|
Plevna March
Plevna March or Osman Pasha March was written in order to commemorate Osman Pasha, who led Ottoman troops in the Siege of Plevna.Büyük Larousse Sözlük ve Ansiklopedisi (1986), v. 18, c. 9433, Gelişim Yayınları. History It was sung under the name of ''Old Plevna March'' by Hafız Yaşar Bey and his group in 1910 (not definite) and underwent some changes before it took its final version. According to Yaşar Bey, it had been written by Mehmet Ali Bey.''Osmanlı Marşları: The Ottoman Military Music in 78 rpm Records'', Muammer Karabey Koleksiyonu Book & CD, Kalan. According to other sources, it was written by Mithat Efendi and composed by Armenian composer Tigran Chukhajian Tigran Gevorki Chukhajian ( hy, Տիգրան Չուխաճեան, tr, Dikran Çuhacıyan; 1837 – March 11, 1898) was an Ottoman Armenian composer and conductor, and the founder of the first opera institution in the Ottoman Empire. Biography .... There are still other sources that claim the song was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osman Nuri Paşa
Osman Nuri Pasha ( ota, عثمان نوری پاشا; 1832, Tokat, Ottoman Empire – 4 to 5 April 1900, Constantinople, Ottoman Empire), also known as Ghazi Osman Pasha ( tr, Gazi Osman Paşa), was an Ottoman Empire, Ottoman field marshal. Being one of the most respected and decorated Ottoman Pasha, pashas of all time, many songs have been written for him, and many places have been named after him. This is mainly because he Siege of Plevna, held the Ottoman Bulgaria, Bulgarian town of Pleven, Plevna for five months against superior Russo-Romanian forces in 1877 during the Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878), Russo-Turkish War, though the city eventually fell. Early life and education Osman Nuri was born into the prominent Turkish Yağcıoğulları family of the city of Tokat. His father was a civil worker who, soon after Osman's birth, was appointed to a position in the Ottoman capital, so the family moved to Ottoman Constantinople, Constantinople (now Istanbul). Osman a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Of The Ottoman Empire
The military of the Ottoman Empire ( tr, Osmanlı İmparatorluğu'nun silahlı kuvvetleri) was the armed forces of the Ottoman Empire. Army The military of the Ottoman Empire can be divided in five main periods. The foundation era covers the years between 1300 (Byzantine expedition) and 1453 (Conquest of Constantinople), the classical period covers the years between 1451 (second enthronement of Sultan Mehmed II) and 1606 (Peace of Zsitvatorok), the reformation period covers the years between 1606 and 1826 ( Vaka-i Hayriye), the modernisation period covers the years between 1826 and 1858 and decline period covers the years between 1861 (enthronement of Sultan Abdülaziz) and 1918 (Armistice of Mudros). The Ottoman army is the forerunner of the Turkish Armed Forces. Foundation period (1300–1453) The earliest form of the Ottoman military was a steppe-nomadic cavalry force.Mesut Uyar, Edward J. Erickson, ''A Military History of the Ottomans: From Osman to Atatürk'', Pleager ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
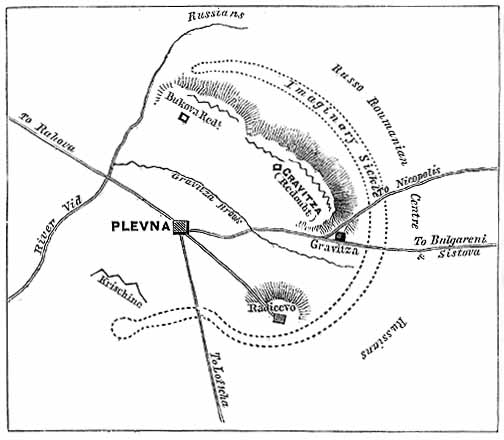
Siege Of Plevna
The siege of Pleven, was a major battle of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878, fought by the joint army of Russia and Romania against the Ottoman Empire. After the Russian army crossed the Danube at Svishtov, it began advancing towards the centre of modern Bulgaria, with the aim of crossing the Balkan Mountains to Constantinople, avoiding the fortified Turkish fortresses on the Black Sea coast. The Ottoman army led by Osman Pasha, returning from Serbia after a conflict with that country, was massed in the fortified city of Pleven, a city surrounded by numerous redoubts, located at an important road intersection. After two unsuccessful assaults, in which he lost valuable troops, the commander of the Russian troops on the Balkan front, Grand Duke Nicholas of Russia insisted by telegram the help of his Romanian ally King Carol I. King Carol I crossed the Danube with the Romanian Army and was placed in command of the Russian-Romanian troops. He decided not to make any more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Armenian Population
The Ottoman Armenian population varied throughout history. The number of Armenians within the empire between 1914 and 1915 is a controversial topic. Most estimates by Western scholars range from 1.5 to 2.4 million. According to Britannica prior to 1915 and Samuel Cox, American Embassy in Istanbul from 1880-1886, it was 1.75 million and 2.4 million, respectively. Establishing the size of this population is very important in determining an accurate estimation of Armenian losses between 1915 and 1923 during the Armenian genocide. Classic Period Values based on taxation data While the Ottoman Empire had population records prior to the 1830s, it was only in 1831 that the Office of Population Registers fund (Ceride-i Nüfus Nezareti) was founded. To draw more accurate data, the Office decentralized in 1839. Registrars, inspectors, and population officials were appointed to the provinces and smaller administrative districts. They recorded births and deaths periodically and compared li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigran Chukhajian
Tigran Gevorki Chukhajian ( hy, Տիգրան Չուխաճեան, tr, Dikran Çuhacıyan; 1837 – March 11, 1898) was an Ottoman Armenian composer and conductor, and the founder of the first opera institution in the Ottoman Empire. Biography Chukhajian was born in Constantinople. He studied at composer Gabriel Yeranian's class, then had classes in Milan. Along with other Armenian intellectuals of that period he fought for the development of national culture, organized Armenian musical societies, theatres, schools, papers and free concerts. In 1862, he took over publication of the Armenian musical journal ''Armenian Lyre''.In his works, Chukhajian used the elements of European musical techniques and eastern music elements He is an author of pieces for piano, songs and romances, chamber and symphonic works, operas. His most successful opera was Leblebici hor-hor agha (1875), it was premiered at the French Theatre in Constantinople, it was so successful that during the season i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish Armed Forces
The Turkish Armed Forces (TAF; tr, Türk Silahlı Kuvvetleri, TSK) are the military forces of the Republic of Turkey. Turkish Armed Forces consist of the General Staff, the Land Forces, the Naval Forces and the Air Forces. The current Chief of the General Staff is General Yaşar Güler. The Chief of the General Staff is the Commander of the Armed Forces. In wartime, the Chief of the General Staff acts as the Commander-in-Chief on behalf of the President, who represents the Supreme Military Command of the TAF on behalf of the Grand National Assembly of Turkey. Coordinating the military relations of the TAF with other NATO member states and friendly states is the responsibility of the General Staff. The history of the Turkish Armed Forces began with its formation after the collapse of the Ottoman Empire. The Turkish military perceived itself as the guardian of Kemalism, the official state ideology, especially of its emphasis on secularism. After becoming a member of N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish Music
The music of Turkey includes mainly Turkic and Byzantine elements as well as partial influences ranging from Ottoman music, Middle Eastern music and Music of Southeastern Europe, as well as references to more modern European and American popular music. Turkey is a country on the northeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea, and is a crossroad of cultures from across Europe, North Africa, the Middle East, the Caucasus and South and Central Asia. The roots of traditional music in Turkey span across centuries to a time when the Seljuk Turks migrated to Anatolia and Persia in the 11th century and contains elements of both Turkic and pre-Turkic influences. Much of its modern popular music can trace its roots to the emergence in the early 1930s drive for Westernization., pp 396-410. With the assimilation of immigrants from various regions the diversity of musical genres and musical instrumentation also expanded. Turkey has also seen documented folk music and recorded popular music prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March Music
A march, as a musical genre, is a piece of music with a strong regular rhythm which in origin was expressly written for marching to and most frequently performed by a military band. In mood, marches range from the moving death march in Wagner's ''Götterdämmerung'' to the brisk military marches of John Philip Sousa and the martial hymns of the late 19th century. Examples of the varied use of the march can be found in Beethoven's ''Eroica'' Symphony, in the Marches Militaires of Franz Schubert, in the Marche funèbre in Chopin's Sonata in B flat minor, the "''Jäger March''" in the by Jean Sibelius, and in the Dead March in Handel's ''Saul''. Characteristics Marches can be written in any time signature, but the most common time signatures are , (''alla breve'' , although this may refer to 2 time of Johannes Brahms, or ''cut time''), or . However, some modern marches are being written in or time. The modern march tempo is typically around 120 beats per minute. Many fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_battlecruiser_Istambul_April_1946_-_cropped.jpg)

