|
Pitt Bank
Pitt Bank is a wholly submerged atoll structure in the Southwest of the Chagos Archipelago. It is almost 56 km long Northwest to Southeast, with a width between 20 and 30 km. It stretches from 06°48'S to 07°16'S and 071°06'E to 071°36'E. The total size is 1317 km, making it the second largest ocean bank in the Chagos Archipelago, after the Great Chagos Bank, and before Speakers Bank. The closest land is Île Lubine of Egmont Atoll, located 22 km northeast off the northern end of Pitt Bank. The least depth is 7 metres at the Southeastern Rim, and the deepest areas of the former lagoon reach 44 metres. The much smaller Wight Bank is located 6 km to the SE off the southeastern tip of Pitt Bank. This submerged atoll was named after William Pitt the Younger, who was a British prime minister in 1783–1801 and 1804–1806. A buoy, marked by a radar reflector, is moored on the NW side of the bank.British Admiralty The Admiralty was a department ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atoll
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon partially or completely. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical oceans and seas where corals can grow. Most of the approximately 440 atolls in the world are in the Pacific Ocean. Two different, well-cited models, the subsidence and antecedent karst models, have been used to explain the development of atolls.Droxler, A.W. and Jorry, S.J., 2021. ''The Origin of Modern Atolls: Challenging Darwin's Deeply Ingrained Theory.'' ''Annual Review of Marine Science'', 13, pp.537-573. According to Charles Darwin's ''subsidence model'', the formation of an atoll is explained by the subsidence of a volcanic island around which a coral fringing reef has formed. Over geologic time, the volcanic island becomes extinct and eroded as it subsides completely beneath the surface of the ocean. As the volcanic island subsides, the coral fringing reef becomes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
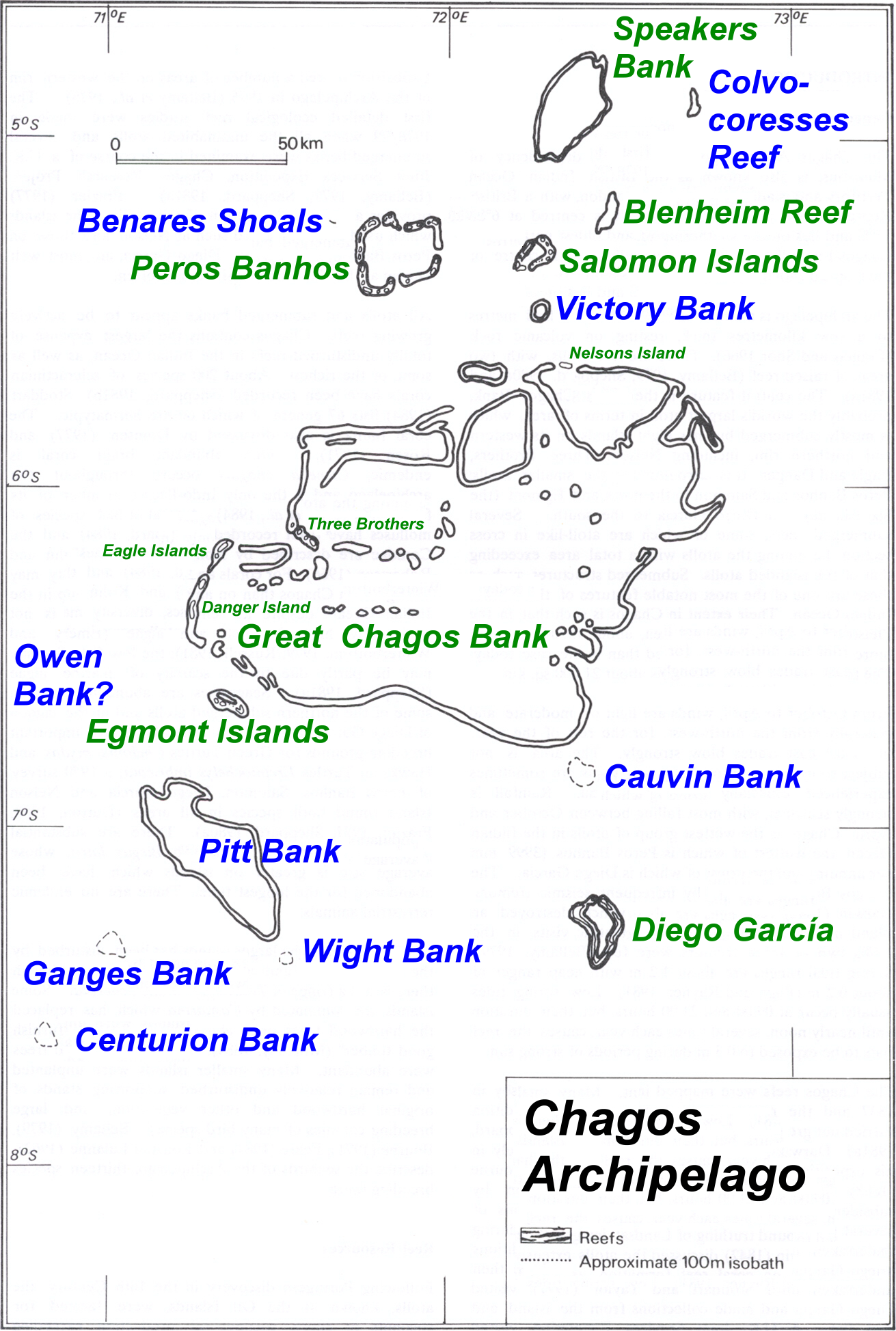
Chagos Archipelago
The Chagos Archipelago () or Chagos Islands (formerly the Bassas de Chagas, and later the Oil Islands) is a group of seven atolls comprising more than 60 islands in the Indian Ocean about 500 kilometres (310 mi) south of the Maldives archipelago. This chain of islands is the southernmost archipelago of the Chagos–Laccadive Ridge, a long submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean. In its north are the Salomon Islands, Nelson's Island and Peros Banhos; towards its south-west are the Three Brothers, Eagle, Egmont and Danger Island(s); southeast of these is Diego Garcia, by far the largest island. All are low-lying atolls, save for a few extremely small instances, set around lagoons. The Chagos Islands had been home to the native Chagossians, a Bourbonnais Creole-speaking people, until the United Kingdom expelled them from the archipelago at the request of the United States between 1967 and 1973 to allow the United States to build a military base on Diego Garcia. Since 197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Bank (topography)
An ocean bank, sometimes referred to as a fishing bank or simply bank, is a part of the seabed that is shallow compared to its surrounding area, such as a shoal or the top of an seamount, underwater hill. Somewhat like continental margin, continental slopes, ocean bank slopes can upwelling, upwell as Tide#Current, tidal and other flows intercept them, sometimes resulting in nutrient-rich currents. Because of this, some large banks, such as Dogger Bank and the Grand Banks of Newfoundland, are among the richest fishing grounds in the world. There are some banks that were reported in the 19th century by navigators, such as Wachusett Reef, whose existence is doubtful. Types Ocean banks may be of volcano, volcanic nature. Banks may be Carbonate platform, carbonate or Continental shelf#Sediments, terrigenous. In tropical areas some banks are submerged atolls. As they are not associated with any landmass, banks have no outside source of sediments. Carbonate banks are typically platfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Chagos Bank
The Great Chagos Bank, in the Chagos Archipelago, about south of Maldives, is the largest atoll structure in the world, with a total area of . The atoll is administered by the United Kingdom through the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT). Islands Despite its enormous size, the Great Chagos Bank is largely a submarine structure. There are only four emerging reefs, mostly located on the western rim of the atoll, except for lonely Nelson Island, which lies wholly isolated in the middle of the northern fringe. These reefs have eight individual low and sandy islands, with a total land area of about . All islands and their surrounding waters are a Strict Nature Reserve since 1998. The total length of the eastern and southern expanses of the bank, as well as the reefs in its central area are wholly submerged. The islands of the Great Chagos Bank, starting clockwise from the south, are: * Danger Island (slightly more than long from North to South, by wide, land area , vege ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speakers Bank
Speakers Bank is a large coral atoll structure in the Northwestern part of the Chagos Archipelago. It is the northernmost feature of the archipelago, located at , 22 km Northwest of Blenheim Reef and is 44 km Northeast-Southwest, and 24 km wide. The total area is 582 km2, most of which is water. Most of the rim of the reef is between 5.5 and 14.5 metres below water. In the south, near the southwest edge, there are some coral heads at 05°04'S, 072°16'E, 0.5 metres of which are dry during low tide, and over which the sea breaks heavily during the southeast trade winds. In the Northeast, at 04°47'S, 072°26'E, there are a number of drying cays, the biggest of which, Big Speaker Reef, just reaches the high water mark. The land area is negligible. Speakers Bank was surveyed in 1856 by British captain J. Speaker on HMS Wallerup. It is the site of many wrecks, also from prior times.British Admiralty nautical chart A nautical chart is a graphic representation of a sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egmont Atoll
Egmont Islands (also known as Egmont Atoll, or Six Iles) is an uninhabited atoll administered by the United Kingdom. They are one of the few emerged coral atolls that make up the Chagos Archipelago, British Indian Ocean Territory. This small atoll lies less than 10km south of the southwestern rim of the Great Chagos Bank submerged coral reef. Its total size is 29km², including the lagoon and the fringing coral reef. The land area totals about 4km². The nearest island is Danger Island on the Great Chagos Bank, less than 30km due north. There are two passages into the lagoon along the Northern Rim, Fausse Passe in the northeast and a wider passage in the northwest. The Egmont Islands are one of the favorite anchoring spots for itinerant yachtsmen passing through the Chagos. Islands The largest island is "Île Sud-Est" (Eastern Egmont), where the settlement was located, with an area of 1.5km². While "Île Lubine" is similar in size, the other islets are smaller. All islands are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') and ''atoll lagoons''. They have also been identified as occurring on mixed-sand and gravel coastlines. There is an overlap between bodies of water classified as coastal lagoons and bodies of water classified as estuaries. Lagoons are common coastal features around many parts of the world. Definition and terminology Lagoons are shallow, often elongated bodies of water separated from a larger body of water by a shallow or exposed shoal, coral reef, or similar feature. Some authorities include fresh water bodies in the definition of "lagoon", while others explicitly restrict "lagoon" to bodies of water with some degree of salinity. The distinction between "lagoon" and "estuary" also varies between authorities. Richard A. Davis Jr. restrict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wight Bank
Wight Bank is a small, wholly submerged atoll structure in the Southwest of the Chagos Archipelago, Indian Ocean. It is located to the SE off the southeastern tip of Pitt Bank at . It is less than in diameter, and its total area is about . The closest piece of land is Île Sudest of Egmont Atoll, at NNW. Diego Garcia is to the east. The least charted depth is .British Admiralty The Admiralty was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom responsible for the command of the Royal Navy until 1964, historically under its titular head, the Lord High Admiral – one of the Great Officers of State. For much of it ... nautical chart 11000030 - 3 Chagos Archipelago, Scale 1:360,000. Wight Bank was first reported in 1886. References External linksIndian Ocean Pilot Chagos Archipelago {{BritishIndianOcean-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Pitt The Younger
William Pitt the Younger (28 May 175923 January 1806) was a British statesman, the youngest and last prime minister of Great Britain (before the Acts of Union 1800) and then first prime minister of the United Kingdom (of Great Britain and Ireland) as of January 1801. He left office in March 1801, but served as prime minister again from 1804 until his death in 1806. He was also Chancellor of the Exchequer for all of his time as prime minister. He is known as "Pitt the Younger" to distinguish him from his father, William Pitt, 1st Earl of Chatham, who had previously served as prime minister and is referred to as "William Pitt the Elder" (or "Chatham" by historians). Pitt's prime ministerial tenure, which came during the reign of King George III, was dominated by major political events in Europe, including the French Revolution and the Napoleonic Wars. Pitt, although often referred to as a Tory, or "new Tory", called himself an "independent Whig" and was generally opposed to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buoy
A buoy () is a floating device that can have many purposes. It can be anchored (stationary) or allowed to drift with ocean currents. Types Navigational buoys * Race course marker buoys are used for buoy racing, the most prevalent form of yacht racing and power boat racing. They delimit the course and must be passed to a specified side. They are also used in underwater orienteering competitions. * Emergency wreck buoys provide a clear and unambiguous means of temporarily marking new wrecks, typically for the first 24–72 hours. They are coloured in an equal number of blue and yellow vertical stripes and fitted with an alternating blue and yellow flashing light. They were implemented following collisions in the Dover Strait in 2002 when vessels struck the new wreck of the . * Ice marking buoys mark holes in frozen lakes and rivers so snowmobiles do not drive over the holes. * Large Navigational Buoys (LNB, or Lanby buoys) are automatic buoys over 10 m high equipped with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving information about the objects' locations and speeds. Radar was developed secretly for military use by several countries in the period before and during World War II. A key development was the cavity magnetron in the United Kingdom, which allowed the creation of relatively small systems with sub-meter resolution. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Admiralty
The Admiralty was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom responsible for the command of the Royal Navy until 1964, historically under its titular head, the Lord High Admiral – one of the Great Officers of State. For much of its history, from the early 18th century until its abolition, the role of the Lord High Admiral was almost invariably put "in commission" and exercised by the Lords Commissioner of the Admiralty, who sat on the governing Board of Admiralty, rather than by a single person. The Admiralty was replaced by the Admiralty Board in 1964, as part of the reforms that created the Ministry of Defence and its Navy Department (later Navy Command). Before the Acts of Union 1707, the Office of the Admiralty and Marine Affairs administered the Royal Navy of the Kingdom of England, which merged with the Royal Scots Navy and the absorbed the responsibilities of the Lord High Admiral of the Kingdom of Scotland with the unification of the Kingdom of Great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |