|
Politics Of The Komi Republic
The Komi Republic (russian: Республика Коми; kv, Коми Республика), sometimes simply referred to as Komi, is a republic of Russia located in Eastern Europe. Its capital is the city of Syktyvkar. The population of the republic as of the 2010 Census was 901,189. History The Komi people first feature in the records of the Novgorod Republic in the 12th century, when East Slavic traders from Novgorod traveled to the Perm region in search of furs and animal hides. The Komi territories came under the influence of Muscovy in the late Middle Ages (late 15th to early 16th centuries). The site of Syktyvkar, settled from the 16th century, was known as Sysolskoye (Сысольскoe). In 1780, under Catherine the Great, it was renamed to Ust-Sysolsk (Усть-Сысольск) and used as a penal colony. Russians explored the Komi territory most extensively in the 19th and early 20th centuries, starting with the expedition led by Alexander von Keyserling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
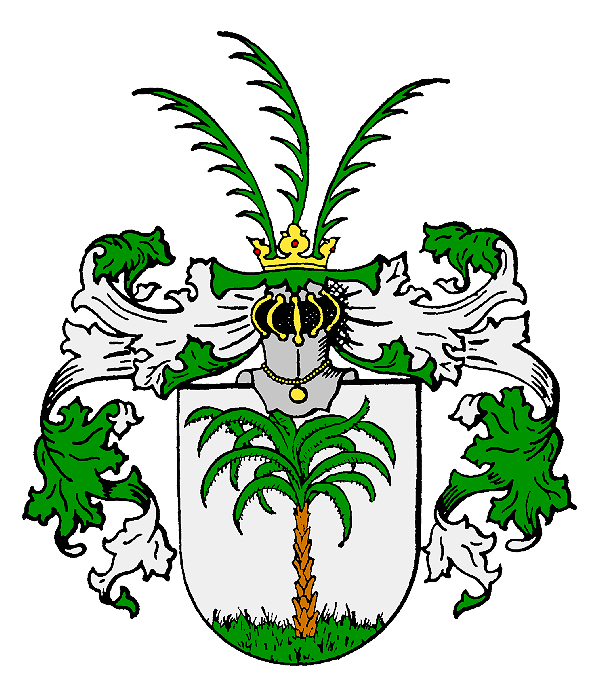
Coat Of Arms Of The Komi Republic
The coat of arms of the Komi Republic (russian: герб Респу́блики Ко́ми; '; kv, Коми республикалӧн канпас; '; State Heraldic Register of the Russian Federation, SHRRF #153), designed by A. Neverov, was instituted by the law No. XII-20/1 on June 6, 1994 and reflects the mythic beliefs of the Komi peoples. The blazon has a field (heraldry), field gules, featuring a bird of prey or (heraldry), or with the face below corresponding with goddess Zarni An, and six unhorned moose, elk heads. On December 17, 1997 the Republican State Council passed the law, which changed the official coat of arms definition in order to agree with the heraldry#The rules of heraldry, rules of heraldry.http://www.gazeta-respublika.ru/article.php/9378 A bird of prey in the traditional interpretation embodies the sun, authority and the upper world, while elk is associated with power, generosity and beauty. The combination of gules and or symbolizes sun, mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Census (2010)
The Russian Census of 2010 (russian: Всеросси́йская пе́репись населе́ния 2010 го́да) was the second census of the Russian Federation population after the dissolution of the Soviet Union. Preparations for the census began in 2007 and it took place between October 14 and October 25. The census The census was originally scheduled for October 2010, before being rescheduled for late 2013, citing financial reasons,Всероссийская перепись населения переносится на 2013 год although it was also speculated that political motives were influential in the decision. However, in late 2009, |
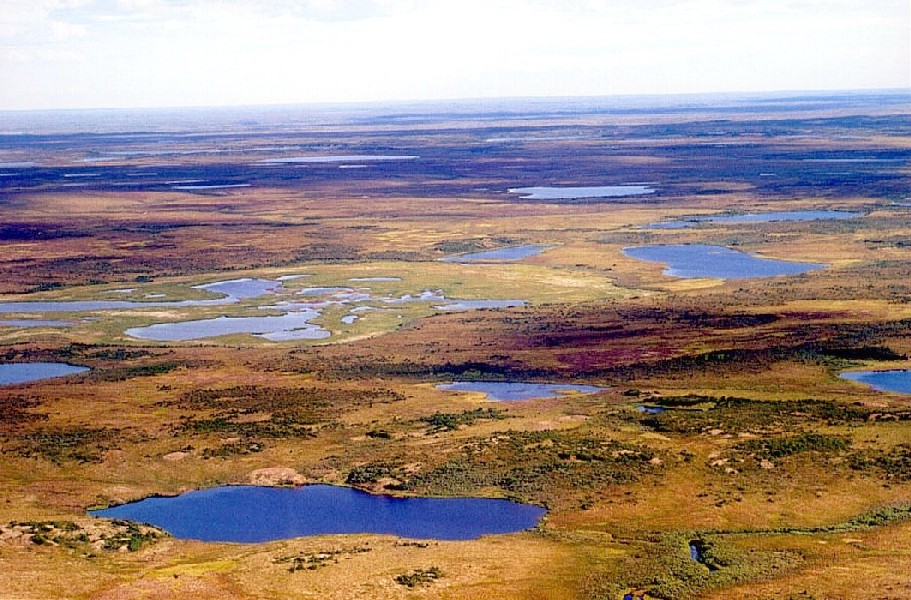
Tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless mountain tract". There are three regions and associated types of tundra: Arctic tundra, alpine tundra, and Antarctic tundra. Tundra vegetation is composed of dwarf shrubs, sedges, grasses, mosses, and lichens. Scattered trees grow in some tundra regions. The ecotone (or ecological boundary region) between the tundra and the forest is known as the tree line or timberline. The tundra soil is rich in nitrogen and phosphorus. The soil also contains large amounts of biomass and decomposed biomass that has been stored as methane and carbon dioxide in the permafrost, making the tundra soil a carbon sink. As global warming heats the ecosystem and causes soil thawing, the permafrost carbon cycle accelerates and releases much of these soil-contained g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulag
The Gulag, an acronym for , , "chief administration of the camps". The original name given to the system of camps controlled by the GPU was the Main Administration of Corrective Labor Camps (, )., name=, group= was the government agency in charge of the Soviet network of forced labour camps which were set up by order of Vladimir Lenin, reaching its peak during Joseph Stalin's rule from the 1930s to the early 1950s. English-language speakers also use the word ''gulag'' in reference to each of the forced-labor camps that existed in the Soviet Union, including the camps that existed in the post-Lenin era. The Gulag is recognized as a major instrument of political repression in the Soviet Union. The camps housed a wide range of convicts, from petty criminals to political prisoners, a large number of whom were convicted by simplified procedures, such as NKVD troikas or other instruments of extrajudicial punishment. In 1918–22, the agency was administered by the Cheka, follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komi Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
The Komi Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (russian: Коми Автономная Советская Социалистическая Республика; kv, Коми Автономнӧй Сӧветскӧй Социалистическӧй Республика), abbreviated as Komi ASSR (Komi and rus, Коми АССР), was an autonomous republic of the RSFSR within the Soviet Union, established in 1936 as successor of Komi-Zyryan Autonomous Oblast. In 1991, it became the Komi Republic, a federal subject of Russia. See also *First Secretary of the Komi Communist Party The First Secretary of the Komi regional branch of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union was the position of highest authority in the Komi AO (1921–1936) and the Komi ASSR (1936–1991) in the Russian SFSR of the Soviet Union. The position was ... States and territories established in 1936 Autonomous republics of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic 1936 establishments in the Sovie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komi-Zyryan Autonomous Oblast
Komi-Zyryan Autonomous Oblast ( Komi: Коми (Зыряна) асвеськӧдлан обласьт, ''Komi (Zyryana) asves’ködlan oblas’t'') created on 22 August 1921. It is one of several autonomous oblasts that existed in the Russian SFSR of the Soviet Union, and it was the predecessor of the Komi ASSR The Komi Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (russian: Коми Автономная Советская Социалистическая Республика; kv, Коми Автономнӧй Сӧветскӧй Социалистическӧй ... created in 1936. The seat of the Oblast was located in Ust-Sysolsk (renamed "Syktyvkar" in 1930). References 1922 establishments in Russia 1936 disestablishments in the Soviet Union Autonomous oblasts of the Soviet Union States and territories established in 1922 States and territories disestablished in 1936 History of the Komi Republic {{Soviet-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Von Keyserling
Alexander Friedrich Michael Lebrecht Nikolaus Arthur Graf von Keyserling (15 August 1815 – 8 May 1891) was a Baltic German geologist and paleontologist from the Keyserlingk family of Baltic German nobility. Career Alexander von Keyserling was born on at the Kabillen Manor, , Courland Governorate (in present-day Kabile, Kuldīga Municipality, Latvia), then part of the Russian Empire. His father was Count Heinrich Diedrich Wilhelm von Keyserling, 3rd Count of Rautenburg, was a spokesman, and in Courland, his mother was Baroness Anna Amalie Benigna . His family was of Westphalian origin and was originated in Herford, they were considered part of the ''Uradel'', or old nobility. The first ever mentioned member was Albert Keserlink (1443-1467 or 1468), the mayor of Herford. Alexander belonged to the ''House of Rautenburg- Telsen-Paddern'', which was a subdivided branch of the Prussian comital branch. The branch's founder Dietrich II von Keyserling, Herr auf und , was ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penal Colony
A penal colony or exile colony is a settlement used to exile prisoners and separate them from the general population by placing them in a remote location, often an island or distant colonial territory. Although the term can be used to refer to a correctional facility located in a remote location, it is more commonly used to refer to communities of prisoners overseen by wardens or governors having absolute authority. Historically penal colonies have often been used for penal labour in an economically underdeveloped part of a state's (usually colonial) territories, and on a far larger scale than a prison farm. British Empire With the passage of the Transportation Act 1717, the British government initiated the penal transportation of indentured servants to Britain's colonies in the Americas. British merchants would be in charge of transporting the convicts across the Atlantic, where in the colonies their indentures would be auctioned off to planters. Many of the indentured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catherine The Great
