|
Poly(phenylene Oxide)
Poly(''p''-phenylene oxide) (PPO), poly(''p''-phenylene ether) (PPE), often referred to simply as polyphenylene oxide, is a high-temperature thermoplastic. It is rarely used in its pure form due to difficulties in processing. It is mainly used as blend with polystyrene, high impact styrene-butadiene copolymer or polyamide. PPO is a registered trademark of SABIC Innovative Plastics IP B.V. under which various polyphenylene ether resins are sold. History Polyphenylene ether was discovered in 1959 by Allan Hay, and was commercialized by General Electric in 1960. While it was one of the cheapest high-temperature resistant plastics, processing was difficult, while the impact and heat resistance gradually decreased with time. Mixing it with polystyrene in any ratio could compensate for the disadvantages. In the 1960s, modified PPE came into the market under the trademark Noryl. Properties PPE is an amorphous high-performance plastic. The glass transition temperature is 215 °C, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoplastic
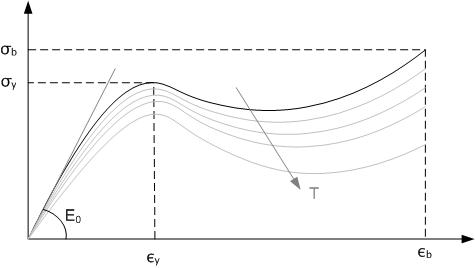
A thermoplastic, or thermosoft plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling. Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate by intermolecular forces, which weaken rapidly with increased temperature, yielding a viscous liquid. In this state, thermoplastics may be reshaped and are typically used to produce parts by various polymer processing techniques such as injection molding, compression molding, calendering, and extrusion. Thermoplastics differ from thermosetting polymers (or "thermosets"), which form irreversible chemical bonds during the curing process. Thermosets do not melt when heated, but typically decompose and do not reform upon cooling. Above its glass transition temperature and below its melting point, the physical properties of a thermoplastic change drastically without an associated phase change. Some thermoplastics do not fully cry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxidase
Peroxidases or peroxide reductases ( EC numberbr>1.11.1.x are a large group of enzymes which play a role in various biological processes. They are named after the fact that they commonly break up peroxides. Functionality Peroxidases typically catalyze a reaction of the form: :ROOR' + \overset + 2H+ -> ce + R'OH Optimal substrates For many of these enzymes the optimal substrate is hydrogen peroxide, but others are more active with organic hydroperoxides such as lipid peroxides. Peroxidases can contain a heme cofactor in their active sites, or alternately redox-active cysteine or selenocysteine residues. The nature of the electron donor is very dependent on the structure of the enzyme. * For example, horseradish peroxidase can use a variety of organic compounds as electron donors and acceptors. Horseradish peroxidase has an accessible active site, and many compounds can reach the site of the reaction. * On the other hand, for an enzyme such as cytochrome c peroxidase, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyethers
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl or aryl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin. Structure and bonding Ethers feature bent C–O–C linkages. In dimethyl ether, the bond angle is 111° and C–O distances are 141 pm. The barrier to rotation about the C–O bonds is low. The bonding of oxygen in ethers, alcohols, and water i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Polymers
A polymer (; Greek ''poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'', meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Electronics
Molecular electronics is the study and application of molecular building blocks for the fabrication of electronic components. It is an interdisciplinary area that spans physics, chemistry, and materials science. The unifying feature is use of molecular building blocks to fabricate electronic components. Due to the prospect of size reduction in electronics offered by molecular-level control of properties, molecular electronics has generated much excitement. It provides a potential means to extend Moore's Law beyond the foreseen limits of small-scale conventional silicon integrated circuits. Molecular scale electronics Molecular scale electronics, also called single-molecule electronics, is a branch of nanotechnology that uses single molecules, or nanoscale collections of single molecules, as electronic components. Because single molecules constitute the smallest stable structures possible, this miniaturization is the ultimate goal for shrinking electrical circuits. Conventio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Rochester
The University of Rochester (U of R, UR, or U of Rochester) is a private university, private research university in Rochester, New York. The university grants Undergraduate education, undergraduate and graduate degrees, including Doctorate, doctoral and professional degrees. The University of Rochester enrolls approximately 6,800 undergraduates and 5,000 graduate students. Its 158 buildings house over 200 academic majors. According to the National Science Foundation, Rochester spent more than $397 million on research and development in 2020, ranking it 66th in the nation. With approximately 28,000 full-time employees, the university is the largest private employer in Upstate New York and the 7th largest in all of New York (state), New York State. The University of Rochester College of Arts Sciences and Engineering, College of Arts, Sciences, and Engineering is home to departments and divisions of note. The Institute of Optics was founded in 1929 through a grant from Eastm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 billion kg/year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceutical drugs. Properties Phenol is an organic compound appreciably soluble in water, with about 84.2 g dissolving in 1000 mL (0.895 M). Homogeneous mixtures of phenol and water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They at oftentimes have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid (C3H7CO2H) is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named as a "carboxy" or "carboxylic acid" substituent on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syringic Acid
Syringic acid is a naturally occurring phenolic compound and dimethoxybenzene that is commonly found as a plant metabolite. Natural occurrence Syringic acid can be found in several plants including '' Ardisia elliptica'' and ''Schumannianthus dichotomus''. Synthesis Syringic acid can be prepared by selectively hydrolyzing ( demethylating) eudesmic acid with 20% sulfuric acid. Presence in food Syringic acid can be found in several fruits including olives, dates, spices, pumpkin, grapes, acai palm, honey, red wine, among others. Its presence in the ancient Egyptian drink shedeh could confirm it was made out of grape, as syringic acid is released by the breakdown of the compound malvidin, also found in red wine. It is also found in vinegar. Applications Various studies have found syringic acid to exhibit useful pharmaceutical properties such as anti-oxidant, anti-microbial, anti-inflammation, anti-cancer, and anti-diabetic. Syringic acid can be enzymatically pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
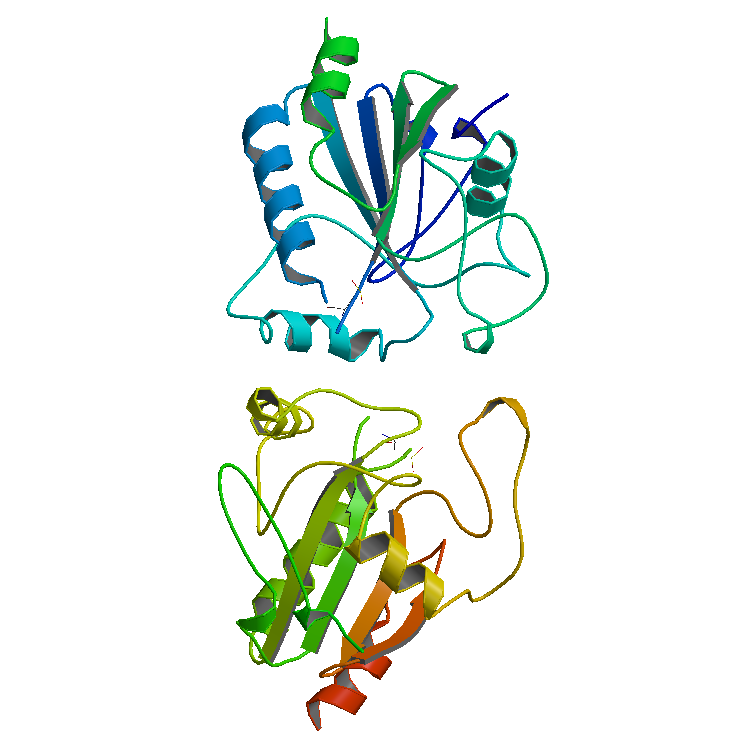
Laccase
Laccases () are multicopper oxidases found in plants, fungi, and bacteria. Laccases oxidize a variety of phenolic substrates, performing one-electron oxidations, leading to crosslinking. For example, laccases play a role in the formation of lignin by promoting the oxidative coupling of monolignols, a family of naturally occurring phenols. Other laccases, such as those produced by the fungus '' Pleurotus ostreatus'', play a role in the degradation of lignin, and can therefore be classed as lignin-modifying enzymes. Other laccases produced by fungi can facilitate the biosynthesis of melanin Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amin ... pigments. Laccases catalyze ring cleavage of aromatic compounds. Laccase was first studied by Hikorokuro Yoshida in 1883 and then by G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SABIC
Saudi Basic Industries Corporation ( ar, الشركة السعودية للصناعات الأساسية), known as SABIC ( ar, سابك), is a Saudi chemical manufacturing company. 70% of SABIC's shares are owned by Saudi Aramco. It is active in petrochemicals, chemicals, industrial polymers, fertilizers, and metals. It is the second largest public company in the Middle East and Saudi Arabia as listed in Tadawul. In 2017, SABIC was ranked fourth in the world among chemical companies by Fortune Global 500. By the end of 2018 SABIC was the world's 281st-largest corporation. In 2014, the company had sales revenues of $50.4 billion, profits of $6.7 billion and assets standing at $90.4 billion. It also has been recognized as the world's second most valuable brand in the chemicals industry by Brand Finance in 2021. History SABIC was founded in 1976 by royal decree to convert oil by-products into useful chemicals, polymers, and fertilizers. The first chairman of the company was Gha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |