|
Platykotta
''Platykotta akaina'' is a species of decapod crustacean from the Triassic of the United Arab Emirates. It is the oldest known fossil from the infraorder Anomura, and is most closely related to '' Eocarcinus praecursor''. Stratigraphy The holotype of ''P. akaina'' was found in the United Arab Emirates on the Musandam Peninsula – the peninsula which separates the Persian Gulf from the Gulf of Oman. From the Permian to the Cretaceous, the area was near the shore of the Tethys Sea, which produced carbonate sedimentary rocks. The strata that contained ''Platykotta'' were part of the Ghalilah Formation, of Norian– Rhaetian age. These rocks contain extensive networks of burrows, and various other fossils, including bivalves of the families Megalodontidae and Wallowaconchidae, brachiopods, crinoids, sponges and corals. The holotype was found at approximately and has been deposited in the Natural History Museum of Geneva, Switzerland. Description ''Platykotta'' is characte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocarcinoidea
Eocarcinoidea is a superfamily of fossil decapod crustaceans. Formerly thought to be the earliest true crabs, they are now thought to be the oldest members of the Anomura Anomura (sometimes Anomala) is a group of Decapoda, decapod crustaceans, including hermit crabs and others. Although the names of many anomurans include the word ''crab'', all true crabs are in the sister group to the Anomura, the Brachyura (the .... Two species are included, each in its own family-taxon: '' Eocarcinus praecursor'' (Eocarcinidae) and '' Platykotta akaina'' (Platykottidae). References Anomura {{paleo-crustacean-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomura
Anomura (sometimes Anomala) is a group of Decapoda, decapod crustaceans, including hermit crabs and others. Although the names of many anomurans include the word ''crab'', all true crabs are in the sister group to the Anomura, the Brachyura (the two groups together form the clade Meiura). Description The name Anomura derives from an old classification in which Reptantia, reptant decapods were divided into Macrura (long-tailed), Brachyura (short-tailed) and Anomura (differently-tailed). The alternative name Anomala reflects the unusual variety of forms in this group; whereas all crabs share some obvious similarities, the various groups of anomurans are quite dissimilar. The group has been moulded by several instances of carcinisation – the development of a crab-like body form. Thus, the king crabs (Lithodidae), porcelain crabs (Porcellanidae) and hairy stone crab (Lomisidae) are all separate instances of carcinisation. As decapods (meaning ''ten-legged''), anomurans have ten pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crinoid
Crinoids are marine animals that make up the class Crinoidea. Crinoids that are attached to the sea bottom by a stalk in their adult form are commonly called sea lilies, while the unstalked forms are called feather stars or comatulids, which are members of the largest crinoid order, Comatulida. Crinoids are echinoderms in the phylum Echinodermata, which also includes the starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins and sea cucumbers. They live in both shallow water and in depths as great as . Adult crinoids are characterised by having the mouth located on the upper surface. This is surrounded by feeding arms, and is linked to a U-shaped gut, with the anus being located on the oral disc near the mouth. Although the basic echinoderm pattern of fivefold symmetry can be recognised, in most crinoids the five arms are subdivided into ten or more. These have feathery pinnules and are spread wide to gather planktonic particles from the water. At some stage in their lives, most crinoids have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachiopod
Brachiopods (), phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of trochozoan animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear end, while the front can be opened for feeding or closed for protection. Two major categories are traditionally recognized, articulate and inarticulate brachiopods. The word "articulate" is used to describe the tooth-and-groove structures of the valve-hinge which is present in the articulate group, and absent from the inarticulate group. This is the leading diagnostic skeletal feature, by which the two main groups can be readily distinguished as fossils. Articulate brachiopods have toothed hinges and simple, vertically-oriented opening and closing muscles. Conversely, inarticulate brachiopods have weak, untoothed hinges and a more complex system of vertical and oblique (diagonal) muscles used to keep the two valves aligned. In many brachiopods, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalodontidae
Megalodontidae is an extinct family of bivalve molluscs that reportedly lived from the Devonian to the Jurassic period. Nomenclature A family of insects was also previously called "Megalodontidae", containing the sawfly genus '' Megalodontes''. In order to remove the homonymy, that family has been renamed Megalodontesidae. Genera *†'' Conchodon'' *†'' Gemmellarodus'' di Stefano, 1912 *†''Megalodon Megalodon (''Otodus megalodon''), meaning "big tooth", is an extinct species of mackerel shark that lived approximately 23 to 3.6 million years ago (Mya), from the Early Miocene to the Pliocene epochs. It was formerly thought to be a membe ...'' Sowerby, 1827 *†'' Neomegalodon'' Guembel, 1864 *†'' Pachyrisma'' *†'' Protomegalodon'' *†'' Pterocardia'' Bayan, 1874 *†'' Quemocuomegalodon'' Yao et al. 2003 *†'' Rhaetomegalodon'' *†'' Triadomegalodon'' Vegh-Neubrandt, 1974 References Bivalve families Prehistoric mollusc families Devonian first app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bivalvia
Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estim ... that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bivalves have no head and they lack some usual molluscan organs, like the radula and the odontophore. They include the clams, oysters, Cockle (bivalve), cockles, mussels, scallops, and numerous other family (biology), families that live in saltwater, as well as a number of families that live in freshwater. The majority are filter feeders. The gills have evolved into Ctenidium (mollusc), ctenidia, specialised organs for feeding and breathing. Most bivalves bury themselves in sediment, where they a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burrow
An Eastern chipmunk at the entrance of its burrow A burrow is a hole or tunnel excavated into the ground by an animal to construct a space suitable for habitation or temporary refuge, or as a byproduct of locomotion. Burrows provide a form of shelter against predation and exposure to the elements, and can be found in nearly every biome and among various biological interactions. Many animal species are known to form burrows. These species range from small invertebrates, such as the ''Corophium arenarium'', to very large vertebrate species such as the polar bear. Burrows can be constructed into a wide variety of substrates and can range in complexity from a simple tube a few centimeters long to a complex network of interconnecting tunnels and chambers hundreds or thousands of meters in total length; an example of the latter level of complexity, a well-developed burrow, would be a rabbit warren. Vertebrate burrows A large variety of vertebrates construct or use burrows in many t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
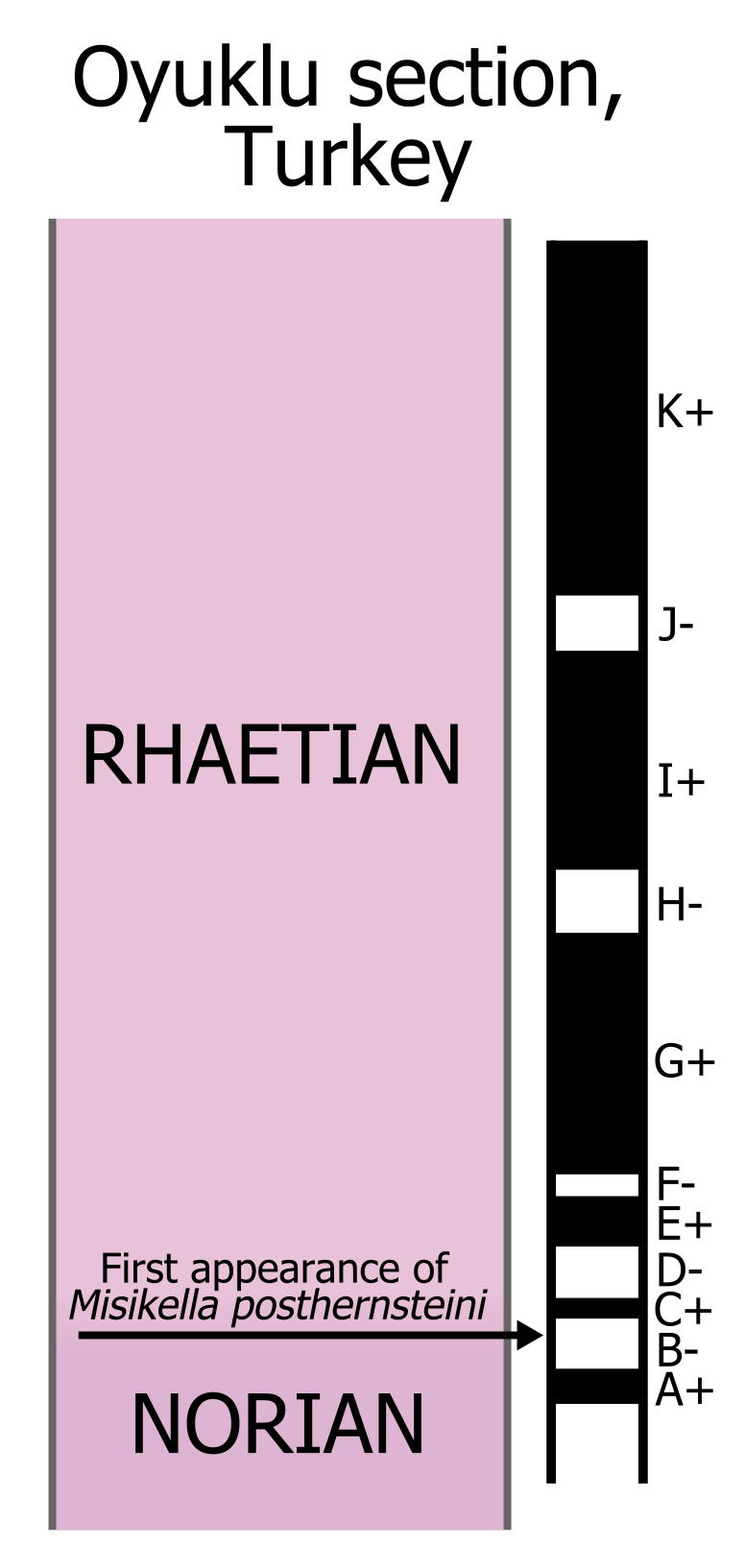
Rhaetian
The Rhaetian is the latest age of the Triassic Period (in geochronology) or the uppermost stage of the Triassic System (in chronostratigraphy). It was preceded by the Norian and succeeded by the Hettangian (the lowermost stage or earliest age of the Jurassic). The base of the Rhaetian lacks a formal GSSP, though candidate sections include Steinbergkogel in Austria (since 2007) and Pignola-Abriola in Italy (since 2016). The end of the Rhaetian (and the base of the overlying Hettangian Stage) is more well-defined. According to the current ICS (International Commission on Stratigraphy) system, the Rhaetian ended ± 0.2 Ma (million years ago). In 2010, the base of the Rhaetian (i.e. the Norian-Rhaetian boundary) was voted to be defined based on the first appearance of '' Misikella posthernsteini'', a marine conodont. However, there is still much debate over the age of this boundary, as well as the evolution of ''M. posthernsteini''. The most comprehensive source of precise age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norian
The Norian is a division of the Triassic Period. It has the rank of an age (geochronology) or stage (chronostratigraphy). It lasted from ~227 to million years ago. It was preceded by the Carnian and succeeded by the Rhaetian. Stratigraphic definitions The Norian was named after the Noric Alps in Austria. The stage was introduced into scientific literature by Austrian geologist Edmund Mojsisovics von Mojsvar in 1869. The Norian Stage begins at the base of the ammonite biozones of '' Klamathites macrolobatus'' and '' Stikinoceras kerri'', and at the base of the conodont biozones of '' Metapolygnathus communisti'' and '' Metapolygnathus primitius''. A global reference profile for the base (a GSSP) had in 2009 not yet been appointed. The top of the Norian (the base of the Rhaetian) is at the first appearance of ammonite species '' Cochloceras amoenum''. The base of the Rheatian is also close to the first appearance of conodont species '' Misikella spp.'' and '' Epigondolella mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |