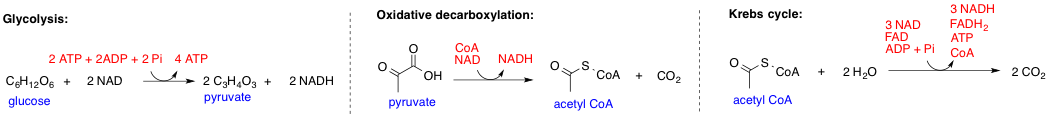|
Poly(lactic-co-glycolic) Acid
PLGA, PLG, or poly(lactic-''co''-glycolic acid) is a copolymer which is used in a host of Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved therapeutic devices, owing to its biodegradability and biocompatibility. PLGA is synthesized by means of ring-opening co-polymerization of two different monomers, the cyclic dimers (1,4-dioxane-2,5-diones) of glycolic acid and lactic acid. Polymers can be synthesized as either random or block copolymers thereby imparting additional polymer properties. Common catalysts used in the preparation of this polymer include tin(II) 2-ethylhexanoate, tin(II) alkoxides, or aluminum isopropoxide. During polymerization, successive monomeric units (of glycolic or lactic acid) are linked together in PLGA by ester linkages, thus yielding a linear, aliphatic polyester as a product. Copolymer Depending on the ratio of lactide to glycolide used for the polymerization, different forms of PLGA can be obtained: these are usually identified in regard to the molar ratio o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PLGA
PLGA, PLG, or poly(lactic-''co''-glycolic acid) is a copolymer which is used in a host of Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved therapeutic devices, owing to its biodegradation, biodegradability and biocompatibility. PLGA is synthesized by means of ring-opening co-polymerization of two different monomers, the cyclic dimers (1,4-dioxane-2,5-diones) of glycolic acid and lactic acid. Polymers can be synthesized as either random or block copolymers thereby imparting additional polymer properties. Common catalysts used in the preparation of this polymer include tin(II) 2-ethylhexanoate, tin(II) alkoxides, or aluminum isopropoxide. During polymerization, successive monomeric units (of glycolic or lactic acid) are linked together in PLGA by ester linkages, thus yielding a linear, aliphatic polyester as a product. Copolymer Depending on the ratio of lactide to glycolide used for the polymerization, different forms of PLGA can be obtained: these are usually identified in regard to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for polar molecules and the most common solvent used by living things; all the ions and proteins in a cell are dissolved in water within the cell. The quantity of solute that can dissolve in a specific volume of solvent varies with temperature. Major uses of solvents are in paints, paint removers, inks, and dry cleaning. Specific uses for organic solvents are in dry cleaning (e.g. tetrachloroethylene); as paint thinners (toluene, turpentine); as nail polish removers and solvents of glue (acetone, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate); in spot removers (hexane, petrol ether); in detergents ( citrus terpenes); and in perfumes (ethanol). Solvents find various applications in chemical, pharmaceutical, oil, and gas industries, including in chemical syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.04% by volume (as of May 2022), having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Burning fossil fuels is the primary cause of these increased CO2 concentrations and also the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic Pathways
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical reactions catalyzed by enzymes. In most cases of a metabolic pathway, the product of one enzyme acts as the substrate for the next. However, side products are considered waste and removed from the cell. These enzymes often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors to function. Different metabolic pathways function based on the position within a eukaryotic cell and the significance of the pathway in the given compartment of the cell. For instance, the, electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation all take place in the mitochondrial membrane. In contrast, glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway, and fatty acid biosynthesis all occur in the cytosol of a cell. There are two types of metabolic pathways that are character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoparticles
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is usually defined as a particle of matter that is between 1 and 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At the lowest range, metal particles smaller than 1 nm are usually called atom clusters instead. Nanoparticles are usually distinguished from microparticles (1-1000 µm), "fine particles" (sized between 100 and 2500 nm), and "coarse particles" (ranging from 2500 to 10,000 nm), because their smaller size drives very different physical or chemical properties, like colloidal properties and ultrafast optical effects or electric properties. Being more subject to the brownian motion, they usually do not sediment, like colloidal particles that conversely are usually understood to range from 1 to 1000 nm. Being much smaller than the wavelengths of visible light (400-700 nm), nano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosthetic Devices
In medicine, a prosthesis (plural: prostheses; from grc, πρόσθεσις, prósthesis, addition, application, attachment), or a prosthetic implant, is an artificial device that replaces a missing body part, which may be lost through trauma, disease, or a condition present at birth (congenital disorder). Prostheses are intended to restore the normal functions of the missing body part. Amputee rehabilitation is primarily coordinated by a physiatrist as part of an inter-disciplinary team consisting of physiatrists, prosthetists, nurses, physical therapists, and occupational therapists. Prostheses can be created by hand or with computer-aided design (CAD), a software interface that helps creators design and analyze the creation with computer-generated 2-D and 3-D graphics as well as analysis and optimization tools. Types A person's prosthesis should be designed and assembled according to the person's appearance and functional needs. For instance, a person may need a transra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implant (medicine)
An implant is a medical device manufactured to replace a missing biological structure, support a damaged biological structure, or enhance an existing biological structure. Medical implants are man-made devices, in contrast to a Organ transplant, transplant, which is a transplanted biomedical tissue. The surface of implants that contact the body might be made of a Biomaterial, biomedical material such as titanium, silicone, or apatite depending on what is the most functional. In some cases implants contain electronics, e.g. artificial pacemaker and cochlear implants. Some implants are Biological activity, bioactive, such as Subcutaneous tissue, subcutaneous drug delivery devices in the form of implantable pills or drug-eluting stents. Applications Implants can roughly be categorized into groups by application: Sensory and neurological Perception, Sensory and Neurotechnology#Implant technologies, neurological implants are used for disorders affecting the major senses and the br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Suture
A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a needle with an attached length of thread. There are numerous types of suture which differ by needle shape and size as well as thread material and characteristics. Selection of surgical suture should be determined by the characteristics and location of the wound or the specific body tissues being approximated. In selecting the needle, thread, and suturing technique to use for a specific patient, a medical care provider must consider the tensile strength of the specific suture thread needed to efficiently hold the tissues together depending on the mechanical and shear forces acting on the wound as well as the thickness of the tissue being approximated. One must also consider the elasticity of the thread and ability to adapt to different tissues, as well as the memory of the threa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
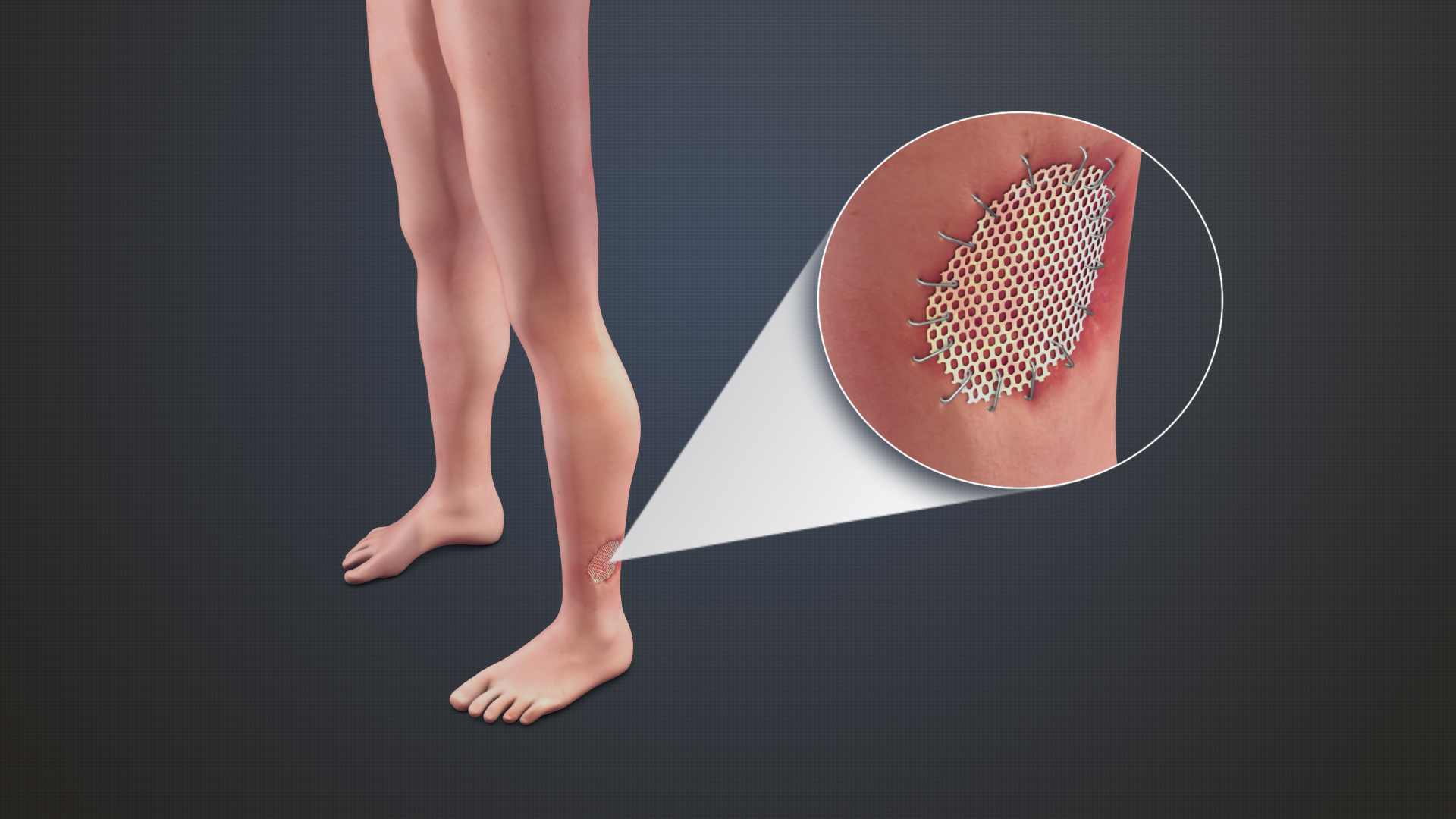
Grafts
Grafting refers to a surgical procedure to move tissue from one site to another on the body, or from another creature, without bringing its own blood supply with it. Instead, a new blood supply grows in after it is placed. A similar technique where tissue is transferred with the blood supply intact is called a flap. In some instances, a graft can be an artificially manufactured device. Examples of this are a tube to carry blood flow across a defect or from an artery to a vein for use in hemodialysis. Classification Autografts and isografts are usually not considered as foreign and, therefore, do not elicit rejection. Allografts and xenografts may be recognized as foreign by the recipient and rejected. * Autograft: graft taken from one part of the body of an individual and transplanted onto another site in the same individual, e.g., skin graft. * Isograft: graft taken from one individual and placed on another individual of the same genetic constitution, e.g., grafts between i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Device
A medical device is any device intended to be used for medical purposes. Significant potential for hazards are inherent when using a device for medical purposes and thus medical devices must be proved safe and effective with reasonable assurance before regulating governments allow marketing of the device in their country. As a general rule, as the associated risk of the device increases the amount of testing required to establish safety and efficacy also increases. Further, as associated risk increases the potential benefit to the patient must also increase. Discovery of what would be considered a medical device by modern standards dates as far back as c. 7000 BC in Baluchistan where Neolithic dentists used flint-tipped drills and bowstrings. Study of archeology and Roman medical literature also indicate that many types of medical devices were in widespread use during the time of ancient Rome. In the United States it wasn't until the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They at oftentimes have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid (C3H7CO2H) is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named as a "carboxy" or "carboxylic acid" substituent on another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
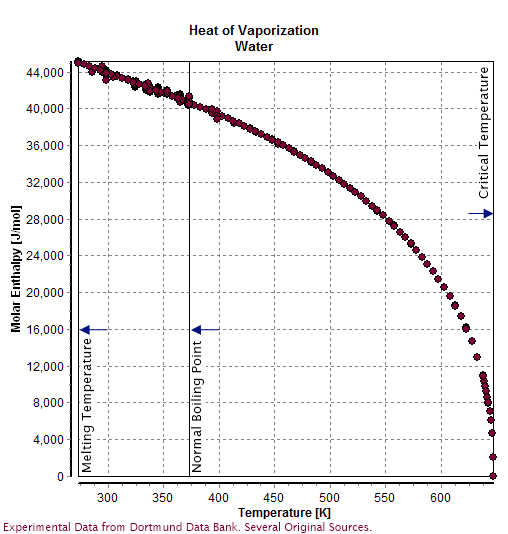
Water (molecule)
Water () is a Chemical polarity, polar inorganic compound that is at room temperature a tasteless and odorless liquid, which is nearly colorless apart from Color of water, an inherent hint of blue. It is by far the most studied chemical compound and is described as the "universal solvent" and the "solvent of life". It is the most abundant substance on the surface of Earth and the only common substance to exist as a ice, solid, liquid, and water vapor, gas on Earth's surface. It is also the third most abundant molecule in the universe (behind Hydrogen, molecular hydrogen and carbon monoxide). Water molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other and are strongly polar. This polarity allows it to dissociate ions in salts and bond to other polar substances such as alcohols and acids, thus dissolving them. Its hydrogen bonding causes its many unique properties, such as having a solid form less dense than its liquid form, a relatively high boiling point of 100 °C for its molar m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |