general of the Dominicans ;Others *Humbert Achamer-Pifrader, Austrian jurist, member of the SS of Nazi Germany and commander of Ein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melfi
Melfi ( Lucano: ) is a town and ''comune'' in the Vulture area of the province of Potenza, in the Southern Italian region of Basilicata. Geographically, it is midway between Naples and Bari. In 2015 it had a population of 17,768. Geography On a hill at the foot of Mount Vulture, Melfi is the most important town in Basilicata's Vulture, both as a tourist resort and economic centre. Its municipality lies next to the borders with Campania and Apulia, and borders with Aquilonia ( AV), Ascoli Satriano ( FG), Candela (FG), Lacedonia (AV), Lavello, Monteverde (AV), Rapolla, Rionero in Vulture and Rocchetta Sant'Antonio (FG). Its hamlets (''frazioni'') are the villages of Camarda, Capannola, Foggianello, Foggiano, Isca ricotta, Leonessa, Masseria Casella, Masseria Catapane, Masseria Menolecchia, Parasacco, San Giorgio di Melfi, San Nicola, Vaccareccia and Villa Mariannina. History Early history and Middle Ages Inhabited by the Daunians and Lucanians, under the Romans, Melfi was include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emirate Of Sicily
The Emirate of Sicily ( ar, إِمَارَة صِقِلِّيَة, ʾImārat Ṣiqilliya) was an Islamic kingdom that ruled the island of Sicily from 831 to 1091. Its capital was Palermo (Arabic: ''Balarm''), which during this period became a major cultural and political center of the Muslim world. Sicily was part of the Byzantine Empire when Muslim forces from Ifriqiya began launching raids in 652. Through a prolonged series of conflicts from 827 to 902, they gradually conquered the entirety of Sicily, with only the stronghold of Rometta, in the far northeast, holding out until 965. Under Muslim rule, the island became increasingly prosperous and cosmopolitan. Trade and agriculture flourished, and Palermo became one of the largest and wealthiest cities in Europe. Sicily became multiconfessional and multilingual, developing a distinct Arab-Byzantine culture that combined elements of its Islamic Arab and Berber migrants with those of the local Greek-Byzantine and Jewish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)