|
Plasma Physicists
This is a list of physicists who have worked in or made notable contributions to the field of plasma physics. {, class="wikitable sortable" , - ! Name !! Known for , - , Hannes Alfvén , , 1970 Nobel Prize in Physics "''for fundamental work and discoveries in magneto-hydrodynamics with fruitful applications in different parts of plasma physics''" , - , Irving Langmuir, , coined the term "plasma" to hint at the lifelike behavior of this state of matter. Developed electron temperature concepts and an electrostatic probe, the Langmuir probe. , - , Ksenia Aleksandrovna Razumova , , first stable plasmas in tokamaks, first experimental measurement of plasma energy with diamagnetic loop, disruption studies, confinement studies, pioneering female leader of Russian fusion research, Alfvén Prize 2017 , - , Anatoly Vlasov , , first suggested the Vlasov equation, a correct description of plasma with long-range interaction between particles , - , Andrey Dmitriyevich Sakharov , , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Physics
Plasma ()πλάσμα , Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek English Lexicon'', on Perseus is one of the . It contains a significant portion of charged particles – s and/or s. The presence of these charged particles is what primarily sets plasma apart from the other fundamental states of matter. It is the most abundant form of |
Félicie Albert
Félicie Albert is a French-born American physicist working on laser plasma accelerators. She is the deputy director for the Center for High Energy Density Science at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and staff scientist at the National Ignition Facility and Photon Science Directorate and the Joint High Energy Density Sciences organization. She received BS in 2003 in engineering from Ecole Nationale Supérieure de Physique de Marseille (now Ecole Centrale de Marseille), in France, her master's degree in optics from the University of Central Florida in 2004 and her PhD from Ecole Polytechnique in 2007, before joining LLNL as a postdoctoral fellow in 2008. Her main expertise are "the generation and applications of novel sources of electrons, X-rays and gamma-rays through laser-plasma interaction, laser-wakefield acceleration and Compton scattering." She received the Katherine E. Weimer Award from the American Physical Society in 2017, and the Presidential Early Career Award ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Wave
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. All of these waves form part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. Depending on the frequency of oscillation, different wavelengths of electromagnetic spectrum are produced. In a vacuum, electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light, commonly denoted ''c''. In homogeneous, isotropic media, the oscillations of the two fields are perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of energy and wave propagation, forming a transverse wave. The position of an electromagnetic wave within the electromagnetic spectrum can be characterized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitaly Ginzburg
Vitaly Lazarevich Ginzburg, ForMemRS (russian: Вита́лий Ла́заревич Ги́нзбург, link=no; 4 October 1916 – 8 November 2009) was a Russian physicist who was honored with the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2003, together with Alexei Abrikosov and Anthony Leggett for their "pioneering contributions to the theory of superconductors and superfluids." His career in physics was spent in the former Soviet Union and was one of the leading figure in former Soviet program of nuclear weapons, working towards designs of the thermonuclear devices. He became a member of the Russian Academy of Sciences and succeeded Igor Tamm as head of the Department of Theoretical Physics of the Lebedev Physical Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences (FIAN). In his later life, Ginzburg become an outspoken atheist and was critical of clergy's influence in Russian society. Biography Vitaly Ginzburg was born to a Jewish family in Moscow on 4 October 1916— the son of an enginee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetic Theory Of Gases
Kinetic (Ancient Greek: κίνησις “kinesis”, movement or to move) may refer to: * Kinetic theory, describing a gas as particles in random motion * Kinetic energy, the energy of an object that it possesses due to its motion Art and entertainment * Kinetic art, a form of art involving mechanical and/or random movement, including optical illusions. * ''Kinetic'', the 13th episode of the first season of the TV series ''Smallville'' * ''Kinetic'' (comics), a comic by Allan Heinberg and Kelley Pucklett * "Kinetic" (song), a song by Radiohead Companies * Kinetic Engineering Limited, Indian automotive manufacturer * Kinetic Group, Australian-based public transport company Technology * "Kinetic", Seiko's trademark for its automatic quartz technology * The ''Kinetic camera system'' by Birt Acres (1854–1918), photographer and film pioneer * Kinetic projectile Military terminology * Kinetic military action See also * * * Kinetics (other) * Dynamics (disambiguatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sydney Chapman (mathematician)
Sydney Chapman (29 January 1888 – 16 June 1970) was a British mathematician and geophysicist. His work on the kinetic theory of gases, solar-terrestrial physics, and the Earth's ozone layer has inspired a broad range of research over many decades. Education and early life Chapman was born in Eccles, near Salford in England and began his advanced studies at a technical institute, now the University of Salford, in 1902. In 1904 at age 16, Chapman entered the University of Manchester. He competed for a scholarship to the university offered by his home county, and was the last student selected. Chapman later reflected, "I sometimes wonder what would have happened if I'd hit one place lower." He initially studied engineering in the department headed by Osborne Reynolds. Chapman was taught mathematics by Horace Lamb, the Beyer professor of mathematics, and J. E. Littlewood, who came from Cambridge in Chapman's final year at Manchester. Although he graduated with an engineerin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saha Ionization Equation
In physics, the Saha ionization equation is an expression that relates the ionization state of a gas in thermal equilibrium to the temperature and pressure. The equation is a result of combining ideas of quantum mechanics and statistical mechanics and is used to explain the spectral classification of stars. The expression was developed by Indian physicist Meghnad Saha in 1920. Description For a gas at a high enough temperature (here measured in energy units, i.e. keV or J) and/or density, the thermal collisions of the atoms will ionize some of the atoms, making an ionized gas. When several or more of the electrons that are normally bound to the atom in orbits around the atomic nucleus are freed, they form an independent electron gas cloud co-existing with the surrounding gas of atomic ions and neutral atoms. In turn, this generates an electric field, where the motion of charges generates currents, making a localised magnetic field, and creates the state of matter called plasma. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meghnad Saha
Meghnad Saha (6 October 1893 – 16 February 1956) was an Indian astrophysicist who developed the Saha ionization equation, used to describe chemical and physical conditions in stars. His work allowed astronomers to accurately relate the spectral classes of stars to their actual temperatures. He was elected to the Parliament of India in 1952 from Calcutta. Biography Meghnad Saha was born in 1893 in a very poor family in Shaoratoli, a village near Dhaka-Bikrampur, in the former Bengal Presidency of British India (in present-day Village- Shaoratoli, Thana- Kaliakair, District- Gazipur, Bangladesh). Son of Jagannath Saha (a grocer) and Smt. Bhubneshwari Devi, Meghnad struggled to rise in life. During his early schooling he was forced to leave Dhaka Collegiate School because he participated in the Swadeshi movement. He earned his Indian School Certificate from Dhaka College. He was also a student at the Presidency College, Kolkata and Rajabazar Science College CU. As a stude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landau Damping
In physics, Landau damping, named after its discoverer,Landau, L. "On the vibration of the electronic plasma". ''JETP'' 16 (1946), 574. English translation in ''J. Phys. (USSR)'' 10 (1946), 25. Reproduced in Collected papers of L.D. Landau, edited and with an introduction by D. ter Haar, Pergamon Press, 1965, pp. 445–460; and in Men of Physics: L.D. Landau, Vol. 2, Pergamon Press, D. ter Haar, ed. (1965). Soviet physicist Lev Davidovich Landau (1908–68), is the effect of damping ( exponential decrease as a function of time) of longitudinal space charge waves in plasma or a similar environment.Chen, Francis F. ''Introduction to Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion''. Second Ed., 1984 Plenum Press, New York. This phenomenon prevents an instability from developing, and creates a region of stability in the parameter space. It was later argued by Donald Lynden-Bell that a similar phenomenon was occurring in galactic dynamics, where the gas of electrons interacting by electrostatic for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lev Landau
Lev Davidovich Landau (russian: Лев Дави́дович Ланда́у; 22 January 1908 – 1 April 1968) was a Soviet- Azerbaijani physicist of Jewish descent who made fundamental contributions to many areas of theoretical physics. His accomplishments include the independent co-discovery of the density matrix method in quantum mechanics (alongside John von Neumann), the quantum mechanical theory of diamagnetism, the theory of superfluidity, the theory of second-order phase transitions, the Ginzburg–Landau theory of superconductivity, the theory of Fermi liquids, the explanation of Landau damping in plasma physics, the Landau pole in quantum electrodynamics, the two-component theory of neutrinos, and Landau's equations for ''S'' matrix singularities. He received the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physics for his development of a mathematical theory of superfluidity that accounts for the properties of liquid helium II at a temperature below (). Life Early years Landau was born ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
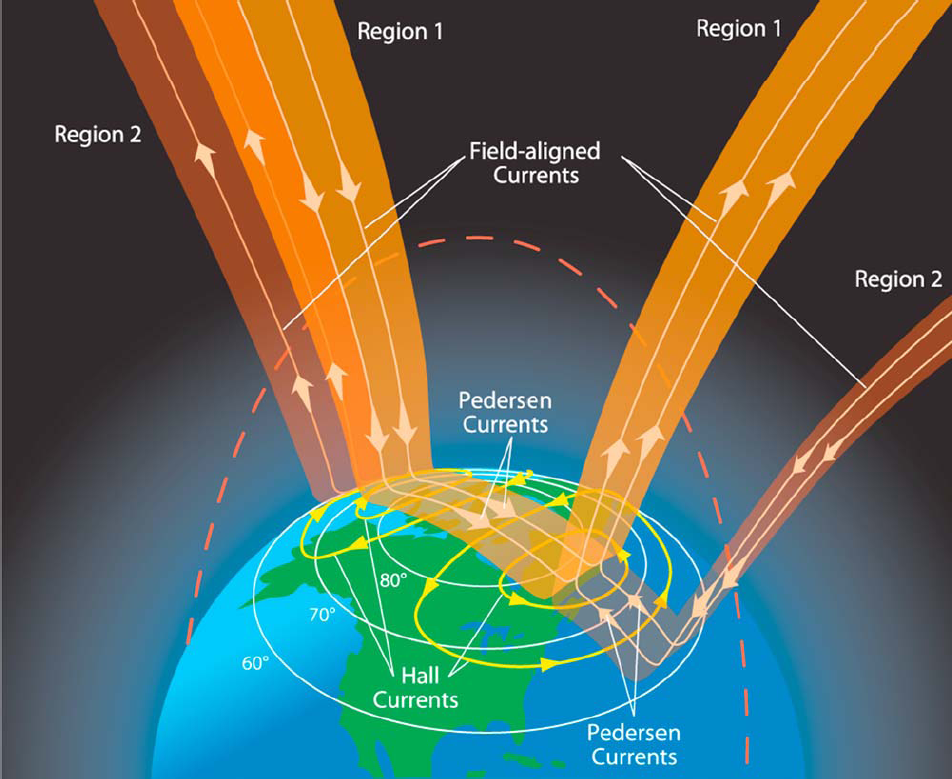
Birkeland Current
A Birkeland current (also known as field-aligned current) is a set of electrical currents that flow along geomagnetic field lines connecting the Earth's magnetosphere to the Earth's high latitude ionosphere. In the Earth's magnetosphere, the currents are driven by the solar wind and interplanetary magnetic field and by bulk motions of plasma through the magnetosphere (convection indirectly driven by the interplanetary environment). The strength of the Birkeland currents changes with activity in the magnetosphere (e.g. during substorms). Small scale variations in the upward current sheets (downward flowing electrons) accelerate magnetospheric electrons which, when they reach the upper atmosphere, create the Auroras Borealis and Australis. In the high latitude ionosphere (or auroral zones), the Birkeland currents close through the region of the auroral electrojet, which flows perpendicular to the local magnetic field in the ionosphere. The Birkeland currents occur in two pairs of fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrojet
An electrojet is an electric current which travels around the E region of the Earth's ionosphere. There are three electrojets: one above the magnetic equator (the equatorial electrojet), and one each near the Northern and Southern Polar Circles (the Auroral Electrojets). Electrojets are Hall currents carried primarily by electrons at altitudes from 100 to 150 km. In this region the electron gyro frequency (Larmor frequency) is much greater than the electron-neutral collision frequency. In contrast, the principal E region ions (O2+ and NO+) have gyrofrequencies much lower than the ion-neutral collision frequency. Kristian Birkeland was the first to suggest that polar electric currents (or auroral electrojets) are connected to a system of filaments (now called "Birkeland currents") that flow along geomagnetic field lines into and away from the polar region. out-of-print, full text online Equatorial Electrojet The worldwide solar-driven wind results in the so-called Sq (sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |