|
Polychotomy
A polychotomy (päl′i kät′ə mē; plural ''polychotomies'') is a division or separation into many parts or classes. Polychotomy is a generalization of dichotomy, which is a polychotomy of exactly two parts. In evolutionary biology, the term polychotomy can also be considered a historically-based misspelling of polytomy.Weiss, David J. (1995). “Polychtomous or Polytomous?,” Applied Psychological Measurement, Vol. 19, No. 1, p. 4 See also * Polychotomous key Polychotomous key refers to the number of alternatives which a decision point may have in a non-temporal hierarchy of independent variables. The number of alternatives are equivalent to the root or nth root of a mathematical or logical variable. D ... References {{Reflist External links Examples of usageAnother Approach to Polychotomous Classification [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichotomy
A dichotomy is a partition of a whole (or a set) into two parts (subsets). In other words, this couple of parts must be * jointly exhaustive: everything must belong to one part or the other, and * mutually exclusive: nothing can belong simultaneously to both parts. If there is a concept A, and it is split into parts B and not-B, then the parts form a dichotomy: they are mutually exclusive, since no part of B is contained in not-B and vice versa, and they are jointly exhaustive, since they cover all of A, and together again give A. Such a partition is also frequently called a bipartition. The two parts thus formed are complements. In logic, the partitions are opposites if there exists a proposition such that it holds over one and not the other. Treating continuous variables or multi categorical variables as binary variables is called dichotomization. The discretization error inherent in dichotomization is temporarily ignored for modeling purposes. Etymology The term '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polychotomous Key
Polychotomous key refers to the number of alternatives which a decision point may have in a non-temporal hierarchy of independent variables. The number of alternatives are equivalent to the root or nth root of a mathematical or logical variable. Decision points or independent variables with two states have a binary root that is referred to as a dichotomous key whereas, the term polychotomous key refers to roots which are greater than one or unitary and usually greater than two or binary. Polychotomous keys are used in troubleshooting to build troubleshooting charts and in classification/identification schemes with characteristics that have more than one attribute and the order of characteristics is not inherently based on the progression of time. See also *Number prefix *Polychotomy A polychotomy (päl′i kät′ə mē; plural ''polychotomies'') is a division or separation into many parts or classes. Polychotomy is a generalization of dichotomy, which is a polychotomy of exact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
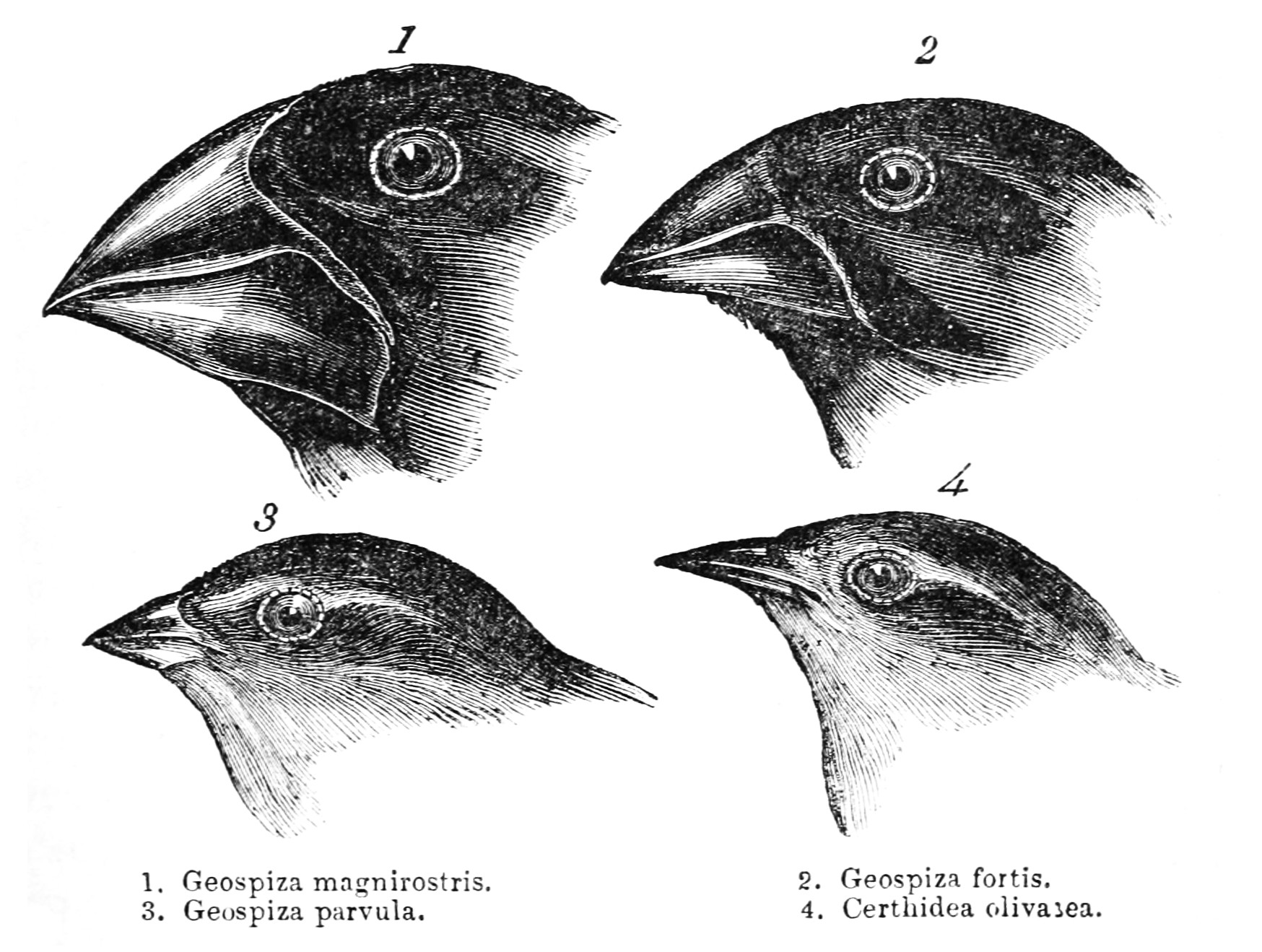
Evolutionary Biology
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes (natural selection, common descent, speciation) that produced the diversity of life on Earth. It is also defined as the study of the history of life forms on Earth. Evolution is based on the theory that all species are related and they gradually change over time. In a population, the genetic variations affect the physical characteristics i.e. phenotypes of an organism. These changes in the phenotypes will be an advantage to some organisms, which will then be passed onto their offspring. Some examples of evolution in species over many generations are the Peppered Moth and Flightless birds. In the 1930s, the discipline of evolutionary biology emerged through what Julian Huxley called the modern synthesis of understanding, from previously unrelated fields of biological research, such as genetics and ecology, systematics, and paleontology. The importance of studying Evolutionary biology is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polytomy
An internal node of a phylogenetic tree is described as a polytomy or multifurcation if (i) it is in a rooted tree and is linked to three or more child subtrees or (ii) it is in an unrooted tree and is attached to four or more branches. A tree that contains any multifurcations can be described as a multifurcating tree. Soft polytomies vs. hard polytomies Two types of polytomies are recognised, soft and hard polytomies. Soft polytomies are the result of insufficient phylogenetic information: though the lineages diverged at different times – meaning that some of these lineages are closer relatives than others, and the available data does not allow recognition of this. Most polytomies are soft, meaning that they would be resolved into a typical tree of dichotomies if better data were available. In contrast, a hard polytomy represents a true divergence event of three or more lineages. Applications Interpretations for a polytomy depend on the individuals, that are represe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |