|
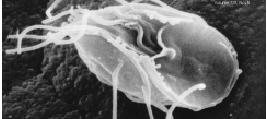
Polychaos Timidum
Polychaos is an amoeboid genus in the Amoebozoa Amoebozoa is a major taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional and currently no longer supported classi ... group. Several characters unite the species in this genus. The pseudopods meld at their bases when the organism is moving, and have dorsal, longitudinal ridges. The nucleus is oval or ellipsoid. Classification ''Polychaos'' includes the following species: * ''Polychaos annulatum'' (Pénard 1902) Smirnov & Goodkov 1998 * '' Polychaos dubium'' (Schaeffer, 1916) Schaeffer 1926 * ''Polychaos fasciculatum'' (Penard, 1902) Schaeffer 1926 * ''Polychaos nitidubium'' Bovee, 1970 * ''Polychaos timidum'' Bovee, 1972 Phylogenetic analysis has shown this that genus belongs to the family Hartmannellidae.Kamyshatskaya OG, Bondarenko NI, Mesentsev YS, Chistyakova LV, Nassonova ES, Smirnov AV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the Three-domain system, three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard (archaea), Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass (ecology), biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated phagotrophs. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoebozoa
Amoebozoa is a major taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional and currently no longer supported classification schemes, Amoebozoa is ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked " supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, variously named Unikonta, Amorphea or Opimoda. Amoebozoa includes many of the best-known amoeboid orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubulinea
The Tubulinea are a major grouping of Amoebozoa, including most of the more familiar amoebae genera like ''Amoeba'', ''Arcella'', ''Difflugia'' and ''Hartmannella''. Characteristics During locomotion most Tubulinea have a roughly cylindrical form or produce numerous cylindrical pseudopods. Each cylinder advances by a single central stream of cytoplasm, granular in appearance, and has no subpseudopodia. This distinguishes them from other amoeboid groups, although in some members this is not the normal type of locomotion. Classification This class was anticipated by some biologists like Jahn, who grouped all amoebae with granular pseudopodia together, but most split the lobose amoebae into testate Testacealobosia and naked Gymnamoebia. These latter are polyphyletic, but molecular trees by Bolivar ''et al.'' identified a core monophyletic subgroup. Subsequent studies showed the testate lobose amoebae belong to the same group, which was thus renamed Lobosea ''sensu stricto'' or Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euamoebida
The Tubulinea are a major grouping of Amoebozoa, including most of the more familiar amoebae genera like ''Amoeba'', ''Arcella'', ''Difflugia'' and '' Hartmannella''. Characteristics During locomotion most Tubulinea have a roughly cylindrical form or produce numerous cylindrical pseudopods. Each cylinder advances by a single central stream of cytoplasm, granular in appearance, and has no subpseudopodia. This distinguishes them from other amoeboid groups, although in some members this is not the normal type of locomotion. Classification This class was anticipated by some biologists like Jahn, who grouped all amoebae with granular pseudopodia together, but most split the lobose amoebae into testate Testacealobosia and naked Gymnamoebia. These latter are polyphyletic, but molecular trees by Bolivar ''et al.'' identified a core monophyletic subgroup. Subsequent studies showed the testate lobose amoebae belong to the same group, which was thus renamed Lobosea ''sensu stricto'' or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hartmannellidae
The Hartmannellidae are a family of amoebozoa, usually found in soils. When active they tend to be roughly cylindrical in shape, with a single leading pseudopod and no subpseudopodia. This form somewhat resembles a slug and as such they are also called limax amoebae. Trees based on rRNA show the Hartmannellidae as usually defined are paraphyletic to the Amoebidae The Amoebidae are a family of Amoebozoa, including naked amoebae that produce multiple pseudopodia of indeterminate length. These are roughly cylindrical with granular endoplasm and no subpseudopodia, as found in other members of the class Tubuli ..., which may adopt similar forms. References External links Amoebozoa families {{Amoebozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoeboid
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; plural ''am(o)ebas'' or ''am(o)ebae'' ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopods. Amoebae do not form a single taxonomic group; instead, they are found in every major lineage of eukaryotic organisms. Amoeboid cells occur not only among the protozoa, but also in fungi, algae, and animals. Microbiologists often use the terms "amoeboid" and "amoeba" interchangeably for any organism that exhibits amoeboid movement. In older classification systems, most amoebae were placed in the class or subphylum Sarcodina, a grouping of single-celled organisms that possess pseudopods or move by protoplasmic flow. However, molecular phylogenetic studies have shown that Sarcodina is not a monophyletic group whose members share common descent. Consequently, amoeboid organisms are no longer classified together in one group.Jan Pawlow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudopod
A pseudopod or pseudopodium (plural: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a eukaryotic cell membrane that is emerged in the direction of movement. Filled with cytoplasm, pseudopodia primarily consist of actin filaments and may also contain microtubules and intermediate filaments. Pseudopods are used for motility and ingestion. They are often found in amoebas. Different types of pseudopodia can be classified by their distinct appearances. Lamellipodia are broad and thin. Filopodia are slender, thread-like, and are supported largely by microfilaments. Lobopodia are bulbous and amoebic. Reticulopodia are complex structures bearing individual pseudopodia which form irregular nets. Axopodia are the phagocytosis type with long, thin pseudopods supported by complex microtubule arrays enveloped with cytoplasm; they respond rapidly to physical contact. Some pseudopodial cells are able to use multiple types of pseudopodia depending on the situation: Most of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
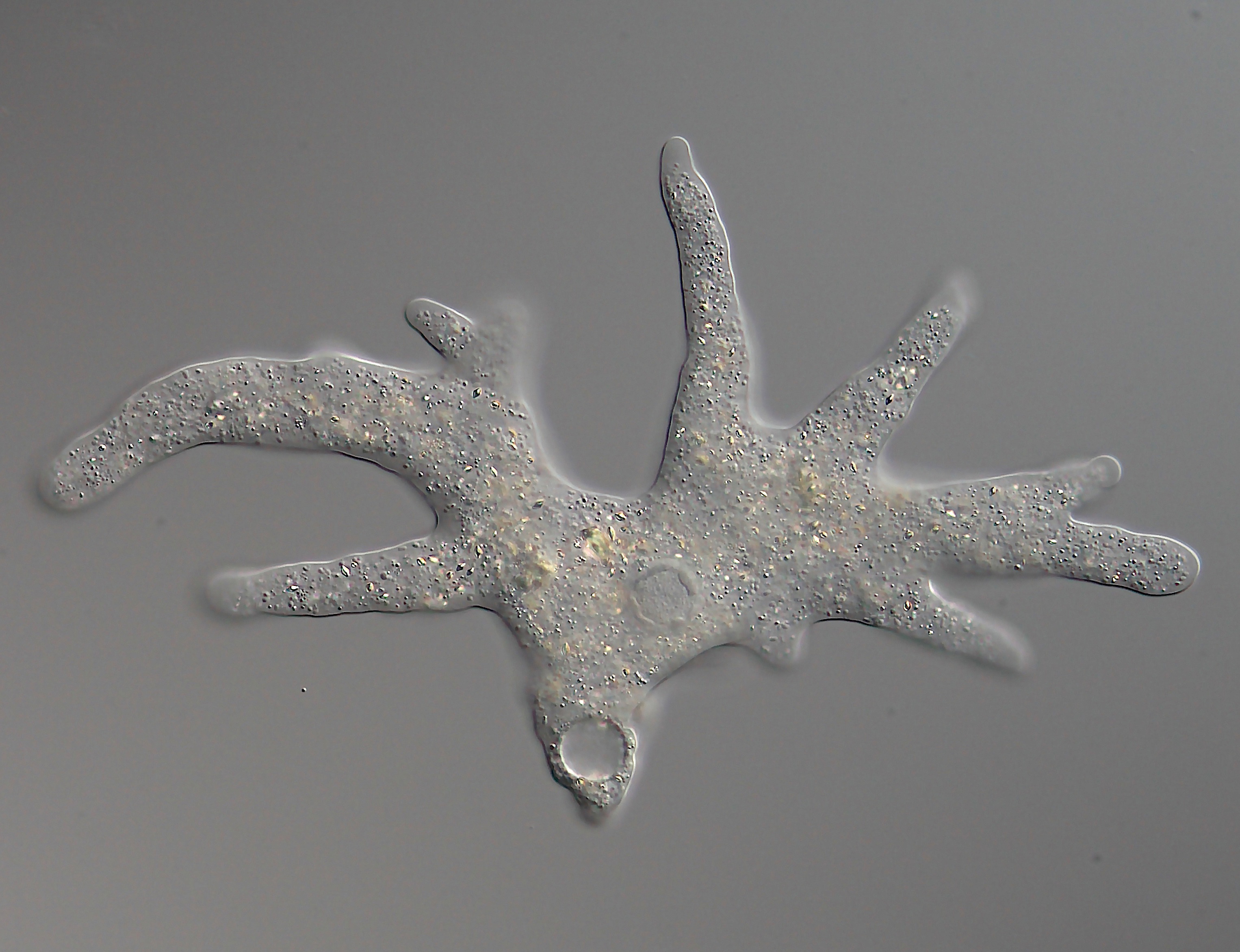
Polychaos Dubium
''Polychaos dubium'' is a freshwater amoeboid and one of the larger species of single-celled eukaryote. Like other amoebozoans, ''P. dubium'' moves by means of temporary projections called pseudopods. ''P. dubium'' reportedly has one of the largest genome size of any organism known, though the authors of a 2004 study suggest treating that measurement with caution. ''Polychaos dubium'' was previously known as ''Amoeba dubia''. The author who named the species later recognized it as different from species of ''Amoeba'', and so designated it the type species of the genus '' Polychaos''. Unlike species of ''Amoeba'', ''P. dubium'' lacks longitudinal ridges on its pseudopods. Physical characteristics A few characteristics distinguish ''Polychaos dubium'' from other species of ''Polychaos''. The crystals floating in its cytoplasm take the shape of flat bipyramids, flat plates, or clustered platelets. The nucleus is ellipsoid in shape, has granules next to the membrane, and lac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |