|
Polaris Missile
The UGM-27 Polaris missile was a two-stage solid-fueled nuclear-armed submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM). As the United States Navy's first SLBM, it served from 1961 to 1980. In the mid-1950s the Navy was involved in the Jupiter missile project with the U.S. Army, and had influenced the design by making it squat so it would fit in submarines. However, they had concerns about the use of liquid fuel rockets on board ships, and some consideration was given to a solid fuel version, Jupiter S. In 1956, during an anti-submarine study known as Project Nobska, Edward Teller suggested that very small hydrogen bomb warheads were possible. A crash program to develop a missile suitable for carrying such warheads began as Polaris, launching its first shot less than four years later, in February 1960. As the Polaris missile was fired underwater from a moving platform, it was essentially invulnerable to counterattack. This led the Navy to suggest, starting around 1959, that they b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral
Cape Canaveral ( es, Cabo Cañaveral) is a cape (geography), cape in Brevard County, Florida, in the United States, near the center of the state's Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast. Officially Cape Kennedy from 1963 to 1973, it lies east of Merritt Island, separated from it by the Banana River. It is part of a region known as the Space Coast, and is the site of the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. Since many U.S. spacecraft have been launched from both the station and the Kennedy Space Center on adjacent Merritt Island, the two are sometimes conflation, conflated with each other. Other features of the cape include Port Canaveral, one of the busiest cruise ports in the world, and the Cape Canaveral Lighthouse. The city of Cape Canaveral, Florida, Cape Canaveral lies just south of the Port Canaveral District. Mosquito Lagoon, the Indian River (Florida), Indian River, Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge and Canaveral National Seashore are also features of this area. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
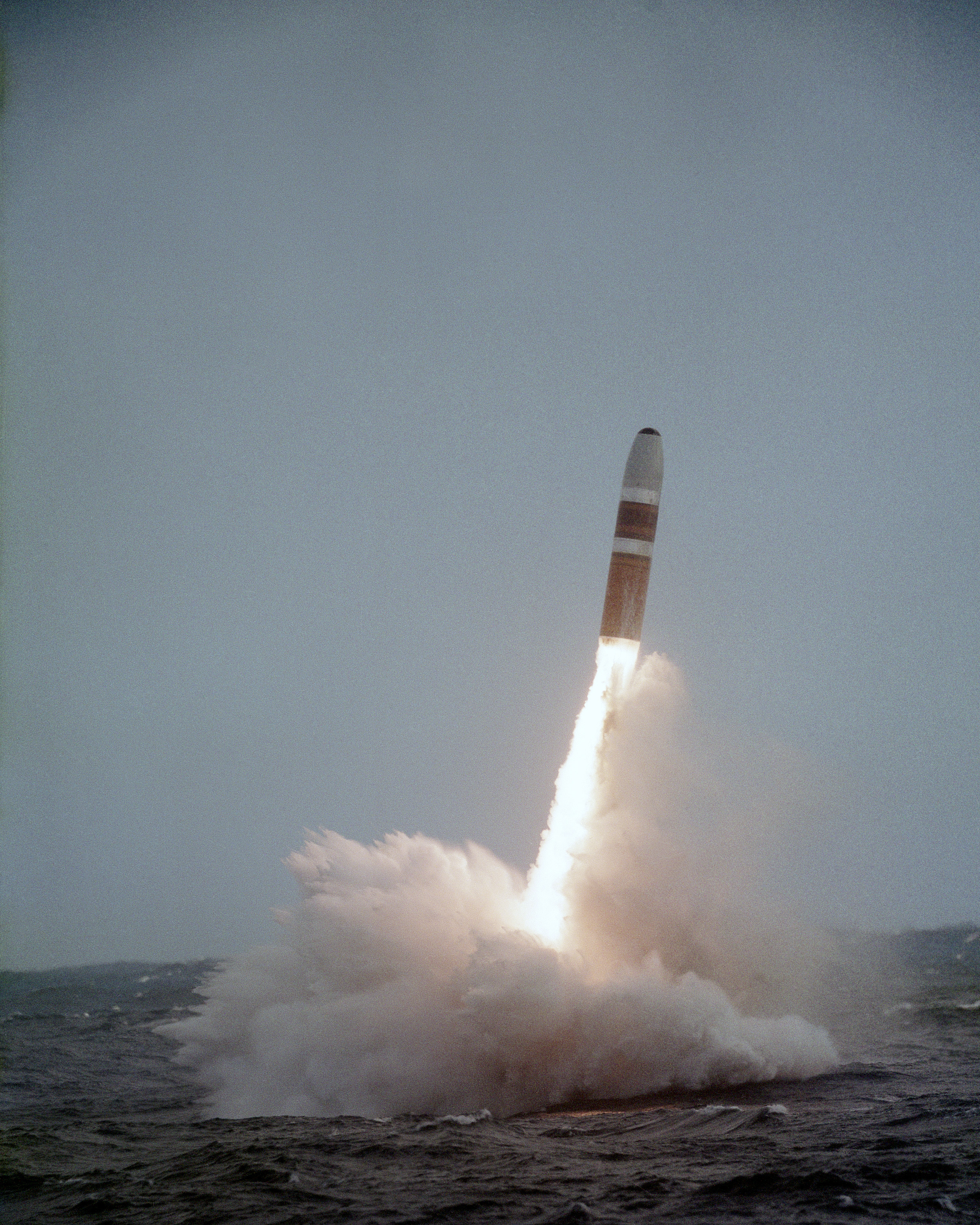
Submarine-launched Ballistic Missile
A submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) is a ballistic missile capable of being launched from submarines. Modern variants usually deliver multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), each of which carries a nuclear warhead and allows a single launched missile to strike several targets. Submarine-launched ballistic missiles operate in a different way from submarine-launched cruise missiles. Modern submarine-launched ballistic missiles are closely related to intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), with ranges of over , and in many cases SLBMs and ICBMs may be part of the same family of weapons. History Origins The first practical design of a submarine-based launch platform was developed by the Germans near the end of World War II involving a launch tube which contained a V-2 ballistic missile variant and was towed behind a submarine, known by the code-name ''Prüfstand XII''. The war ended before it could be tested, but the engineers who had worked o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many List of islands of the United Kingdom, smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares Republic of Ireland–United Kingdom border, a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polaris Sales Agreement
The Polaris Sales Agreement was a treaty between the United States and the United Kingdom which began the UK Polaris programme. The agreement was signed on 6 April 1963. It formally arranged the terms and conditions under which the UGM-27 Polaris, Polaris missile system was provided to the United Kingdom. The United Kingdom had been planning to buy the air-launched GAM-87 Skybolt, Skybolt missile to extend the operational life of the British V bombers, but the United States decided to cancel the Skybolt program in 1962 as it no longer needed the missile. The crisis created by the cancellation prompted an emergency meeting between the President of the United States, John F. Kennedy, and the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Harold Macmillan, which resulted in the Nassau Agreement, under which the United States agreed to provide Polaris missiles to the United Kingdom instead. The Polaris Sales Agreement provided for the implementation of the Nassau Agreement. The United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexible Response
Flexible response was a defense strategy implemented by John F. Kennedy in 1961 to address the Kennedy administration's skepticism of Dwight Eisenhower's New Look and its policy of massive retaliation. Flexible response calls for mutual deterrence at strategic, tactical, and conventional levels, giving the United States the capability to respond to aggression across the spectrum of war, not limited only to nuclear arms. History The New Look policy, though initially useful, quickly became obsolete with the introduction of inter-continental delivery systems that undermined the credibility of a deterrence threat. The cornerstone of U.S. and European defense strategy was then threatened as the U.S. could no longer rely on nuclear threats to provide security for it and its allies. John F. Kennedy won the presidency by claiming that the Republican Party had allowed the U.S. to fall behind the Soviets into a missile gap. Upon entering office Kennedy cited General Maxwell Taylor' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
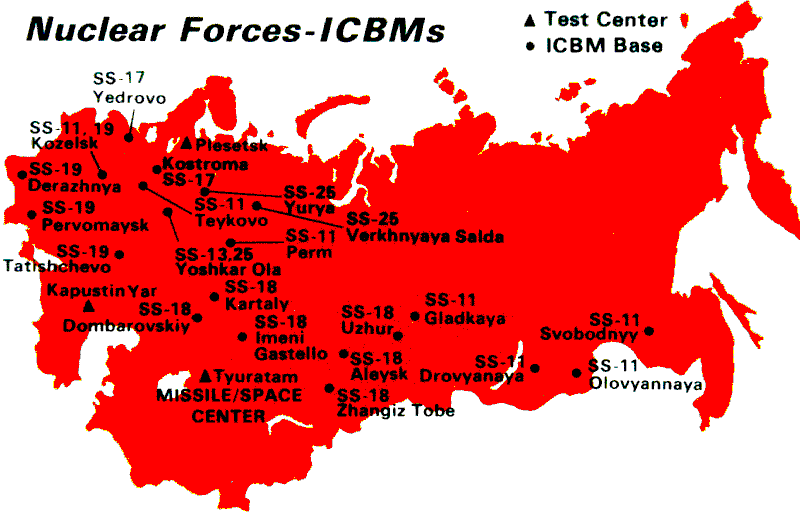
ICBM
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. Russia, the United States, China, France, India, the United Kingdom, and North Korea are the only countries known to have operational ICBMs. Early ICBMs had limited precision, which made them suitable for use only against the largest targets, such as cities. They were seen as a "safe" basing option, one that would keep the deterrent force close to home where it would be difficult to attack. Attacks against military targets (especially hardened ones) still demanded t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
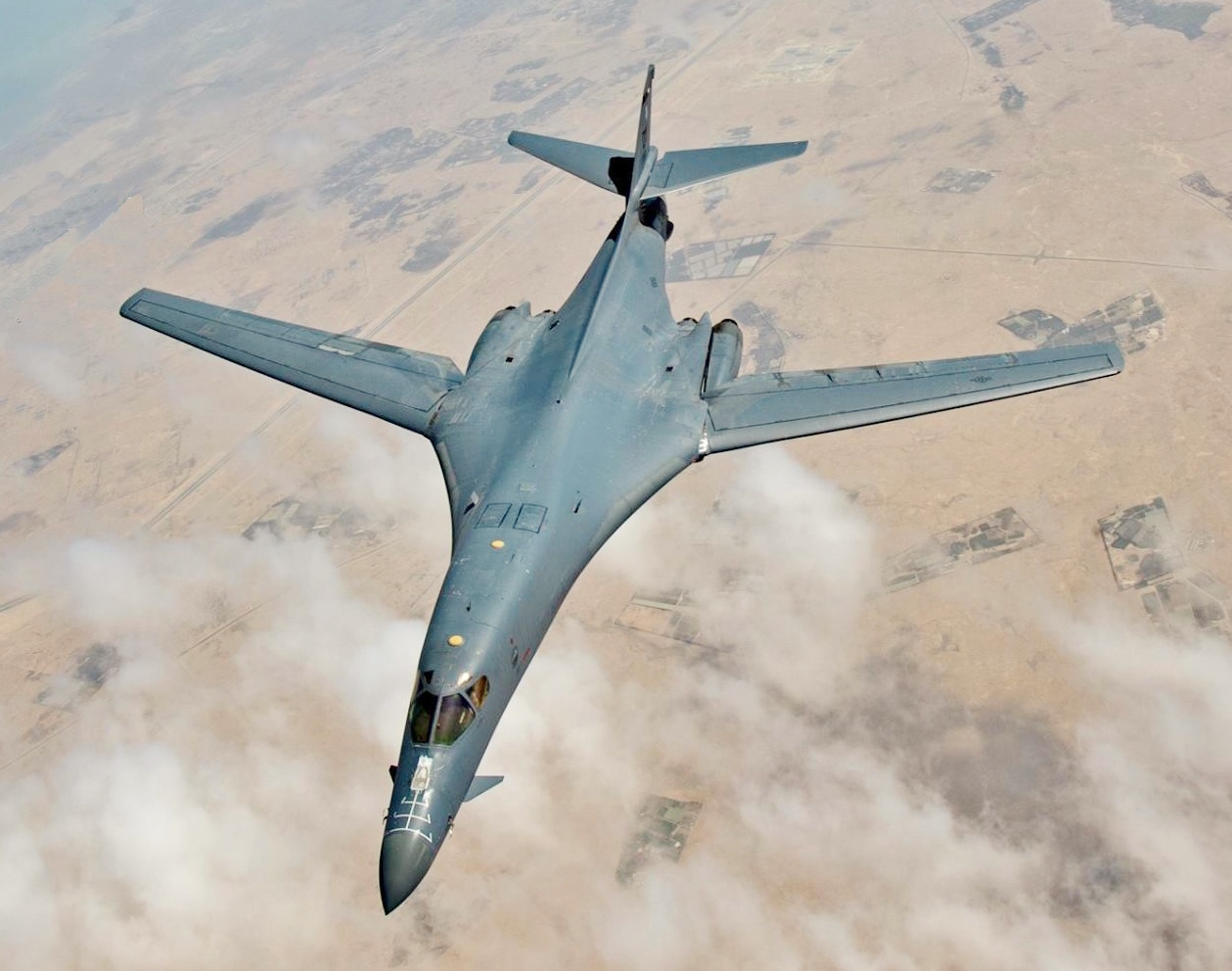
Strategic Bomber
A strategic bomber is a medium- to long-range penetration bomber aircraft designed to drop large amounts of air-to-ground weaponry onto a distant target for the purposes of debilitating the enemy's capacity to wage war. Unlike tactical bombers, penetrators, fighter-bombers, and attack aircraft, which are used in air interdiction operations to attack enemy combatants and military equipment, strategic bombers are designed to fly into enemy territory to destroy strategic targets (e.g., infrastructure, logistics, military installations, factories, etc.). In addition to strategic bombing, strategic bombers can be used for tactical missions. There are currently only three countries that operate strategic bombers: the United States, Russia and China. The modern strategic bomber role appeared after strategic bombing was widely employed, and atomic bombs were first used in combat during World War II. Nuclear strike missions (i.e., delivering nuclear-armed missiles or bombs) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterforce
In nuclear strategy, a counterforce target is one that has a military value, such as a launch silo for intercontinental ballistic missiles, an airbase at which nuclear-armed bombers are stationed, a homeport for ballistic missile submarines, or a command and control installation. The intent of a counterforce strategy (attacking counterforce targets with nuclear weapons) is to conduct a pre-emptive nuclear strike which has as its aim to disarm an adversary by destroying its nuclear weapons before they can be launched. That would minimize the impact of a retaliatory second strike. However, counterforce attacks are possible in a second strike as well, especially with weapons like UGM-133 Trident II. A counterforce target is distinguished from a countervalue target, which includes an adversary's population, knowledge, economic, or political resources. In other words, a counterforce strike is against an adversary's military, and a countervalue strike is against an adversary's cities. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Deterrent
Nuclear strategy involves the development of doctrines and strategies for the production and use of nuclear weapons. As a sub-branch of military strategy, nuclear strategy attempts to match nuclear weapons as means to political ends. In addition to the actual use of nuclear weapons whether in the battlefield or strategically, a large part of nuclear strategy involves their use as a bargaining tool. Some of the issues considered within nuclear strategy include: *Conditions which serve a nation's interest to develop nuclear weapons *Types of nuclear weapons to be developed *How and when weapons are to be used Many strategists argue that nuclear strategy differs from other forms of military strategy. The immense and terrifying power of the weapons makes their use, in seeking victory in a traditional military sense, impossible. Perhaps counterintuitively, an important focus of nuclear strategy has been determining how to prevent and deter their use, a crucial part of mutual as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Bomb
A thermonuclear weapon, fusion weapon or hydrogen bomb (H bomb) is a second-generation nuclear weapon design. Its greater sophistication affords it vastly greater destructive power than first-generation nuclear bombs, a more compact size, a lower mass, or a combination of these benefits. Characteristics of nuclear fusion reactions make possible the use of non-fissile depleted uranium as the weapon's main fuel, thus allowing more efficient use of scarce fissile material such as uranium-235 () or plutonium-239 (). The first full-scale thermonuclear test was carried out by the United States in 1952; the concept has since been employed by most of the world's nuclear powers in the design of their weapons. Modern fusion weapons consist essentially of two main components: a nuclear fission primary stage (fueled by or ) and a separate nuclear fusion secondary stage containing thermonuclear fuel: the heavy hydrogen isotopes deuterium and tritium, or in modern weapons lithium deu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Teller
Edward Teller ( hu, Teller Ede; January 15, 1908 – September 9, 2003) was a Hungarian-American theoretical physicist who is known colloquially as "the father of the hydrogen bomb" (see the Teller–Ulam design), although he did not care for the title, considering it to be in poor taste. Throughout his life, Teller was known both for his scientific ability and for his difficult interpersonal relations and volatile personality. Born in Hungary in 1908, Teller emigrated to the United States in the 1930s, one of the many so-called "Martians", a group of prominent Hungarian scientist émigrés. He made numerous contributions to nuclear and molecular physics, spectroscopy (in particular the Jahn–Teller and Renner–Teller effects), and surface physics. His extension of Enrico Fermi's theory of beta decay, in the form of Gamow–Teller transitions, provided an important stepping stone in its application, while the Jahn–Teller effect and the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Nobska
Project Nobska was a 1956 summer study on anti-submarine warfare (ASW) for the United States Navy ordered by Chief of Naval Operations Admiral Arleigh Burke. It is also referred to as the Nobska Study, named for its location on Nobska Point near the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) on Cape Cod, Massachusetts. The focus was on the ASW implications of nuclear submarines, particularly on new technologies to defend against them. The study was coordinated by the Committee on Undersea Warfare (CUW) of the National Academy of Sciences (NAS). It was notable for including 73 representatives from numerous organizations involved in submarine design, submarine-related fields, and weapons design, including senior scientists from the Atomic Energy Commission's nuclear weapons laboratories. Among the participants were Nobel laureate Isidor Rabi, Paul Nitze, and Edward Teller. The study's recommendations influenced all subsequent US Navy submarine designs, as well as submarine-laun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(2).jpg)





.jpg)