|
Polarization Ripples
Polarization ripples are parallel oscillations which have been observed since the 1960s on the bottom of pulsed laser irradiation of semiconductors. They have the property to be very dependent to the orientation of the laser electric field. Since the wide availability of femtosecond lasers, such structures have been observed on metals, semiconductors, but also on dielectrics. Moreover, the ripples can reach far sub-wavelength periodicities until 100 nm as recently observed in titanium. The "cumulative" changes occurring from pulse to pulse in the material properties are still under investigation. Formation mechanisms The formation mechanisms are still under debate. However, two types of formation mechanisms can be underlined: * the resonant mechanisms, which are based on electromagnetic aspects, as periodic energy deposition due to roughness, as surface plasmon polariton excitation during the laser illumination; * the non-resonant mechanisms, more related with thermal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
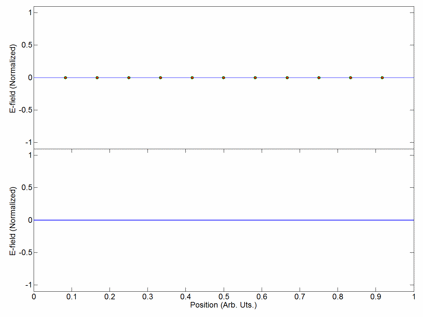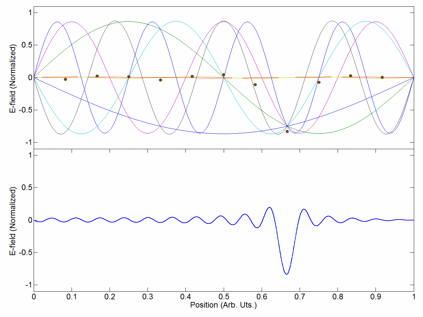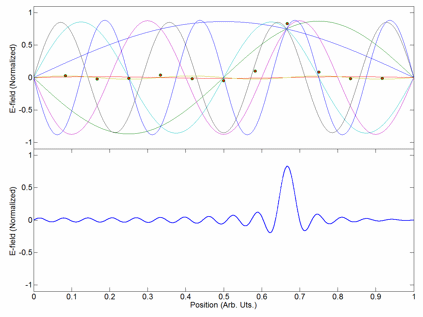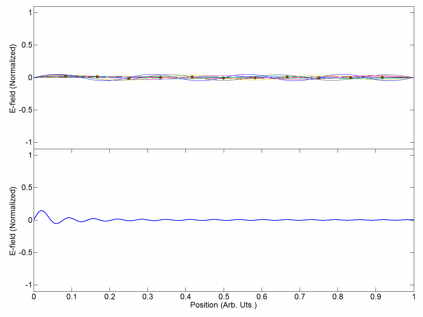
Scheme Of Near-wavelength Periodic Surface Structures Induced By Ultrasort Laser Irradiation
A scheme is a systematic plan for the implementation of a certain idea. Scheme or schemer may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''The Scheme'' (TV series), a BBC Scotland documentary series * The Scheme (band), an English pop band * ''The Scheme'', an action role-playing video game for the PC-8801, made by Quest Corporation * Schemer (comics), Richard Fisk, a Marvel Comics villain turned antihero * Horace Schemer, a fictional character in the TV series ''Shining Time Station'' * Schemee, a fictional child character and Schemer's nephew in the TV Series ''Shining Time Station'' * ''Schemers'' (film), a Scottish film Other uses * Classification scheme, eg a thesaurus, a taxonomy, a data model, or an ontology * Scheme (programming language), a minimalist dialect of Lisp * Scheme (mathematics), a concept in algebraic geometry * Scheme (linguistics), a figure of speech that changes a sentence's structure * Scam, an attempt to swindle or cheat people through deception **Get-rich-quick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femtosecond Laser
Mode locking is a technique in optics by which a laser can be made to produce pulses of light of extremely short duration, on the order of picoseconds (10−12 s) or femtoseconds (10−15 s). A laser operated in this way is sometimes referred to as a femtosecond laser, for example, in modern refractive surgery. The basis of the technique is to induce a fixed phase relationship between the longitudinal modes of the laser's resonant cavity. Constructive interference between these modes can cause the laser light to be produced as a train of pulses. The laser is then said to be "phase-locked" or "mode-locked". Laser cavity modes Although laser light is perhaps the purest form of light, it is not of a single, pure frequency or wavelength. All lasers produce light over some natural bandwidth or range of frequencies. A laser's bandwidth of operation is determined primarily by the gain medium from which the laser is constructed, and the range of frequencies over which a lase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metals
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into wires) and malleable (they can be hammered into thin sheets). These properties are the result of the ''metallic bond'' between the atoms or molecules of the metal. A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polymeric sulfur nitride. In physics, a metal is generally regarded as any substance capable of conducting electricity at a temperature of absolute zero. Many elements and compounds that are not normally classified as metals become metallic under high pressures. For example, the nonmetal iodine gradually becomes a metal at a pressure of between 40 and 170 thousand times atmospheric pressure. Equally, some materials regarded as metals c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductors
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conductivity value falling between that of a electrical conductor, conductor, such as copper, and an insulator (electricity), insulator, such as glass. Its electrical resistivity and conductivity, resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities ("doping (semiconductor), doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dielectrics
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in an electrical conductor, because they have no loosely bound, or free, electrons that may drift through the material, but instead they shift, only slightly, from their average equilibrium positions, causing dielectric polarisation. Because of dielectric polarisation, positive charges are displaced in the direction of the field and negative charges shift in the direction opposite to the field (for example, if the field is moving parallel to the positive ''x'' axis, the negative charges will shift in the negative ''x'' direction). This creates an internal electric field that reduces the overall field within the dielectric itself. If a dielectric is composed of weakly bonded molecules, those molecules not only become polarise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Plasmon Polariton
Surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) are electromagnetic waves that travel along a metal–dielectric or metal–air interface, practically in the infrared or visible-frequency. The term "surface plasmon polariton" explains that the wave involves both charge motion in the metal ("surface plasmon") and electromagnetic waves in the air or dielectric ("polariton"). They are a type of surface wave, guided along the interface in much the same way that light can be guided by an optical fiber. SPPs have a shorter wavelength than light in vacuum at the same frequency (photons). Hence, SPPs can have a higher momentum and local field intensity. Perpendicular to the interface, they have subwavelength-scale confinement. An SPP will propagate along the interface until its energy is lost either to absorption in the metal or scattering into other directions (such as into free space). Application of SPPs enables subwavelength optics in microscopy and photolithography beyond the diffraction limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capillary Waves
A capillary wave is a wave traveling along the phase boundary of a fluid, whose dynamics and phase velocity are dominated by the effects of surface tension. Capillary waves are common in nature, and are often referred to as ripples. The wavelength of capillary waves on water is typically less than a few centimeters, with a phase speed in excess of 0.2–0.3 meter/second. A longer wavelength on a fluid interface will result in gravity–capillary waves which are influenced by both the effects of surface tension and gravity, as well as by fluid inertia. Ordinary gravity waves have a still longer wavelength. When generated by light wind in open water, a nautical name for them is cat's paw waves. Light breezes which stir up such small ripples are also sometimes referred to as cat's paws. On the open ocean, much larger ocean surface waves (seas and swells) may result from coalescence of smaller wind-caused ripple-waves. Dispersion relation The dispersion relation describes the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffraction Grating
In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical component with a periodic structure that diffracts light into several beams travelling in different directions (i.e., different diffraction angles). The emerging coloration is a form of structural coloration. The directions or diffraction angles of these beams depend on the wave (light) incident angle to the diffraction grating, the spacing or distance between adjacent diffracting elements (e.g., parallel slits for a transmission grating) on the grating, and the wavelength of the incident light. The grating acts as a dispersive element. Because of this, diffraction gratings are commonly used in monochromators and spectrometers, but other applications are also possible such as optical encoders for high precision motion control and wavefront measurement. For typical applications, a reflective grating has ridges or ''rulings'' on its surface while a transmissive grating has transmissive or hollow slits on its surface. Such a grating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Silicon
Black silicon is a semiconductor material, a surface modification of silicon with very low reflectivity and correspondingly high absorption of visible (and infrared) light. The modification was discovered in the 1980s as an unwanted side effect of reactive ion etching (RIE).Black Silicon as a functional layer of the micro-system technology Other methods for forming a similar structure include electrochemical etching, stain etching, metal-assisted chemical etching, and laser treatment (which is developed in 's laboratory at ). Black silic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |