|
Plantagenets
The House of Plantagenet () was a royal house which originated from the lands of Anjou in France. The family held the English throne from 1154 (with the accession of Henry II at the end of the Anarchy) to 1485, when Richard III died in battle. Under the Plantagenets, England was transformed. The Plantagenet kings were often forced to negotiate compromises such as Magna Carta, which had served to constrain their royal power in return for financial and military support. The king was no longer considered an absolute monarch in the nation—holding the prerogatives of judgement, feudal tribute, and warfare—but now also had defined duties to the kingdom, underpinned by a sophisticated justice system. A distinct national identity was shaped by their conflict with the French, Scots, Welsh and Irish, as well as by the establishment of the English language as the primary language. In the 15th century, the Plantagenets were defeated in the Hundred Years' War and beset with social, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of York
The House of York was a cadet branch of the English royal House of Plantagenet. Three of its members became kings of England in the late 15th century. The House of York descended in the male line from Edmund of Langley, 1st Duke of York, the fourth surviving son of Edward III. In time, it also represented Edward III's senior line, when an heir of York married the heiress-descendant of Lionel, Duke of Clarence, Edward III's second surviving son. It is based on these descents that they claimed the English crown. Compared with its rival, the House of Lancaster, it had a superior claim to the throne of England according to cognatic primogeniture, but an inferior claim according to agnatic primogeniture. The reign of this dynasty ended with the death of Richard III of England at the Battle of Bosworth Field in 1485. It became extinct in the male line with the death of Edward Plantagenet, 17th Earl of Warwick, in 1499. Descent from Edward III Edmund of Langley, 1st Duk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Lancaster
The House of Lancaster was a cadet branch of the royal House of Plantagenet. The first house was created when King Henry III of England created the Earldom of Lancasterfrom which the house was namedfor his second son Edmund Crouchback in 1267. Edmund had already been created Earl of Leicester in 1265 and was granted the lands and privileges of Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, after de Montfort's death and attainder at the end of the Second Barons' War. When Edmund's son Thomas, 2nd Earl of Lancaster, inherited his father-in-law's estates and title of Earl of Lincoln he became at a stroke the most powerful nobleman in England, with lands throughout the kingdom and the ability to raise vast private armies to wield power at national and local levels. This brought himand Henry, his younger brotherinto conflict with their cousin King Edward II, leading to Thomas's execution. Henry inherited Thomas's titles and he and his son, who was also called Henry, gave loyal service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Aquitaine
The Duke of Aquitaine ( oc, Duc d'Aquitània, french: Duc d'Aquitaine, ) was the ruler of the medieval region of Aquitaine (not to be confused with modern-day Aquitaine) under the supremacy of Frankish, English, and later French kings. As successor states of the Visigothic Kingdom (418–721), Aquitania (Aquitaine) and Languedoc (Toulouse) inherited both Visigothic law and Roman Law, which together allowed women more rights than their contemporaries would enjoy until the 20th century. Particularly under the Liber Judiciorum as codified 642/643 and expanded by the Code of Recceswinth in 653, women could inherit land and title and manage it independently from their husbands or male relations, dispose of their property in legal wills if they had no heirs, represent themselves and bear witness in court from the age of 14, and arrange for their own marriages after the age of 20.Klapisch-Zuber, Christiane; A History of Women: Book II Silences of the Middle Ages, The Belknap Press of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. On 12 July 927, the various Anglo-Saxon kings swore their allegiance to Æthelstan of Wessex (), unifying most of modern England under a single king. In 1016, the kingdom became part of the North Sea Empire of Cnut the Great, a personal union between England, Denmark and Norway. The Norman conquest of England in 1066 led to the transfer of the English capital city and chief royal residence from the Anglo-Saxon one at Winchester to Westminster, and the City of London quickly established itself as England's largest and principal commercial centre. Histories of the kingdom of England from the Norman conquest of 1066 conventionally distinguish periods named after successive ruling dynasties: Norman (1066–1154), Plantagenet (1154–1485), Tudor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
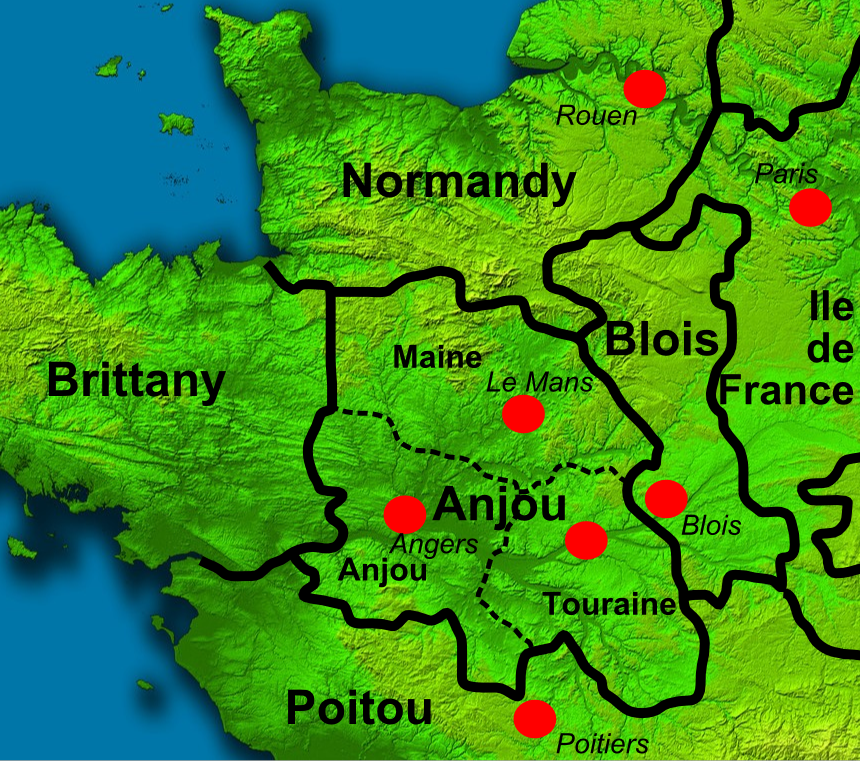
Geoffrey V Of Anjou
Geoffrey V (24 August 1113 – 7 September 1151), called the Handsome, the Fair (french: link=no, le Bel) or Plantagenet, was the count of Anjou, Touraine and Maine by inheritance from 1129, and also Duke of Normandy by conquest from 1144. His marriage to Empress Matilda, daughter of King Henry I of England, led to the centuries-long reign of the Plantagenet dynasty in England. The name "Plantagenet" was taken from Geoffrey's epithet. Geoffrey's ancestral domain of Anjou gave rise to the name Angevin, and what modern historians name as the Angevin Empire in the 12th century. Early life Geoffrey was the elder son of Fulk V of Anjou and Ermengarde of Maine. Geoffrey received his nickname from the yellow sprig of broom blossom (''genêt'' is the French name for the ''planta genista'', or broom shrub) he wore in his hat. The chronicler John of Marmoutier described Geoffrey as handsome, red haired, jovial, and a great warrior. King Henry I of England, having heard reports o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Châteaudun
The House of Anjou-Châteaudun was a medieval house that once possessed the County of Anjou, the Viscounty of Châteaudun and the significant, wealthy Kingdom of Jerusalem. Origin of the House of Châteaudun The House of Châteaudun descended from Gauzfred I (or Geoffrey I) whom Count Theobald I of Blois made viscount of Châteaudun in 956. Recent research makes him a direct-line agnatic descendant of the Frankish family Rorgonides. Branches of the House of Châteaudun The House of Châteaudun split in distinct branches. Descended from Fulcuich, probably the second son of Gauzfred I, were: * The lineage of the counts of Perche, extinct by 1217, with William II * The line of viscounts of Châteaudun, extinct by 1249, with Geoffrey VI * The lineage of the counts of Anjou, who acquired the land by the marriage of a grandson of Fulcois, Count Geoffrey II of Gâtinais with Ermengarde of Anjou, heiress of the House of Ingelger, and from whom the Plantagenets were descended G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Gascony
The Duchy of Gascony or Duchy of Vasconia ( eu, Baskoniako dukerria; oc, ducat de Gasconha; french: duché de Gascogne, duché de Vasconie) was a duchy located in present-day southwestern France and northeastern Spain, an area encompassing the modern region of Gascony. The Duchy of Gascony, then known as ''Wasconia'', was originally a Frankish march formed to hold sway over the Basques. However, the duchy went through different periods, from its early years with its distinctively Basque element to the merger in personal union with the Duchy of Aquitaine to the later period as a dependency of the Plantagenet kings of England. In the Hundred Years' War, Charles V of France conquered most of Gascony by 1380, and under Charles VII of France it was incorporated into the Kingdom of France in its entirety in 1453. The corresponding portion within the Iberian Peninsula became the Kingdom of Navarre. History Formation Gascony was the core territory of Roman Gallia Aquitania. This p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count Of Mortain
The County of Mortain was a medieval county in France centered on the town of Mortain. A choice landholding, usually either kept within the family of the duke of Normandy (or the king of France) or granted to a noble in return for service and favor. This was the main reason Mortain had so many counts, as shown below, during its long history. Norman counts of Mortain * Mauger of Corbeil (988–1032) * There are apparently few certain facts about William Warlenc, who was deprived of the County to the benefit of Robert (sometimes said to have been c.1055).(1032–1048) * Robert, Count of Mortain (1049–1104) * William, Count of Mortain (1104–1106) * Robert II of Vitré (1106–1112) * Stephen of England (1112–1135) * Eustace IV of Boulogne (1135–1141) * Geoffrey of Anjou (1141–1144) * William of Blois (1154–1159) * ''Vacant'' * Marie of Boulogne and Matthew of Alsace (1167–1173) * ''Vacant'' * John I of England (1189–1199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count Of Maine
This is a list of counts and dukes of Maine. The capital of Maine was Le Mans. In the thirteenth century it was annexed by France to the royal domain. Dukes of Maine (''duces Cenomannici'') * Charivius ( fl. 723) – appears as ''dux'' in a document of 723. Controlled twelve counties and the Diocese of Le Mans * Grifo (748–749) – given the twelve counties of Maine by his brother, Pepin the Short, as appeasement, but rebelled the next year. * Charles the Younger (790–811) – given the ''ducatus Cenomannicus'' to govern by his father, Charlemagne. * Lothair I (817–831) – given the ''ducatus'' as part of a division of the realm by his father, Louis the Pious. * Pepin I (831–838) – given the ''ducatus'' as part of a re-division of the realm by his father, Louis the Pious. * Charles the Bald (838–851) – given the ''ducatus'' on the death of Pepin by their father, Louis the Pious. * Robert the Strong (851/3–856) – given Maine, Anjou, and Touraine as ''dux'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count Of Anjou
The Count of Anjou was the ruler of the County of Anjou, first granted by Charles the Bald in the 9th century to Robert the Strong. Ingelger and his son, Fulk the Red, were viscounts until Fulk assumed the title of Count of Anjou. The Robertians and their Capetian successors were distracted by wars with the Vikings and other concerns and were unable to recover the county until the reign of Philip II Augustus, more than 270 years later. Ingelger's male line ended with Geoffrey II. Subsequent counts of Anjou were descended from Geoffrey's sister Ermengarde and Count Geoffrey II of Gâtinais. Their agnatic descendants, who included the Angevin kings of England, continued to hold these titles and property until the French monarchy gained control of the area. In 1360, the Count was raised to a Dukedom becoming known as Duke of Anjou, subsequently leading the Duchy of Anjou. The title was held by Philip V of Spain before his accession in 1700. Since then, some Spanish legitimist clai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Of Wales
Prince of Wales ( cy, Tywysog Cymru, ; la, Princeps Cambriae/Walliae) is a title traditionally given to the heir apparent to the English and later British throne. Prior to the conquest by Edward I in the 13th century, it was used by the rulers of independent Wales. The first native Welsh prince was Gruffudd ap Cynan of Gwynedd, in 1137, although his son Owain Gwynedd (Owain ap Gruffudd) is often cited as having established the title. Llywelyn the Great is typically regarded as the strongest leader, holding power over the vast majority of Wales for 45 years. One of the last independent princes was Llywelyn ap Gruffydd (Llywelyn the Last), who was killed at the Battle of Orewin Bridge in 1282. His brother, Dafydd ap Gruffydd, was executed the following year. After these two deaths, Edward I of England invested his son Edward of Caernarfon as the first English prince of Wales in 1301. The title was later claimed by the heir of Gwynedd, Owain Glyndŵr (Owain ap Gruffydd), from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Aumale
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are ranked below princess nobility and grand dukes. The title comes from French ''duc'', itself from the Latin ''dux'', 'leader', a term used in republican Rome to refer to a military commander without an official rank (particularly one of Germanic or Celtic origin), and later coming to mean the leading military commander of a province. In most countries, the word ''duchess'' is the female equivalent. Following the reforms of the emperor Diocletian (which separated the civilian and military administrations of the Roman provinces), a ''dux'' became the military commander in each province. The title ''dux'', Hellenised to ''doux'', survived in the Eastern Roman Empire where it continued in several contexts, signifying a rank equivalent to a captain o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |