|
Playa De Oro Virus
Playa de Oro virus (OROV) is a probable species of orthohantavirus found in the rodents ''Oryzomys couesi'' and ''Sigmodon mascotensis'' in the Mexican state of Colima. The former is thought to be the main host (biology), host. The DNA sequence, sequences of parts of the virus's RNA-based genome have been determined; they differ by 7–10% in amino acid composition and 22–24% in nucleotide composition from closely related viruses. Playa de Oro virus was identified as a new species in 2008 and is most closely related to Bayou virus, Catacamas virus, Muleshoe virus, and Black Creek Canal virus, found in other species of ''Oryzomys'' and ''Sigmodon''. Catacamas virus is found in a different population of ''Oryzomys couesi'', and the presence of different viruses in these two species has been used as an argument for classifying the two populations of the host as separate species. History and occurrence Playa de Oro virus was first identified in rodents collected in 2004 as part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunyavirales
''Bunyavirales'' is an order of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses with mainly tripartite genomes. Member viruses infect arthropods, plants, protozoans, and vertebrates. It is the only order in the class ''Ellioviricetes''. The name ''Bunyavirales'' derives from Bunyamwera, where the original type species ''Bunyamwera orthobunyavirus'' was first discovered. ''Ellioviricetes'' is named in honor of late virologist Richard M. Elliott for his early work on bunyaviruses. Bunyaviruses belong to the fifth group of the Baltimore classification system, which includes viruses with a negative-sense, single-stranded RNA genome. They have an enveloped, spherical virion. Though generally found in arthropods or rodents, certain viruses in this order occasionally infect humans. Some of them also infect plants. In addition, there is a group of bunyaviruses whose replication is restricted to arthropods and is known as insect-specific bunyaviruses. A majority of bunyaviruses are vector-borne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsh Rice Rat
The marsh rice rat (''Oryzomys palustris'') is a semiaquatic North American rodent in the family Cricetidae. It usually occurs in wetland habitats, such as swamps and salt marshes. It is found mostly in the eastern and southern United States, from New Jersey and Kansas south to Florida and northeasternmost Tamaulipas, Mexico; its range previously extended further west and north, where it may have been a commensalism, commensal in corn-cultivating communities. Weighing about , the marsh rice rat is a medium-sized rodent that resembles the common black rat, black and brown rat. The upperparts are generally gray-brown, but are reddish in many Florida populations. The feet show several specializations for life in the water. The skull is large and flattened, and is short at the front. John Bachman discovered the marsh rice rat in 1816, and it was formally described in 1837. Several subspecies have been described since the 1890s, mainly from Florida, but disagreement exists over their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
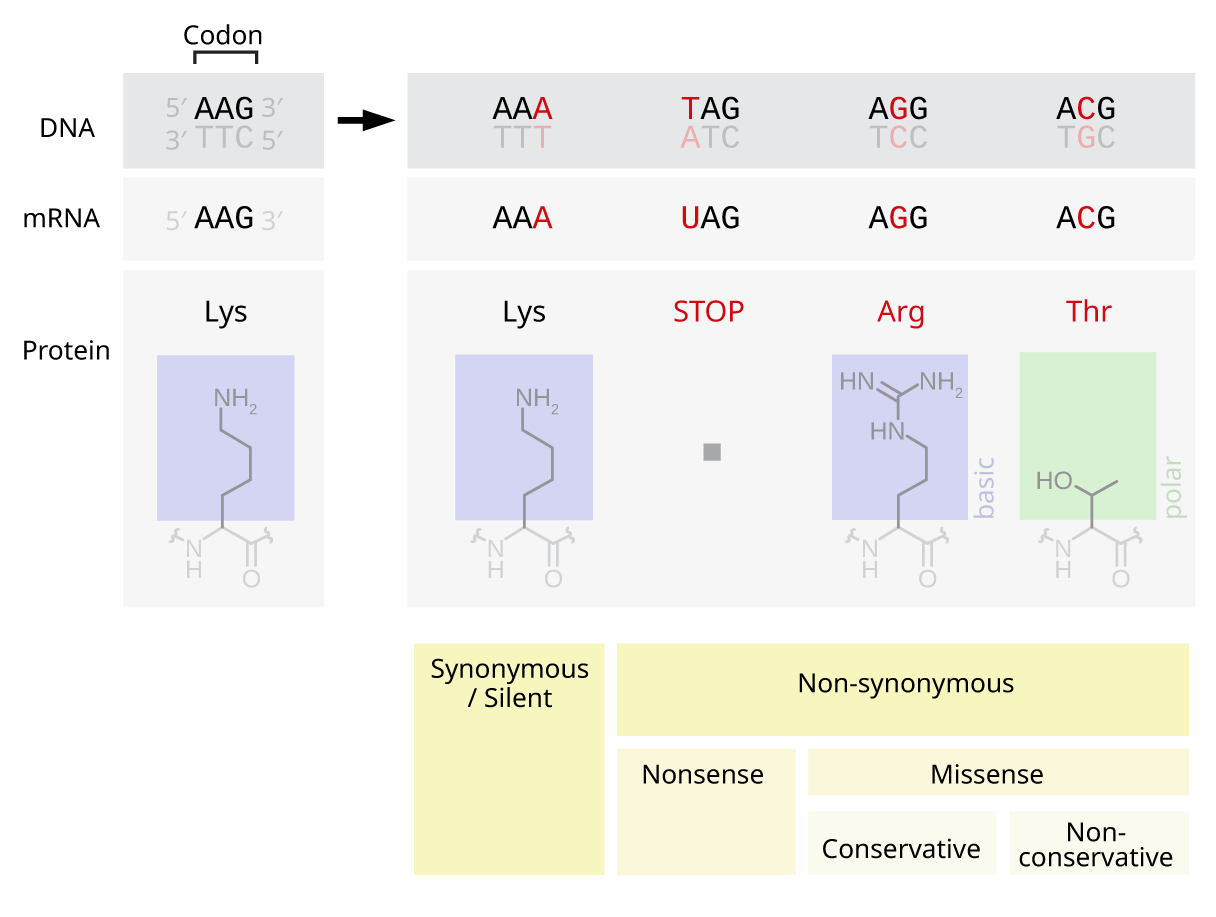
Silent Mutation
Silent mutations are mutations in DNA that do not have an observable effect on the organism's phenotype. They are a specific type of neutral mutation. The phrase ''silent mutation'' is often used interchangeably with the phrase '' synonymous mutation''; however, synonymous mutations are not always silent, nor vice versa. Synonymous mutations can affect transcription, splicing, mRNA transport, and translation, any of which could alter phenotype, rendering the synonymous mutation non-silent. The substrate specificity of the tRNA to the rare codon can affect the timing of translation, and in turn the co-translational folding of the protein. This is reflected in the codon usage bias that is observed in many species. Mutations that cause the altered codon to produce an amino acid with similar functionality (''e.g.'' a mutation producing leucine instead of isoleucine) are often classified as silent; if the properties of the amino acid are conserved, this mutation does not usually signif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Reading Frame
In molecular biology, open reading frames (ORFs) are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible reading frames will be "open" (the "reading", however, refers to the RNA produced by transcription of the DNA and its subsequent interaction with the ribosome in translation). Such an ORF may contain a start codon (usually AUG in terms of RNA) and by definition cannot extend beyond a stop codon (usually UAA, UAG or UGA in RNA). That start codon (not necessarily the first) indicates where translation may start. The transcription termination site is located after the ORF, beyond the translation stop codon. If transcription were to cease before the stop codon, an incomplete protein would be made during translation. In eukaryotic genes with multiple exons, introns are removed and exons are then joined together after transcription to yield the final ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleocapsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may not correspond to individual proteins, are called capsomeres. The proteins making up the capsid are called capsid proteins or viral coat proteins (VCP). The capsid and inner genome is called the nucleocapsid. Capsids are broadly classified according to their structure. The majority of the viruses have capsids with either helical or icosahedral structure. Some viruses, such as bacteriophages, have developed more complicated structures due to constraints of elasticity and electrostatics. The icosahedral shape, which has 20 equilateral triangular faces, approximates a sphere, while the helical shape resembles the shape of a spring, taking the space of a cylinder but not being a cylinder itself. The capsid faces may consist of one or more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replication
Replication may refer to: Science * Replication (scientific method), one of the main principles of the scientific method, a.k.a. reproducibility ** Replication (statistics), the repetition of a test or complete experiment ** Replication crisis * Self-replication, the process in which an entity (a cell, virus, program, etc.) makes a copy of itself ** DNA replication or DNA synthesis, the process of copying a double-stranded DNA molecule ** Semiconservative replication, mechanism of DNA replication ** Viral replication, the process by which viruses produce copies of themselves * Replication (metallography), the use of thin plastic films to duplicate the microstructure of a component * Self-replicating machines Computing * Replication (computing), the use of redundant resources to improve reliability, fault-tolerance, or performance * Replication (optical media) In optical disc manufacturing, replication is the process of producing discs via methods that do not involve "burn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hantavirus
''Orthohantavirus'' is a genus of single-stranded, enveloped, negative-sense RNA viruses in the family ''Hantaviridae'' within the order ''Bunyavirales''. Members of this genus may be called orthohantaviruses or simply hantaviruses. Orthohantaviruses typically cause chronic asymptomatic infection in rodents. Humans may become infected with hantaviruses through contact with rodent urine, saliva, or feces. Some strains cause potentially fatal diseases in humans, such as hantavirus hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS), or hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS), also known as hantavirus cardiopulmonary syndrome (HCPS), while others have not been associated with known human disease (e.g. Prospect Hill virus). HPS (HCPS) is a "rare respiratory illness associated with the inhalation of aerosolized rodent excreta (urine and feces) contaminated by hantavirus particles." Human infections of hantaviruses have almost entirely been linked to human contact with rodent excrement; however, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baiomys Musculus
The southern pygmy mouse (''Baiomys musculus'') is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, and Nicaragua Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the cou .... Habitat Coastal animals are larger on average. They prefer open canopy areas with grasses and less dead wood or bare ground. In general they are found in open areas with thick low vegetation. They are also found in rocky areas. Description The outer coat of the southern pygmy mouse varies from a reddish brown to almost black. The under belly is lighter in tone than the back ranging from pinkish buff to white. Juveniles are born with a gray coat that slowly turns brown as they mature. Uncharacteristically of other members in the family Cricetidae they have 14 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baiomys
''Baiomys'' is the genus of New World pygmy mice. Together with ''Scotinomys'', it forms the tribe Baiomyini. It currently contains two extant species: *Southern pygmy mouse, ''Baiomys musculus'' *Northern pygmy mouse, ''Baiomys taylori The northern pygmy mouse (''Baiomys taylori'') is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is known as ''ratón-pigmeo norteño'' in the Spanish-speaking areas of its range. It is found in Mexico and the United States. Parasite ...'' References *Amman, B R., R. D. Bradley. 2003. Molecular evolution in ''Baiomys'' (Rodentia: Sigmodontinae): Evidence for a genetic subdivision in ''B. musculus''. Journal of Mammalogy 85:162-166. *Integrated Taxonomic Information Syste Accessed 3 April 2007. Baiomys, Rodent genera Taxa named by Frederick W. True {{Cricetidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton Rat
A cotton rat is any member of the rodent genus ''Sigmodon''. Their name derives from their damaging effects on cotton as well as other plantation crops, such as sugarcane, corn, peanut and rice. Cotton rats have small ears and dark coats, and are found in North and South America. Members of this genus are distributed in the Southwestern United States, Mexico, Central America, and South American countries of: Venezuela, Ecuador, Colombia, Peru, Brazil, Guyana, and Suriname. Many of the species are found in Mexico. They are primarily herbivores. The molars of cotton rats are S-shaped when viewed from above. The genus name literally means S-tooth. ''Sigmodon hispidus'' was the first model organism to be used in polio research. Classification *Genus ''Sigmodon'' **Subgenus ''Sigmodon'' ***''Sigmodon hispidus'' species group ****'' Sigmodon alleni'' - Allen's cotton rat ****'' Sigmodon arizonae'' - Arizona cotton rat ****'' Sigmodon hirsutus'' - Southern cotton rat ****''Sigmodon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oryzomyini
Oryzomyini is a tribe of rodents in the subfamily Sigmodontinae of the family Cricetidae. It includes about 120 species in about thirty genera,Weksler et al., 2006, table 1 distributed from the eastern United States to the southernmost parts of South America, including many offshore islands. It is part of the clade Oryzomyalia, which includes most of the South American Sigmodontinae. The name ''Oryzomyini'' derives from that of its type genus, ''Oryzomys'', which means "rice rat" or "rice mouse". Many species are also known as rice rats. Taxonomy Contents of Oryzomyini An oryzomyine group was first envisaged by Oldfield Thomas in the early 20th century. He defined it to include pentalophodont species, which have a mesoloph(id) on the upper and lower molars, with a long palate (extending past the third molars). Thomas included ''Oligoryzomys'', ''Oecomys'', and ''Oryzomys'' (which included many species now in other genera), as well as '' Rhagomys'', which is currently classified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.gif)