|
Polish–Ottoman Wars
Polish–Ottoman Wars can refer to one of the several conflicts between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Ottoman Empire: * Crusade of Varna (1443–1444) * Polish–Ottoman War (1485–1503) ** Jan Olbracht's Moldavian expedition of 1497 and Ottoman's retribution raid a year later * Moldavian Magnate Wars, a period of near constant warfare at the end of the 16th century and the beginning of the 17th century. ** Jan Zamoyski's expedition to Moldavia * Polish–Ottoman War (1620–21) * Polish–Ottoman War (1633–34) * Polish–Cossack–Tatar War (1666–71) * Polish–Ottoman War (1672–76) * As part of the Great Turkish War The Great Turkish War () or The Last Crusade, also called in Ottoman sources The Disaster Years (), was a series of conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and the Holy League (1684), Holy League consisting of the Holy Roman Empire, Polish–Lith ...: ** Polish–Ottoman War (1683–99) See also * * * Polish–Ottoman alliance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, existing from 1569 to 1795. This state was among the largest, most populated countries of 16th- to 18th-century Europe. At its peak in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth spanned approximately and supported a multi-ethnic population of around 12 million as of 1618. The official languages of the Commonwealth were Polish language, Polish and Latin Language, Latin, with Catholic Church, Catholicism as the state religion. The Union of Lublin established the Commonwealth as a single entity on 1 July 1569. The two nations had previously been in a personal union since the Union of Krewo, Krewo Agreement of 1385 (Polish–Lithuanian union) and the subsequent marriage of Queen Jadwiga of Poland to Grand Duke Jogaila of Lithuania, who was cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Central Europe, between the early 16th and early 18th centuries. The empire emerged from a Anatolian beyliks, ''beylik'', or principality, founded in northwestern Anatolia in by the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. His successors Ottoman wars in Europe, conquered much of Anatolia and expanded into the Balkans by the mid-14th century, transforming their petty kingdom into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the Fall of Constantinople, conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed II. With its capital at History of Istanbul#Ottoman Empire, Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and control over a significant portion of the Mediterranean Basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
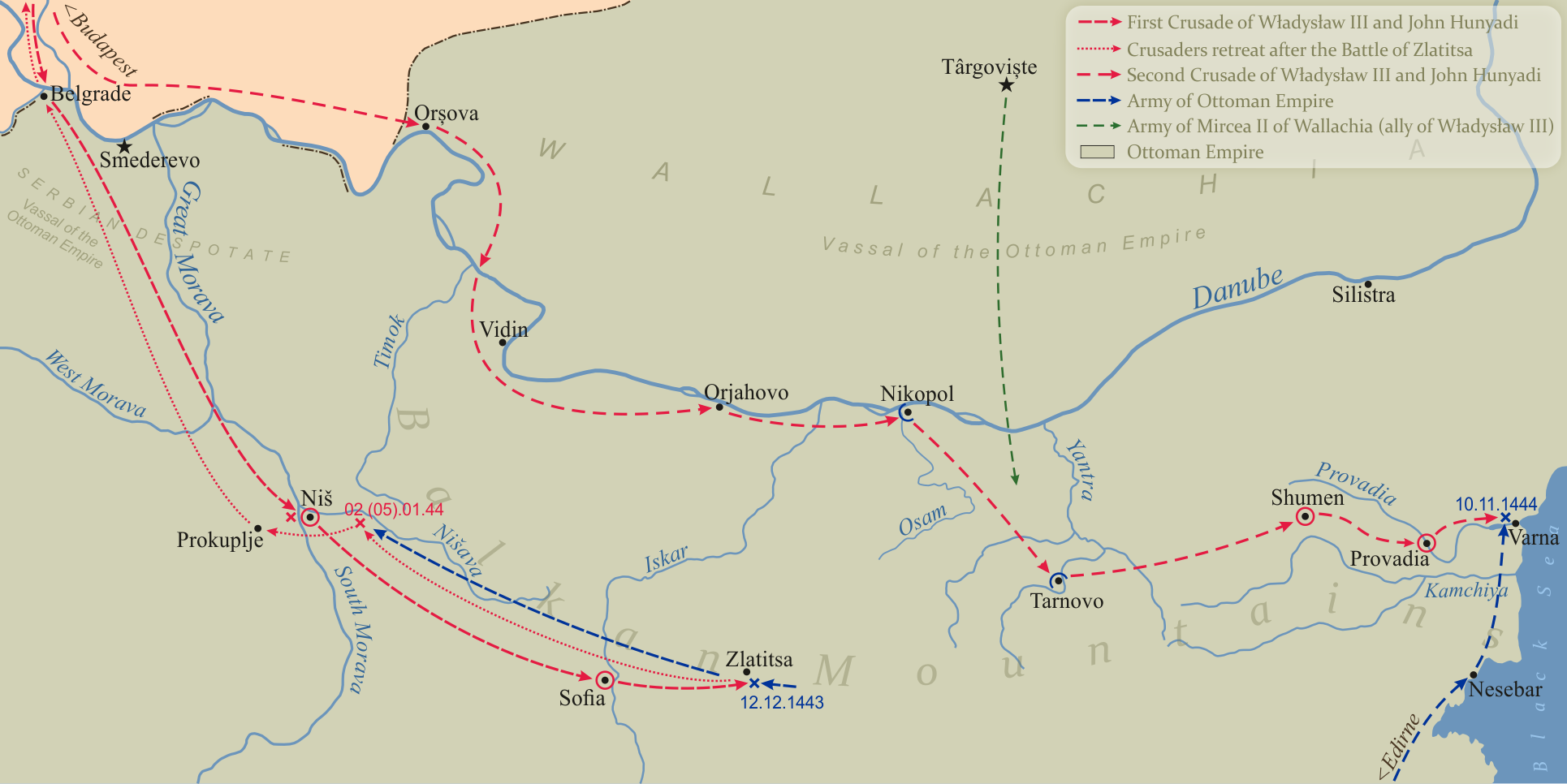
Crusade Of Varna
The Crusade of Varna was an unsuccessful military campaign mounted by several European leaders to check the expansion of the Ottoman Empire into Central Europe, specifically the Balkans between 1443 and 1444. It was called by Pope Eugene IV on 1 January 1443 and led by King Władysław III of Poland, John Hunyadi, Voivode of Transylvania, and Duke Philip the Good of Burgundy. The Crusade of Varna culminated in a decisive Ottoman victory over the crusader alliance at the Battle of Varna on 10 November 1444, during which Władysław and the expedition's papal legate Julian Cesarini were killed. Background In 1428, while the Ottoman Empire was fighting a war with the Republic of Venice and the Kingdom of Hungary they achieved a temporary peace by establishing the Serbian Despotate as a buffer state. After the war ended in 1430, the Ottomans returned to their earlier objective of controlling all lands south of the Danube. In 1432, Sultan Murad II began raiding into Tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Ottoman War (1485–1503)
The Polish–Turkish War of 1485–1503 was a prolonged conflict, rather a series of conflicts, between the Kingdom of Poland and the Ottoman Empire. The conflict formally lasted eighteen years, but during this time hostilities were ceased on several occasions due to temporary treaties being signed between the warring parties. In the war the Kingdom of Poland was supported by its fiefs, the Duchy of Mazovia and the State of the Teutonic Order, as well as the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The Ottoman Empire on the other hand, was allied with the Crimean Khanate and by the Principality of Moldavia during the Moldavian Campaign of 1497–1499. For most of the 15th century, Moldavia was a vassal of Poland, but other states, notably the Kingdom of Hungary, the Ottoman Empire and the Crimean Khanate, meanwhile tried to subdue Moldavia. After the Fall of Constantinople (1453), the Ottomans directed their expansion northwards towards the lower Danube and behind the mighty river and also thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moldavian Campaign (1497–1499)
The Moldavian campaign or the Polish–Ottoman War of 1497–1499 was an unsuccessful war led by John Albert of Poland against the Moldavians, supported by their Ottoman suzerains. John Albert set out with an army of 80,000 men with the objectives of deposing Stephen the Great of Moldavia and replacing him with Sigismund Jagiellon, reconquering the fortresses on the northern Black Sea coast and taking control of Crimea and the Danube Delta. Background John I Albert was elected due to his advocacy for an offensive policy against the Ottomans, and he made an alliance with Venice and Hungary for a joint effort against them.History of the Ottoman Empire and Modern Turkey: Volume 1, Empire of the Gazis: The Rise and Decline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moldavian Magnate Wars
The Moldavian Magnate Wars, or Moldavian Ventures, refer to the period at the end of the 16th century and the beginning of the 17th century when the magnates of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth intervened in the affairs of Moldavia, clashing with the Habsburgs and the Ottoman Empire for domination and influence over the principality. The Magnate Wars (1593–1617) Causes Jan Zamoyski, Polish grand crown chancellor ('' kanclerz'') and military commander (grand crown hetman), known for his opposition towards the Habsburgs, had been a vocal supporter of Commonwealth expansion in the southern direction. Since the early plans made by Commonwealth King Stefan Batory for the war against the Ottomans, Zamoyski supported them, viewing those plans as a good long-term strategy for the Commonwealth. Any policy that was against the Ottomans was also supported by the Holy See, and Pope Sixtus V strongly expressed his support for any war between the Commonwealth and the Ottomans. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Zamoyski's Expedition To Moldavia
Jan Zamoyski's expedition to Moldavia was a successful military campaign in 1595 that aimed to establish Moldavia as a Polish vassal state. Background In early 1595 Sigismund Báthory, Prince of Transylvania, convinced Ștefan Răzvan, a commander of Hungarian mercenaries in the service of the Hospodar Aaron the Tyrant to rebel. Ștefan captured Aaron and sent him to Transylvania, then proclaimed himself as the new Hospodar and a vassal of Sigismund. In response the Ottoman Sultan Mehmed III, who had been Aaron's protector and sovereign, decided to put an end to the ongoing power struggles in Moldavia, Wallachia, and Transylvania between various magnates. While Wallachia was to receive a new Turkish sponsored ruler, Moldavia was to be simply incorporated into the Ottoman Empire as a province. The Ottoman intervention aroused alarms in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth which sought to reestablish its influence in the region, having lost sovereignty over Moldavia some hundred ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Turkish War
The Great Turkish War () or The Last Crusade, also called in Ottoman sources The Disaster Years (), was a series of conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and the Holy League (1684), Holy League consisting of the Holy Roman Empire, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Poland-Lithuania, Republic of Venice, Venice, Tsardom of Russia, Russia, and Kingdom of Hungary (1526–1867), the Kingdom of Hungary. Intensive fighting began in 1683 and ended with the signing of the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699. The war was a resounding defeat for the Ottoman Empire, which for the first time lost substantial territory, in Ottoman Hungary, Hungary and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, as well as in part of the western Balkans. The war was significant also for being the first instance of Russia joining an alliance with Western Europe. Historians have labeled the war as the Fourteenth Crusade launched against the Turks by the papacy. The French did not join the Holy League, as France had agreed to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |