|
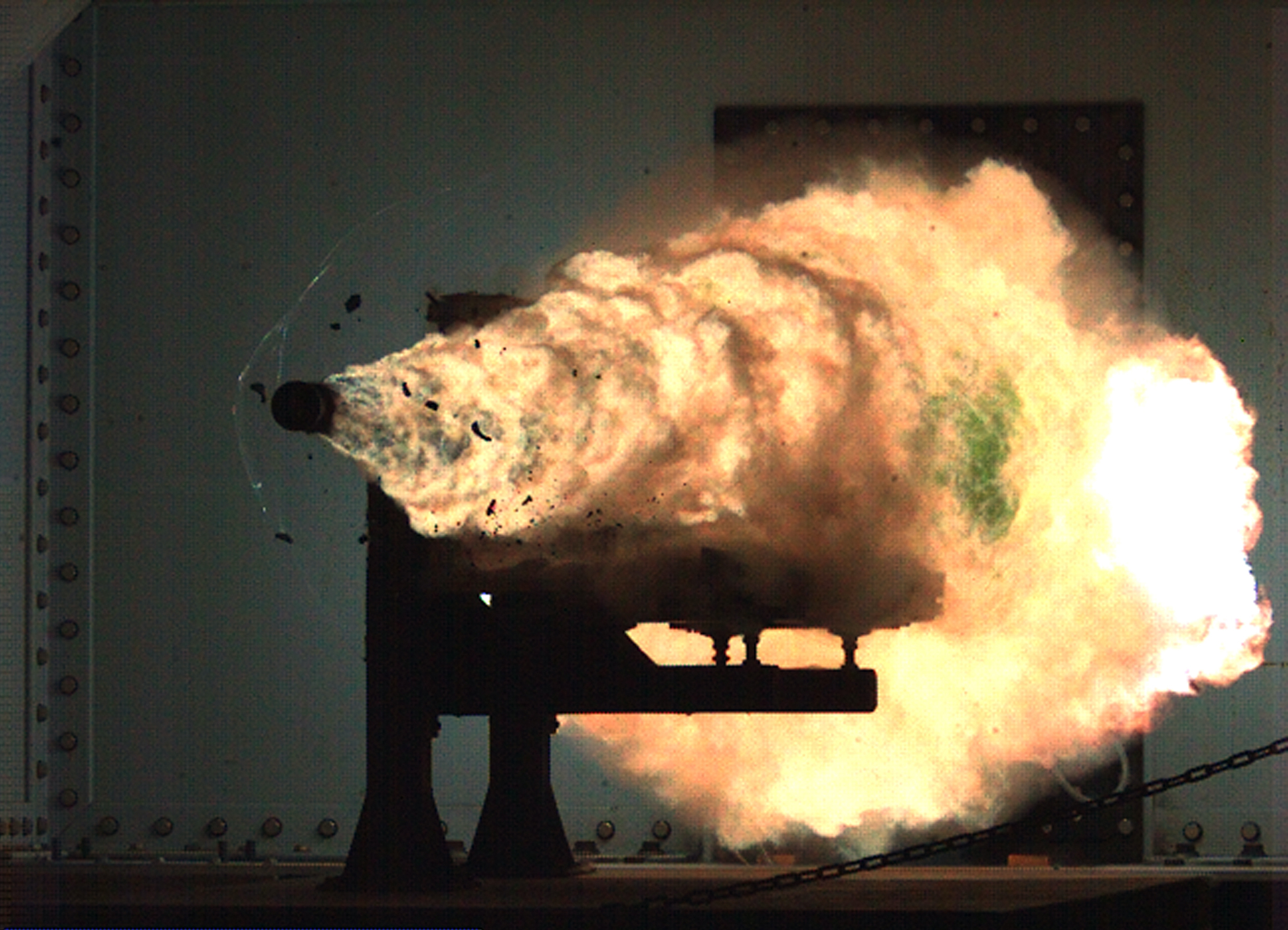
Plasma Railgun
A plasma railgun is a linear accelerator which, like a projectile railgun, uses two long parallel electrodes to accelerate a "sliding short" armature. However, in a plasma railgun, the armature and ejected projectile consists of plasma, or hot, ionized, gas-like particles, instead of a solid slug of material. Scientific plasma railguns are typically operated in vacuum and not at air pressure. They are of value because they produce muzzle velocities of up to several hundreds of kilometers per second. Because of this, these devices have applications in magnetic confinement fusion (MCF), magneto-inertial fusion (MIF), high energy density physics research (HEDP), laboratory astrophysics, and as a plasma propulsion engine for spacecraft. Theory Plasma railguns appear in two principal topologies, linear and coaxial. Linear railguns consist of two flat plate electrodes separated by insulating spacers and accelerate sheet armatures. Coaxial railguns accelerate toroidal plasma armatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
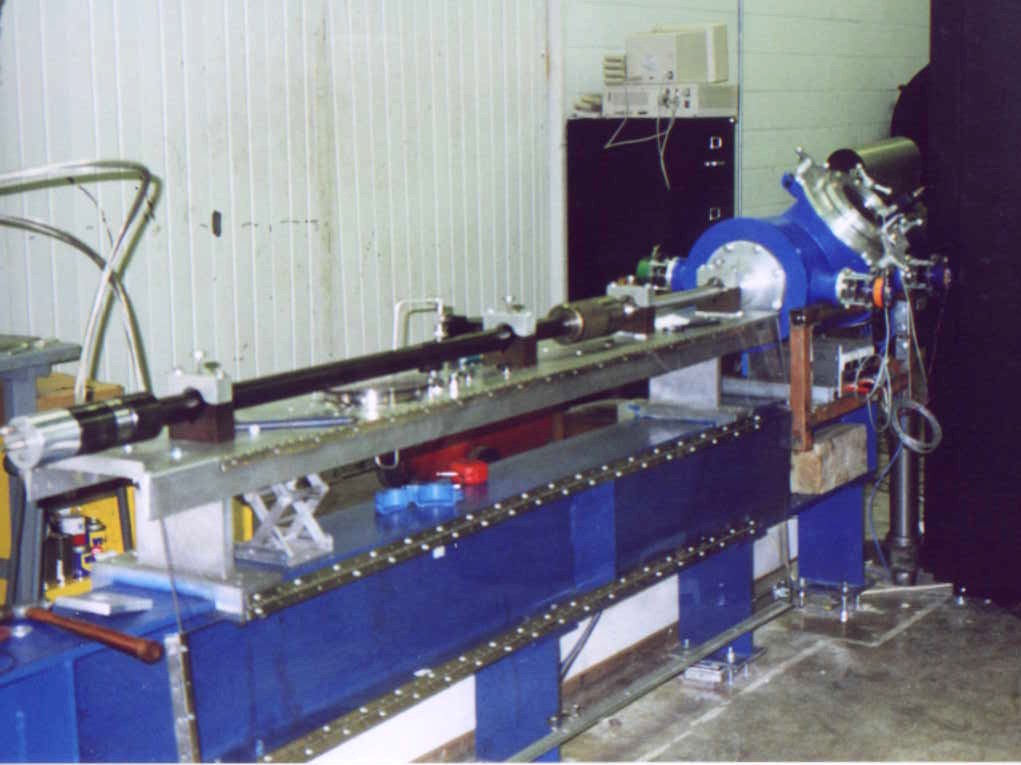
Railgun
A railgun or rail gun is a linear motor device, typically designed as a weapon, that uses Electromagnet, electromagnetic force to launch high velocity projectiles. The projectile normally does not contain explosives, instead relying on the projectile's high speed, mass, and kinetic energy to inflict damage. The railgun uses a pair of parallel conductors (rails), along which a sliding Armature (electrical engineering), armature is accelerated by the electromagnetic effects of a current that flows down one rail, into the armature and then back along the other rail. It is based on principles similar to those of the homopolar motor. As of 2020, railguns have been researched as weapons utilizing electromagnetic forces to impart a very high kinetic energy to a projectile (e.g. APFSDS) rather than using conventional propellants. While explosive-powered military guns cannot readily achieve a muzzle velocity of more than ≈, railguns can readily exceed . For a similar projectile, the ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is a federal research facility in Livermore, California, United States. The lab was originally established as the University of California Radiation Laboratory, Livermore Branch in 1952 in response to the detonation of the first atomic bomb by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. It later became autonomous in 1971 and was designated a national laboratory in 1981. A federally funded research and development center, Lawrence Livermore Lab is primarily funded by the U.S. Department of Energy and it is managed privately and operated by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC (a partnership of the University of California), Bechtel, BWX Technologies, AECOM, and Battelle Memorial Institute in affiliation with the Texas A&M University System. In 2012, the laboratory had the synthetic chemical element livermorium (element 116) named after it. Overview LLNL is self-described as a "premier research and development institution for sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combustion Light-gas Gun
A combustion light-gas gun (CLGG) is a projectile weapon that utilizes the explosive force of low molecular-weight combustible gases, such as hydrogen mixed with oxygen, as propellant. When the gases are ignited, they burn, expand and propel the projectile out of the barrel with higher efficiency relative to solid propellant and have achieved higher muzzle velocities in experiments. Combustion light-gas gun technology is one of the areas being explored in an attempt to achieve higher velocities from artillery to gain greater range. Conventional guns use solid propellants, usually nitrocellulose-based compounds, to develop the chamber pressures needed to accelerate the projectiles. CLGGs' gaseous propellants are able to increase the propellant's specific impulse. Therefore, hydrogen is typically the first choice; however, other propellants like methane can be used. While this technology does appear to provide higher velocities, the main drawback with gaseous or liquid propellants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma-powered Cannon
A plasma cannon (also called an electrothermal accelerator) is an experimental projectile weapon, which accelerates a projectile by means of a plasma discharge between electrodes at the rear of the barrel, generating a rapid increase in pressure. It functions similarly to other types of firearms, except that it uses a plasma discharge instead of a chemical propellant (e.g. black powder or nitrocellulose). Design To generate the energy required to make a plasma discharge, a high current, high voltage source, and a large capacitor bank are used. Both are attached in series to the electrode system in the cannon's barrel. The capacitor is loaded with as high a voltage as possible. However, militarily useful energy is achieved with as little as several kilojoules. The capacitor is then discharged. The gap between the electrodes ionizes, turning the non-flammable propellant medium into a super heated conductive plasma. Associated volumetric expansion propels the projectile fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulsed Plasma Thruster
A pulsed plasma thruster (PPT), also known as a plasma jet engine, is a form of electric spacecraft propulsion. PPTs are generally considered the simplest form of electric spacecraft propulsion and were the first form of electric propulsion to be flown in space, having flown on two Soviet probes ( Zond 2 and Zond 3) starting in 1964. PPTs are generally flown on spacecraft with a surplus of electricity from abundantly available solar energy. Operation Most PPTs use a solid material (normally PTFE, more commonly known as Teflon) for propellant, although very few use liquid or gaseous propellants. The first stage in PPT operation involves an arc of electricity passing through the fuel, causing ablation and sublimation of the fuel. The heat generated by this arc causes the resultant gas to turn into plasma, thereby creating a charged gas cloud. Due to the force of the ablation, the plasma is propelled at low speed between two charged plates (an anode and cathode). Since the plas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-gas Gun
The light-gas gun is an apparatus for physics experiments. It is a highly specialized gun designed to generate extremely high velocities. It is usually used to study high-speed impact phenomena (hypervelocity research), such as the formation of impact craters by meteorites or the erosion of materials by micrometeoroids. Some basic material research relies on projectile impact to create high pressure; such systems are capable of forcing liquid hydrogen into a metallic state. Operation A light-gas gun works on the same principle as a spring piston airgun. A large-diameter piston is used to force a gaseous working fluid through a smaller-diameter barrel containing the projectile to be accelerated. This reduction in diameter acts as a lever, increasing the speed while decreasing the pressure. In an airgun, the large piston is powered by a spring or compressed air, and the working fluid is atmospheric air. In a light-gas gun, the piston is powered by a chemical reaction (usually g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ram Accelerator
A ram accelerator is a device for accelerating projectiles or just a single projectile to extremely high speeds using jet-engine-like propulsion cycles based on ramjet or scramjet combustion processes. It is thought to be possible to achieve non-rocket spacelaunch with this technology. It consists of a long tube (barrel) filled with a mixture of combustible gases with a frangible diaphragm at either end to contain the gases. The projectile is fired by another means (e.g., a light-gas gun or railgun) supersonically through the first diaphragm into the tube. Then the projectile burns the gases as fuel, because it is shaped like a ramjet or scramjet core, and accelerates under jet propulsion. Other physics come into play at higher velocities. Description In a normal ramjet, air is compressed between a spike-shaped centerbody and an outer cowling, fuel is added and burned, and high speed exhaust gases are expanded supersonically out of the nozzle to generate thrust. In a ram acceler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Driver
A mass driver or electromagnetic catapult is a proposed method of non-rocket spacelaunch which would use a linear motor to Acceleration, accelerate and catapult Payload (air and space craft), payloads up to high speeds. Existing and contemplated mass drivers use coils of wire energized by electricity to make electromagnets, though a rotary mass driver has also been proposed. Sequential firing of a row of electromagnets accelerates the payload along a path. After leaving the path, the payload continues to move due to momentum. Although any device used to propel a Ballistics, ballistic payload is technically a mass driver, in this context a mass driver is essentially a coilgun that magnetically accelerates a package consisting of a magnetizable holder containing a payload. Once the payload has been accelerated, the two separate, and the holder is slowed and recycled for another payload. Mass drivers can be used to propel spacecraft in three different ways: A large, ground-based mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
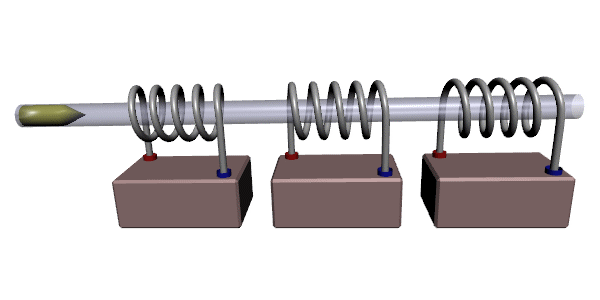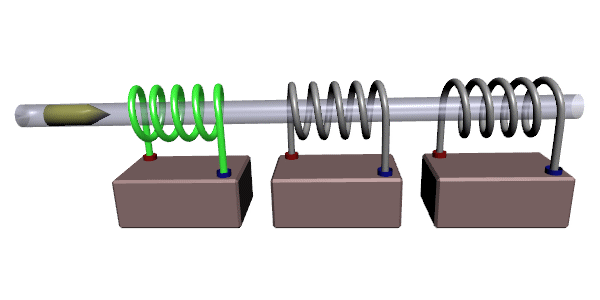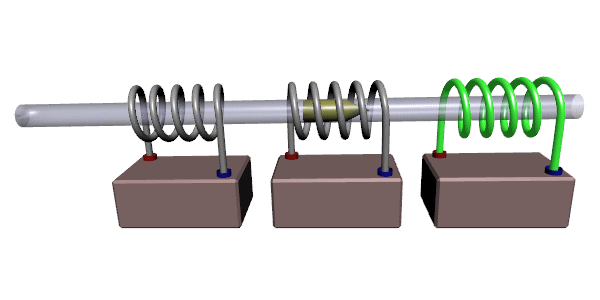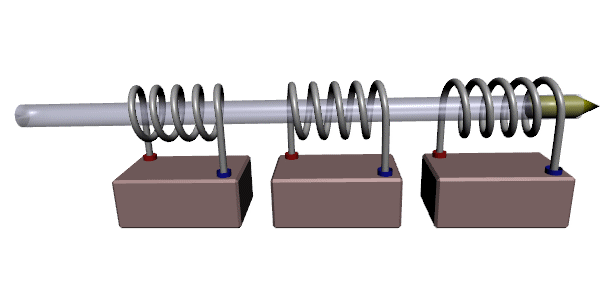
Coilgun
A coilgun, also known as a Gauss rifle, is a type of mass driver consisting of one or more coils used as electromagnets in the configuration of a linear motor that accelerate a ferromagnetic or conducting projectile to high velocity. In almost all coilgun configurations, the coils and the gun barrel are arranged on a common axis. A coilgun is not a rifle as the barrel is smoothbore (not rifled). The name "Gauss" is in reference to Carl Friedrich Gauss, who formulated mathematical descriptions of the magnetic effect used by magnetic accelerator cannons. Coilguns generally consist of one or more coils arranged along a barrel, so the path of the accelerating projectile lies along the central axis of the coils. The coils are switched on and off in a precisely timed sequence, causing the projectile to be accelerated quickly along the barrel via magnetic forces. Coilguns are distinct from railguns, as the direction of acceleration in a railgun is at right angles to the central axi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helical Railgun
Helical railguns are multi-turn railguns that reduce rail and brush current by a factor equal to the number of turns. Two rails are surrounded by a helical barrel and the projectile or re-usable carrier is cylindrical. The projectile is energized continuously by two brushes sliding along the rails, and two or more additional brushes on the projectile serve to energize and commute several windings of the helical barrel direction in front of and/or behind the projectile. The helical railgun is a cross between a railgun and a coilgun. They do not currently exist in a practical, usable form. A helical railgun was built at MIT in 1980 and was powered by several banks of, for the time, large capacitors (approximately 4 farads). It was about 3 meters long, consisting of 2 meters of accelerating coil and 1 meter of decelerating coil. It was able to launch a glider or projectile about 500 meters. See also *Railgun *Plasma railgun *Coilgun *Mass driver *Ram accelerator *Light-gas gun *Electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Fusion
General Fusion is a Canadian company based in Vancouver, British Columbia, which is developing a fusion power device based on magnetized target fusion (MTF). The company was founded in 2002 by Dr. Michel Laberge. The company has more than 200 employees in three countries, with additional centers co-located with fusion research laboratories near London, and Oak Ridge, Tennessee, US. The device under development injects the magnetized target, a plasma mass in the form of a compact toroid, into a cylinder of spinning liquid metal. The target is mechanically compressed to fusion-relevant densities and pressures, by anywhere from a dozen to hundreds (in various designs) of steam-driven pistons. In 2018, the firm published papers on a spherical tokamak, instead of a toroid. It is unclear if this represents a major design change. In June 2021, the company announced it would build 70% of a full scale fusion demonstration plant in the UK as part of a public-private partnership with the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Washington
The University of Washington (UW, simply Washington, or informally U-Dub) is a public research university in Seattle, Washington. Founded in 1861, Washington is one of the oldest universities on the West Coast; it was established in Seattle approximately a decade after the city's founding. The university has a 703 acre main campus located in the city's University District, as well as campuses in Tacoma and Bothell. Overall, UW encompasses over 500 buildings and over 20 million gross square footage of space, including one of the largest library systems in the world with more than 26 university libraries, art centers, museums, laboratories, lecture halls, and stadiums. The university offers degrees through 140 departments, and functions on a quarter system. Washington is the flagship institution of the six public universities in Washington state. It is known for its medical, engineering, and scientific research. Washington is a member of the Association of American Universiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |