|
Planemo
A planetary-mass object (PMO), planemo, or planetary body is by geophysical definition of celestial objects any celestial object massive enough to achieve hydrostatic equilibrium (to be rounded under its own gravity), but not enough to sustain core fusion like a star. The purpose of this term is to refer to a broader range of celestial objects than the concept of planet, since many objects similar in geophysical terms do not conform to typical expectations for a planet. Planetary-mass objects can be quite distinguished in origin and location. Planetary-mass objects include dwarf planets, planetary-mass satellite or free-floating planemos, which may have been ejected from a system (rogue planets) or formed through cloud-collapse rather than accretion (sometimes called sub-brown dwarfs). Types Planetary-mass satellite The three largest satellites Ganymede, Callisto, and Titan are of similar size or larger than the planet Mercury; these and four more – Io, Moon, Europa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrostatic Equilibrium
In fluid mechanics, hydrostatic equilibrium (hydrostatic balance, hydrostasy) is the condition of a fluid or plastic solid at rest, which occurs when external forces, such as gravity, are balanced by a pressure-gradient force. In the planetary physics of Earth, the pressure-gradient force prevents gravity from collapsing the planetary atmosphere into a thin, dense shell, whereas gravity prevents the pressure-gradient force from diffusing the atmosphere into outer space. Hydrostatic equilibrium is the distinguishing criterion between dwarf planets and small solar system bodies, and features in astrophysics and planetary geology. Said qualification of equilibrium indicates that the shape of the object is symmetrically ellipsoid, where any irregular surface features are consequent to a relatively thin solid crust. In addition to the Sun, there are a dozen or so equilibrium objects confirmed to exist in the Solar System. Mathematical consideration For a hydrostatic fluid o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Stern
Sol Alan Stern (born November 22, 1957) is an American engineer and planetary scientist. He is the principal investigator of the ''New Horizons'' mission to Pluto and the Chief Scientist at Moon Express. Stern has been involved in 24 suborbital, orbital, and planetary space missions, including eight for which he was the mission principal investigator. One of his projects was the Southwest Ultraviolet Imaging System, an instrument which flew on two space shuttle missions, STS-85 in 1997 and STS-93 in 1999. Stern has also developed eight scientific instruments for planetary and near-space research missions and has been a guest observer on numerous NASA satellite observatories, including the International Ultraviolet Explorer, the Hubble Space Telescope, the International Infrared Observer and the Extreme Ultraviolet Observer. Stern was executive director of the Southwest Research Institute's Space Science and Engineering Division until becoming Associate Administrator of NASA's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
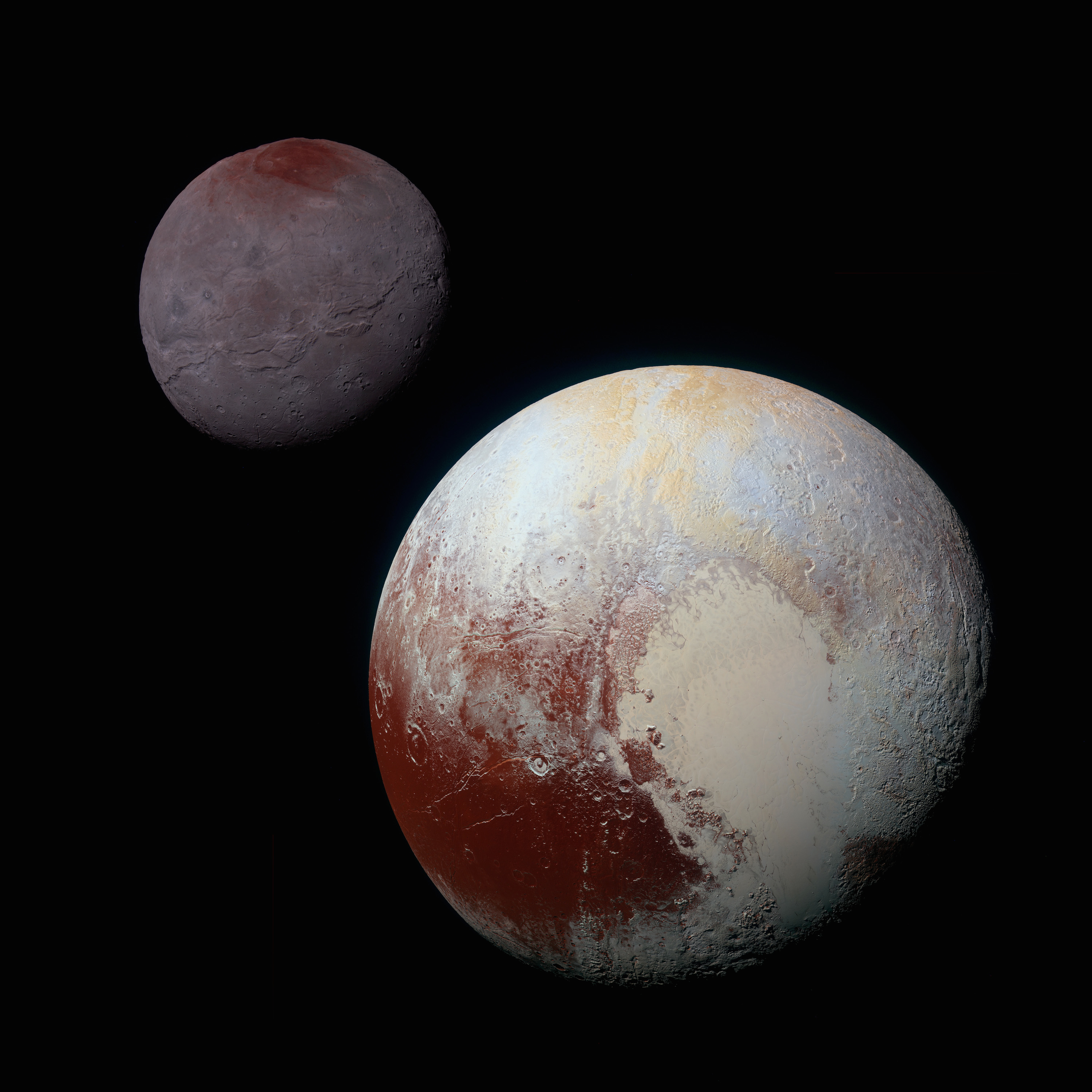
Dwarf Planet
A dwarf planet is a small planetary-mass object that is in direct orbit of the Sun, smaller than any of the eight classical planets but still a world in its own right. The prototypical dwarf planet is Pluto. The interest of dwarf planets to planetary geologists is that they may be geologically active bodies, an expectation that was borne out in 2015 by the '' Dawn'' mission to and the '' New Horizons'' mission to Pluto. Astronomers are in general agreement that at least the nine largest candidates are dwarf planets: Pluto, , , , , , , , and . Of these and the tenth-largest candidate , all but Sedna have either been visited by spacecraft (Pluto and Ceres) or have at least one known moon (Pluto, Eris, Haumea, Makemake, Gonggong, Quaoar, Orcus, and Salacia), which allows their masses and thus an estimate of their densities to be determined. Mass and density in turn can be fit into geophysical models in an attempt to determine the nature of these worlds. Some astronomers includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary-mass Moon
A planetary-mass moon is a planetary-mass object that is also a natural satellite. They are large and ellipsoidal (sometimes spherical) in shape. Two moons in the Solar System are larger than the planet Mercury (though less massive): Ganymede and Titan, and seven are larger and more massive than the dwarf planet . The concept of ''satellite planets'' – the idea that planetary-mass objects, including planetary-mass moons, are planets – is used by some planetary scientists, such as Alan Stern, who are more concerned with whether a celestial body has planetary geology (that is, whether it is a planetary body) than its solar or non-solar orbit ( planetary dynamics). This conceptualization of planets as three classes of objects (classical planets, dwarf planets and satellite planets) has not been accepted by the International Astronomical Union (the IAU). In addition, the IAU definition of 'hydrostatic equilibrium' is quite restrictive – that the object's mass be sufficient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rogue Planet
A rogue planet (also termed a free-floating planet (FFP), interstellar, nomad, orphan, starless, unbound or wandering planet) is an interstellar object of planetary-mass, therefore smaller than fusors (stars and brown dwarfs) and without a host planetary system. Such objects have been ejected from the planetary system in which they formed or have never been gravitationally bound to any star or brown dwarf. The Milky Way alone may have billions to trillions of rogue planets, a range the upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will likely be able to narrow down. Some planetary-mass objects may have formed in a similar way to stars, and the International Astronomical Union has proposed that such objects be called sub-brown dwarfs. A possible example is Cha 110913−773444, which may have been ejected and become a rogue planet, or formed on its own to become a sub-brown dwarf. Astronomers have used the Herschel Space Observatory and the Very Large Telescope to observe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
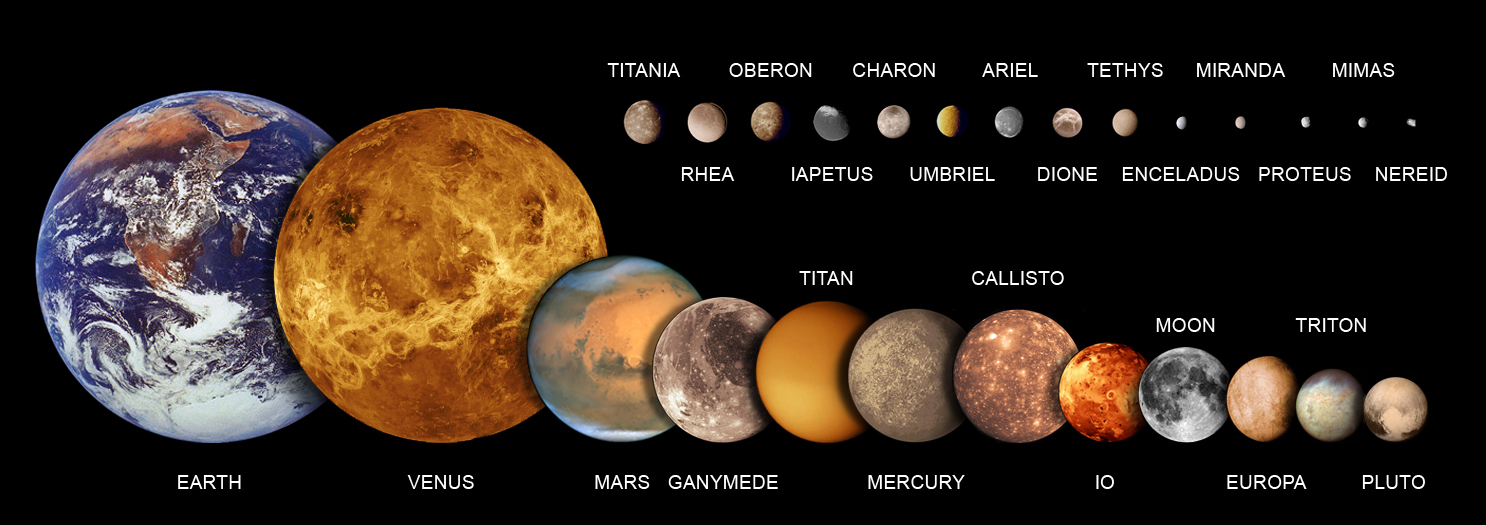
25 Solar System Objects Smaller Than Earth
5 (five) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number, and cardinal number, following 4 and preceding 6, and is a prime number. It has attained significance throughout history in part because typical humans have five digits on each hand. In mathematics 5 is the third smallest prime number, and the second super-prime. It is the first safe prime, the first good prime, the first balanced prime, and the first of three known Wilson primes. Five is the second Fermat prime and the third Mersenne prime exponent, as well as the third Catalan number, and the third Sophie Germain prime. Notably, 5 is equal to the sum of the ''only'' consecutive primes, 2 + 3, and is the only number that is part of more than one pair of twin primes, ( 3, 5) and (5, 7). It is also a sexy prime with the fifth prime number and first prime repunit, 11. Five is the third factorial prime, an alternating factorial, and an Eisenstein prime with no imaginary part and real part of the for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSR J1719-1438
PSR may refer to: Organizations * Pacific School of Religion, Berkeley, California, US * Palestinian Center for Policy and Survey Research * Physicians for Social Responsibility, US ;Political parties: * Revolutionary Socialist Party (Portugal) (''Partido Socialista Revolucionário'') * Romanian Socialist Party (present-day) Places * Abruzzo Airport (IATA airport code), near Pescara, Italy * Pasir Ris MRT station (MRT station abbreviation), Singapore * Pioneer Scout Reservation, a Boy Scout camp in Ohio, US Science and technology * Pulsar, a kind of star * Primary radar * Perimeter surveillance radar * Posthumous sperm retrieval from dead men Computing * PHP Standard Recommendation * Predictive state representation of a system * Problem Steps Recorder, psr.exe, a Microsoft utility * Panel Self-Refresh in Embedded DisplayPort Law enforcement and military * US Precision Sniper Rifle * PSR-90, a Pakistani Precision Sniper Rifle Other uses * Portuguese Sign Language (ISO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Star
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in which case they are called ''visual binaries''. Many visual binaries have long orbital periods of several centuries or millennia and therefore have orbits which are uncertain or poorly known. They may also be detected by indirect techniques, such as spectroscopy (''spectroscopic binaries'') or astrometry (''astrometric binaries''). If a binary star happens to orbit in a plane along our line of sight, its components will eclipse and transit each other; these pairs are called ''eclipsing binaries'', or, together with other binaries that change brightness as they orbit, ''photometric binaries''. If components in binary star systems are close enough they can gravitationally distort their mutual outer stellar atmospheres. In some cases, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accretion-powered Pulsars
X-ray pulsars or accretion-powered pulsars are a class of astronomical objects that are X-ray sources displaying strict periodic variations in X-ray intensity. The X-ray periods range from as little as a fraction of a second to as much as several minutes. Characteristics An X-ray pulsar consists of a magnetized neutron star in orbit with a normal stellar companion and is a type of binary star system. The magnetic-field strength at the surface of the neutron star is typically about 108 Tesla, over a trillion times stronger than the strength of the magnetic field measured at the surface of the Earth (60 μT). Gas is accreted from the stellar companion and is channeled by the neutron star's magnetic field on to the magnetic poles producing two or more localized X-ray hot spots, similar to the two auroral zones on Earth, but far hotter. At these hotspots the infalling gas can reach half the speed of light before it impacts the neutron star surface. So much gravitational potentia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulsar
A pulsar (from ''pulsating radio source'') is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its magnetic poles. This radiation can be observed only when a beam of emission is pointing toward Earth (similar to the way a lighthouse can be seen only when the light is pointed in the direction of an observer), and is responsible for the pulsed appearance of emission. Neutron stars are very dense and have short, regular rotational periods. This produces a very precise interval between pulses that ranges from milliseconds to seconds for an individual pulsar. Pulsars are one of the candidates for the source of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays. (See also centrifugal mechanism of acceleration.) The periods of pulsars make them very useful tools for astronomers. Observations of a pulsar in a binary neutron star system were used to indirectly confirm the existence of gravitational radiation. The first extrasolar planets were discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
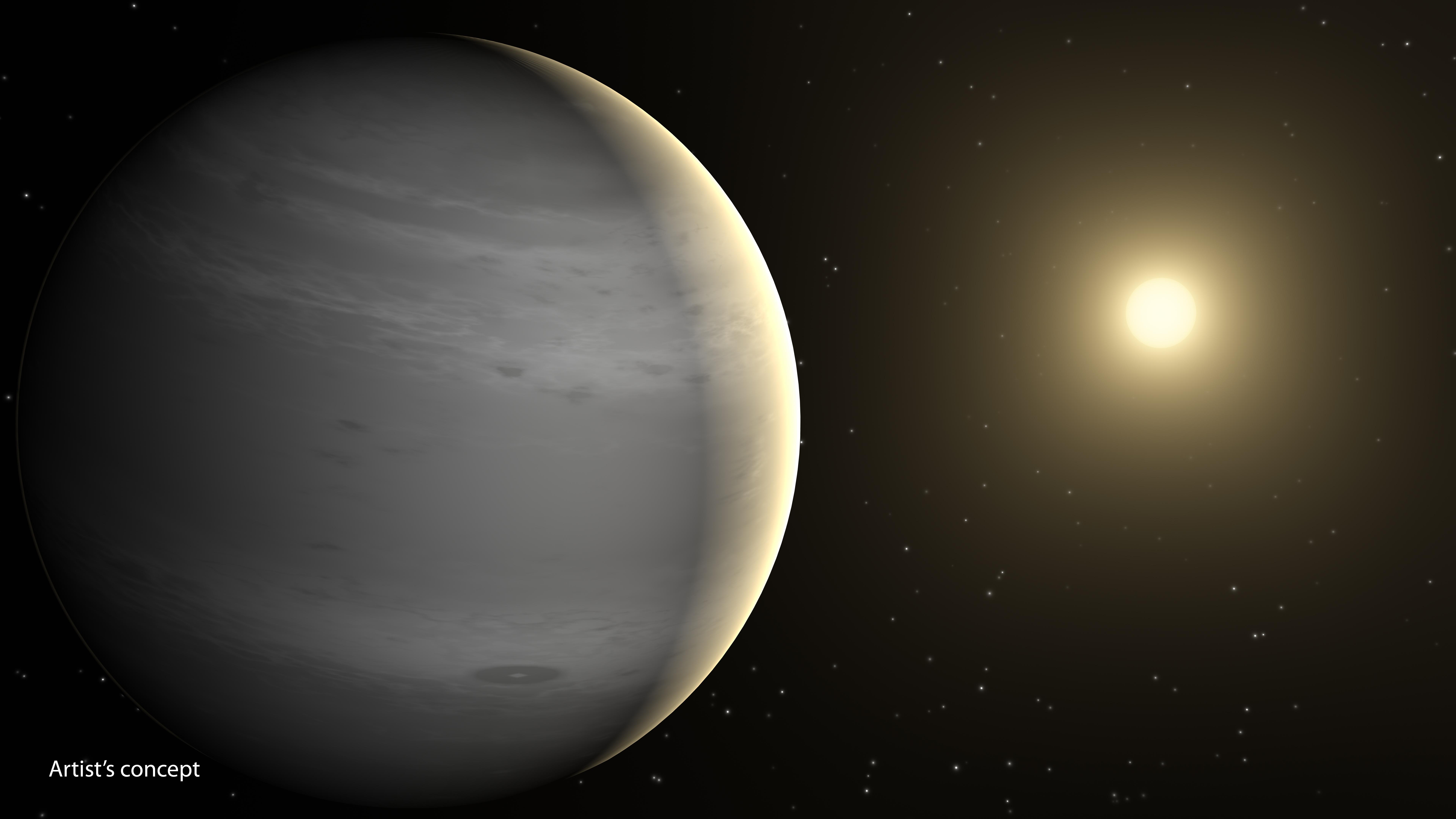
Helium Planet
A helium planet is a planet with a helium-dominated atmosphere. This contrasts with ordinary gas giants such as Jupiter and Saturn, whose atmospheres consist primarily of hydrogen, with helium as a secondary component only. Helium planets might form in a variety of ways. Gliese 436 b is a possible helium planet. Formation There are several hypotheses for how a helium planet might form. Hydrogen evaporation from giant planets A helium planet might form via hydrogen evaporation from a gaseous planet orbiting close to a star. The star will drive off lighter gases more effectively through evaporation than heavier gasses, and over time deplete the hydrogen, leaving a greater proportion of helium behind. A scenario for forming helium planets from regular giant planets involves an ice giant, in an orbit so close to its host star that the hydrogen effectively boils out of the atmosphere, evaporating from and escaping the gravitational hold of the planet. The planet's atmosphere wil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


