|
Pomáz
Pomáz (german: Paumasch) is a small town in Pest County, Hungary. It is located on the HÉV commuter train line from Budapest to Szentendre Teje. Sights Pomáz is famous for its Serbian Orthodox church. Just as in nearby Szentendre, a Serbian community existed in the town since the time of the Ottoman presence in Eastern Europe. There are also a Roman Catholic and a Calvinist church in the town. The town also features the Teleki-Wattay castle, built in 1773 in baroque style, but extensively renovated in the second half of the 19th century. After the Second World War, it was converted to an orphanage, and successively a child-care institute; in the early 21st century it was renovated once again under the EU Phare programme, and became a venue for choir projects, known as the Choral Castle. Notable people The Teleki family, which owned the castle, counted among its members controversial prime minister Pál Teleki (in office 1920-1921 and 1939–1941). *Max Kopfstein, (1856– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ádám György
Ádám György (; born 28 January 1982) is a Hungarian pianist. György started his music studies at the age of four. While studying under Katalin Halmagyi, he was accepted to the Béla Bartók Conservatory of Budapest in 1994. György won the National Youth Piano Competition in 1998 and the Hungary's Pianist 2000 award two years later. From 2000 to 2006, Ádám attended the Franz Liszt Academy of Music in Budapest, where he studied under György Nador and Balázs Reti. Currently, he is pursuing graduate studies at the Franz Liszt Academy, and he is director of thAdam György Castle Academy On 8 June 2012, he performed at the opening ceremony of the UEFA Euro 2012 in Warsaw, Poland. On 10 June 2023, György performed the piano version of the UEFA Champions League Anthem prior to the final in Istanbul. Awards * 2004 – First International Chopin Piano Competition in Budapest Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyula Glykais
Gyula Glykais (9 April 1893 – 12 June 1948) was a Hungarian fencer. He won a gold medal in the team sabre event at the 1928 and 1932 Summer Olympics The 1932 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the X Olympiad and also known as Los Angeles 1932) were an international multi-sport event held from July 30 to August 14, 1932 in Los Angeles, California, United States. The Games were held duri .... References External links * 1893 births 1948 deaths Hungarian male sabre fencers Olympic fencers for Hungary Fencers at the 1928 Summer Olympics Fencers at the 1932 Summer Olympics Olympic gold medalists for Hungary Olympic medalists in fencing People from Pomáz Medalists at the 1928 Summer Olympics Medalists at the 1932 Summer Olympics Sportspeople from Pest County {{Hungary-fencing-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sándor Egervári
Sándor Egervári (born 15 July 1950) is a Hungarian football manager. He attended the University of Physical Education in Budapest and qualified as a football coach in 1983. He has completed the UEFA A and B course and as well as the pro license course. He has managed clubs to the domestic title and cup success. Playing career 1971–1972 Hungarian First Division – Spartacus S.E 1972–1981 Hungarian First Division – Budapest Honvéd and MTK VM 1974 Member of the national Olympic team Management career Egervári's coaching career began as an assistant coach in Hungary's last appearance at a world cup. This was in the Mexico 1986 tournament, when Hungary were one of the best European sides in the world. He was assistant coach for the national team for three years in total. He then had a two-year spell, as assistant coach, to the Kuwaiti national team from 1986–88. Egervári then returned home to Hungary, with a growing reputation as a top coach. He assisted Józse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andreas Alföldi
András (Andreas) Ede Zsigmond Alföldi (27 August 1895 – 12 February 1981) was a Hungarian historian, art historian, epigraphist, numismatist and archaeologist, specializing in the Late Antique period. He was one of the most productive 20th-century scholars of the ancient world and is considered one of the leading researchers of his time. Although some of his research results are controversial, his work in several areas is viewed as groundbreaking. Professor Alföldi contributed significantly to the massive ''Cambridge Ancient History'', including Vol. 12: The Imperial Crisis and Recovery. He became a professor at the Institute for Advanced Study in 1955. Life and career The son of a doctor, Alföldi was born in 1895 in the Austro-Hungarian empire. Although the family finances were damaged after the death of his father in 1910, Alföldi was able to begin his studies of classical history after his graduation from high school. His first area of interest was in classical numi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities And Towns Of Hungary
Hungary has 3,152 Municipality, municipalities as of July 15, 2013: 346 towns (Hungarian term: ''város'', plural: ''városok''; the terminology doesn't distinguish between city, cities and towns – the term town is used in official translations) and 2,806 villages (Hungarian: ''község'', plural: ''községek'') of which 126 are classified as large villages (Hungarian: ''nagyközség'', plural: ''nagyközségek''). The number of towns can change, since villages can be elevated to town status by act of the President. The capital Budapest has a special status and is not included in any county while 23 of the towns are so-called urban counties (''megyei jogú város'' – town with county rights). All county seats except Budapest are urban counties. Four of the cities (Budapest, Miskolc, Győr, and Pécs) have agglomerations, and the Hungarian Statistical Office distinguishes seventeen other areas in earlier stages of agglomeration development. The largest city is the capital, Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gmina Krzywiń
__NOTOC__ Gmina Krzywiń is an urban-rural gmina (administrative district) in Kościan County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. Its seat is the town of Krzywiń, which lies approximately south-east of Kościan and south of the regional capital Poznań. The gmina covers an area of , and as of 2006 its total population is 9,892 (out of which the population of Krzywiń amounts to 1,547, and the population of the rural part of the gmina is 8,345). The gmina contains part of the protected area called Chłapowski Landscape Park. Villages Apart from the town of Krzywiń, Gmina Krzywiń contains the villages and settlements of Bielewo, Bieżyń, Boża Wola, Cichowo, Czerwona Wieś, Gierłachowo, Jerka, Jurkowo, Jurkowo-Huby, Kopaszewo, Kuszkowo, Łagowo, Lubiń, Łuszkowo, Mościszki, Nowy Dwór, Polesie, Rąbiń, Rąbinek, Rogaczewo Małe, Rogaczewo Wielkie, Stary Dębiec, Świniec, Szurkowo, Teklimyśl, Wieszkowo, Wymysłowo, Zbęchy, Zb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister City
A sister city or a twin town relationship is a form of legal or social agreement between two geographically and politically distinct localities for the purpose of promoting cultural and commercial ties. While there are early examples of international links between municipalities akin to what are known as sister cities or twin towns today dating back to the 9th century, the modern concept was first established and adopted worldwide during World War II. Origins of the modern concept The modern concept of town twinning has its roots in the Second World War. More specifically, it was inspired by the bombing of Coventry on 14 November 1940, known as the Coventry Blitz. First conceived by the then Mayor of Coventry, Alfred Robert Grindlay, culminating in his renowned telegram to the people of Stalingrad (now Volgograd) in 1942, the idea emerged as a way of establishing solidarity links between cities in allied countries that went through similar devastating events. The comradesh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1919 in the Palace of Versailles, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, which led to the war. The other Central Powers on the German side signed separate treaties. Although the armistice of 11 November 1918 ended the actual fighting, it took six months of Allied negotiations at the Paris Peace Conference to conclude the peace treaty. The treaty was registered by the Secretariat of the League of Nations on 21 October 1919. Of the many provisions in the treaty, one of the most important and controversial was: "The Allied and Associated Governments affirm and Germany accepts the responsibility of Germany and her allies for causing all the loss and damage to which the Allied and Associated Governments and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Kopfstein
Max or MAX may refer to: Animals * Max (dog) (1983–2013), at one time purported to be the world's oldest living dog * Max (English Springer Spaniel), the first pet dog to win the PDSA Order of Merit (animal equivalent of OBE) * Max (gorilla) (1971–2004), a western lowland gorilla at the Johannesburg Zoo who was shot by a criminal in 1997 Brands and enterprises * Australian Max Beer * Max Hamburgers, a fast-food corporation * MAX Index, a Hungarian domestic government bond index * Max Fashion, an Indian clothing brand Computing * MAX (operating system), a Spanish-language Linux version * Max (software), a music programming language * Commodore MAX Machine * Multimedia Acceleration eXtensions, extensions for HP PA-RISC Films * ''Max'' (1994 film), a Canadian film by Charles Wilkinson * ''Max'' (2002 film), a film about Adolf Hitler * ''Max'' (2015 film), an American war drama film Games * '' Dancing Stage Max'', a 2005 game in the ''Dance Dance Revolution'' series * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pál Teleki
Count Pál János Ede Teleki de Szék (1 November 1879 – 3 April 1941) was a Hungarian politician who served as Prime Minister of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1920 to 1921 and from 1939 to 1941. He was also an expert in geography, a university professor, a member of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, and chief scout of the Hungarian Scout Association. He descended from an aristocratic family from Transylvania. Teleki tried to keep Hungary neutral during the early stages of the Second World War despite cooperating with Nazi Germany to regain Hungarian territory lost in the Treaty of Trianon. When Teleki learned that German troops had entered Hungary en route to invade Yugoslavia, effectively killing hopes of Hungarian neutrality, he committed suicide. He is a controversial figure in Hungarian history because as prime minister he tried to preserve Hungarian autonomy under difficult political circumstances, but also proposed and enacted far-reaching anti-Jewish laws. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
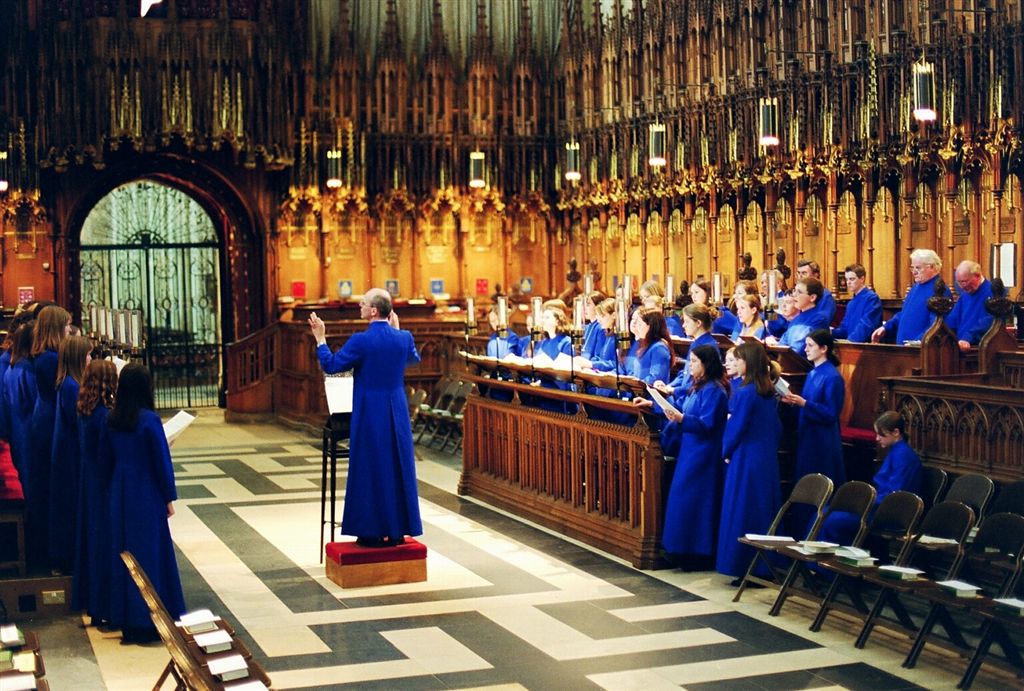
Choir
A choir ( ; also known as a chorale or chorus) is a musical ensemble of singers. Choral music, in turn, is the music written specifically for such an ensemble to perform. Choirs may perform music from the classical music repertoire, which spans from the medieval era to the present, or popular music repertoire. Most choirs are led by a conductor, who leads the performances with arm, hand, and facial gestures. The term ''choir'' is very often applied to groups affiliated with a church (whether or not they actually occupy the quire), whereas a ''chorus'' performs in theatres or concert halls, but this distinction is not rigid. Choirs may sing without instruments, or accompanied by a piano, pipe organ, a small ensemble, or an orchestra. A choir can be a subset of an ensemble; thus one speaks of the "woodwind choir" of an orchestra, or different "choirs" of voices or instruments in a polychoral composition. In typical 18th century to 21st century oratorios and masses, 'choru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)