, en, Catherine Alexeievna Romanova, link=yes , house = , father = Christian August, Prince of Anhalt-Zerbst , mother = Joanna Elisabeth of Holstein-Gottorp , birth_date = , birth_name = Princess Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst , birth_place = Stettin, Pomerania, Prussia, Holy Roman Empire(now Szczecin, Poland) , death_date = (aged 67) , death_place = Winter Palace, Saint Petersburg, Russian Empire , burial_date = , burial_place = Saints Peter and Paul Cathedral, Saint Petersburg , signature = Catherine The Great Signature.svg , religion = Catherine II (born Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst; 2 May 172917 November 1796), most commonly known as Catherine the Great, was the reigning empress of Russia from 1762 to 1796. She came to power following the overthrow of her husband, Peter III. Under her long reign, inspired by the ideas of the Enlightenment, Russia experienced a renaissance of culture and sciences, which led to the founding of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Moscow
The Grand Duchy of Moscow, Muscovite Russia, Muscovite Rus' or Grand Principality of Moscow (russian: Великое княжество Московское, Velikoye knyazhestvo Moskovskoye; also known in English simply as Muscovy from the Latin ) was a Rus' principality of the Late Middle Ages centered on Moscow, and the predecessor state of the Tsardom of Russia in the early modern period. It was ruled by the Rurik dynasty, who had ruled Rus' since the foundation of Novgorod in 862. Ivan III the Great titled himself as Sovereign and Grand Duke of All Rus' (russian: государь и великий князь всея Руси, gosudar' i velikiy knyaz' vseya Rusi). The state originated with the rule of Alexander Nevsky of the Rurik dynasty, when in 1263, his son, Daniel I, was appointed to rule the newly created Grand Principality of Moscow, which was a vassal state to the Mongol Empire (under the "Tatar Yoke"), and which eclipsed and eventually absorbed its parent duchy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Perm
Great Perm, or simply Perm, in Latin ''Permia'', was a medieval historical region in what is now the Perm Krai of the Russian Federation. Cherdyn is said to have been its capital. The origin of the name ''Perm'' is uncertain. Most common explanation derives the name "Perm" from "parma" ("forested highlands" in Komi language). While the city of Perm is a modern foundation named for Permia, the town of Cherdyn was reportedly itself known as the capital of "Great Perm" in the past. Cherdyn acted as a central market town, and it is sometimes suggested that ''perm'' was simply a term for "merchants" or "market" in a local language, but there have been other suggestions. The same name is likely reflected in the toponym Bjarmaland in Norse sagas. The general region of Great Perm was known as ''wisu'' (وِيسُو ''wīsū'') in medieval Arab ethnography, so referred to in the works of Ahmad ibn Fadlan, Al-Gharnati, Zakariya al-Qazwini and Yaqut al-Hamawi (in his '' Dictionary of Coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Slavs
The East Slavs are the most populous subgroup of the Slavs. They speak the East Slavic languages, and formed the majority of the population of the medieval state Kievan Rus', which they claim as their cultural ancestor.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of Russia'' (Penguin, 1995), p. 16. Today, the East Slavs consist of Belarusians, Russians, Rusyns, and Ukrainians. History Sources Researchers know relatively little about the Eastern Slavs prior to approximately 859 AD when the first events recorded in the '' Primary Chronicle'' occurred. The Eastern Slavs of these early times apparently lacked a written language. The few known facts come from archaeological digs, foreign travellers' accounts of the Rus' land, and linguistic comparative analyses of Slavic languages. Very few native Rus' documents dating before the 11th century (none before the 10th century) have survived. The earliest major manuscript with information on Rus' history, the '' Prim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
