|
Pisiform Joint
The pisiform joint is a joint between the pisiform and triquetrum. It includes the pisohamate ligament and pisometacarpal ligament The pisometacarpal ligament joins the pisiform to the base of the fifth metacarpal bone. It is a continuation of the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris The flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) is a muscle of the forearm that flexes and adducts at the wrist .... References {{Authority control Hand Joints Upper limb anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scaphoid Bone
The scaphoid bone is one of the carpal bones of the wrist. It is situated between the hand and forearm on the thumb side of the wrist (also called the lateral or radial side). It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel. The scaphoid bone is the largest bone of the proximal row of wrist bones, its long axis being from above downward, lateralward, and forward. It is approximately the size and shape of a medium cashew. Structure The scaphoid is situated between the proximal and distal rows of carpal bones. It is located on the radial side of the wrist, and articulates with the radius, lunate, trapezoid, trapezium, and capitate. Over 80% of the bone is covered in articular cartilage. Bone The palmar surface of the scaphoid is concave, and forming a distal tubercle, giving attachment to the transverse carpal ligament. The proximal surface is triangular, smooth and convex. The lateral surface is narrow and gives attachment to the radial collateral ligament. The medial surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
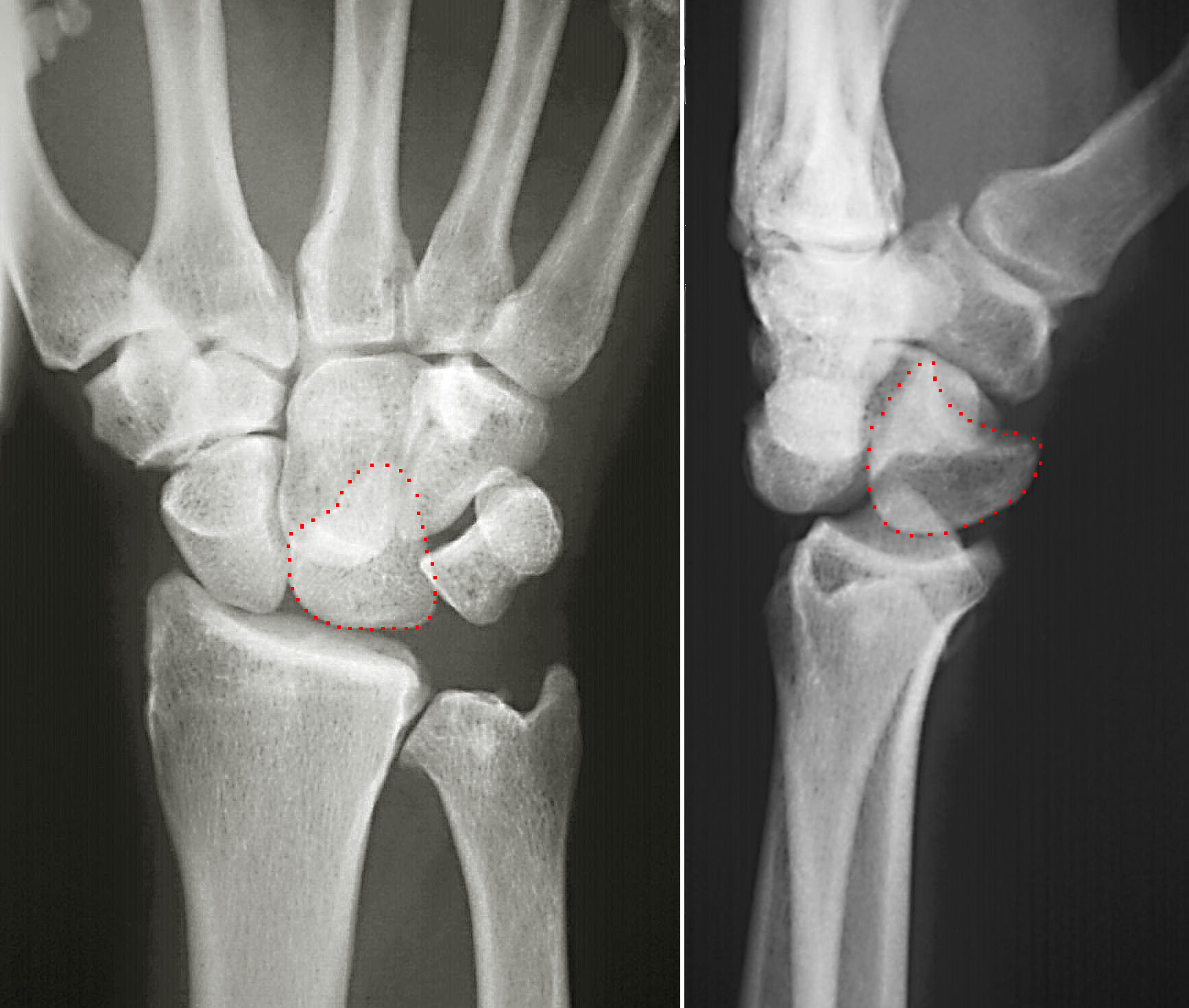
Lunate Bone
The lunate bone (semilunar bone) is a carpal bone in the human hand. It is distinguished by its deep concavity and crescentic outline. It is situated in the center of the proximal row carpal bones, which lie between the ulna and radius and the hand. The lunate carpal bone is situated between the lateral scaphoid bone and medial triquetral bone. Structure The lunate is a crescent-shaped carpal bone found within the hand. The lunate is found within the proximal row of carpal bones. Proximally, it abuts the radius. Laterally, it articulates with the scaphoid bone, medially with the triquetral bone, and distally with the capitate bone. The lunate also articulates on its distal and medial surface with the hamate bone. The lunate is stabilised by a medial ligament to the scaphoid bone and a lateral ligament to the triquetral bone. Ligaments between the radius and carpal bone also stabilise the position of the lunate, as does its position in the lunate fossa of the radius. Bone The pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triquetral Bone
The triquetral bone (; also called triquetrum, pyramidal, three-faced, and formerly cuneiform bone) is located in the wrist on the medial side of the proximal row of the carpus between the lunate and pisiform bones. It is on the ulnar side of the hand, but does not directly articulate with the ulna, however it is connected and articulate with the ulna through Triangular fibrocartilage discManaster, B. J., Julia Crim "Imaging Anatomy: Musculoskeletal E-Book" Elsevier Health Sciences, 2016, p. 326. and ligament, which forming the part of the ulnocarpal joint capsule. It connects with the pisiform, hamate, and lunate bones. It is the 2nd most commonly fractured carpal bone. Structure The triquetral is one of the eight carpal bones of the hand. It is a three-faced bone found within the proximal row of carpal bones. Situated beneath the pisiform, it is one of the carpal bones that form the carpal arch, within which lies the carpal tunnel. The triquetral bone may be distinguished by i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisiform Bone
The pisiform bone ( or ), also spelled pisiforme (from the Latin ''pisifomis'', pea-shaped), is a small knobbly, sesamoid bone that is found in the wrist. It forms the ulnar border of the carpal tunnel. Structure The pisiform is a sesamoid bone, with no covering membrane of periosteum. It is the last carpal bone to ossify. The pisiform bone is a small bone found in the proximal row of the wrist (carpus). It is situated where the ulna joins the wrist, within the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. It only has one side that acts as a joint, articulating with the triquetral bone. It is on a plane anterior to the other carpal bones and is spheroidal in form. The pisiform bone has four surfaces: # The ''dorsal surface'' is smooth and oval, and articulates with the triquetral: this facet approaches the superior, but not the inferior border of the bone. # The ''palmar surface'' is rounded and rough, and gives attachment to the transverse carpal ligament, the flexor carpi ulnaris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trapezium Bone
The trapezium bone (greater multangular bone) is a carpal bone in the hand. It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel. Structure The trapezium is distinguished by a deep groove on its anterior surface. It is situated at the radial side of the carpus, between the scaphoid and the first metacarpal bone (the metacarpal bone of the thumb). It is homologous with the first distal carpal of reptiles and amphibians. Surfaces The trapezium is an irregular-shaped carpal bone found within the hand. The trapezium is found within the distal row of carpal bones, and is directly adjacent to the metacarpal bone of the thumb. On its ulnar surface are found the trapezoid and scaphoid bones. The '' superior surface'' is directed upward and medialward; medially it is smooth, and articulates with the scaphoid; laterally it is rough and continuous with the lateral surface. The '' inferior surface'' is oval, concave from side to side, convex from before backward, so as to form a saddle-shaped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trapezoid Bone
The trapezoid bone (lesser multangular bone) is a carpal bone in tetrapods, including humans. It is the smallest bone in the distal row of carpal bones that give structure to the palm of the hand. It may be known by its wedge-shaped form, the broad end of the wedge constituting the dorsal, the narrow end the palmar surface; and by its having four articular facets touching each other, and separated by sharp edges. It is homologous with the "second distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians. Structure The trapezoid is a four-sided carpal bone found within the hand. The trapezoid is found within the distal row of carpal bones. Surfaces The '' superior surface'', quadrilateral, smooth, and slightly concave, articulates with the scaphoid. The '' inferior surface'' articulates with the proximal end of the second metacarpal bone; it is convex from side to side, concave from before backward and subdivided by an elevated ridge into two unequal facets. The ''dorsal'' and '' palmar surfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitate Bone
The capitate bone is a bone in the human wrist found in the center of the carpal bone region, located at the distal end of the radius and ulna bones. It articulates with the third metacarpal bone (the middle finger) and forms the third carpometacarpal joint. The capitate bone is the largest of the carpal bones in the human hand. It presents, above, a rounded portion or head, which is received into the concavity formed by the scaphoid and lunate bones; a constricted portion or neck; and below this, the body.''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918). See infobox. The bone is also found in many other mammals, and is homologous with the "third distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians. Structure The capitate is the largest carpal bone found within the hand. The capitate is found within the distal row of carpal bones. The capitate lies directly adjacent to the metacarpal of the ring finger on its distal surface, has the hamate on its ulnar surface and trapezoid on its radial surface, and abuts the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamate Bone
The hamate bone (from Latin hamatus, "hooked"), or unciform bone (from Latin ''uncus'', "hook"), Latin os hamatum and occasionally abbreviated as just hamatum, is a bone in the human wrist readily distinguishable by its wedge shape and a hook-like process ("hamulus") projecting from its palmar surface. Structure The hamate is an irregularly shaped carpal bone found within the hand. The hamate is found within the distal row of carpal bones, and abuts the metacarpals of the little finger and ring finger. Adjacent to the hamate on the ulnar side, and slightly above it, is the pisiform bone. Adjacent on the radial side is the capitate, and proximal is the lunate bone. Surfaces The hamate bone has six surfaces: * The ''superior'', the apex of the wedge, is narrow, convex, smooth, and articulates with the lunate. * The ''inferior'' articulates with the fourth and fifth metacarpal bones, by concave facets which are separated by a ridge. * The ''dorsal'' is triangular and rough for l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisiform
The pisiform bone ( or ), also spelled pisiforme (from the Latin ''pisifomis'', pea-shaped), is a small knobbly, sesamoid bone that is found in the wrist. It forms the ulnar border of the carpal tunnel. Structure The pisiform is a sesamoid bone, with no covering membrane of periosteum. It is the last carpal bone to ossify. The pisiform bone is a small bone found in the proximal row of the wrist (carpus). It is situated where the ulna joins the wrist, within the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. It only has one side that acts as a joint, articulating with the triquetral bone. It is on a plane anterior to the other carpal bones and is spheroidal in form. The pisiform bone has four surfaces: # The ''dorsal surface'' is smooth and oval, and articulates with the triquetral: this facet approaches the superior, but not the inferior border of the bone. # The ''palmar surface'' is rounded and rough, and gives attachment to the transverse carpal ligament, the flexor carpi ulnaris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triquetral Bone
The triquetral bone (; also called triquetrum, pyramidal, three-faced, and formerly cuneiform bone) is located in the wrist on the medial side of the proximal row of the carpus between the lunate and pisiform bones. It is on the ulnar side of the hand, but does not directly articulate with the ulna, however it is connected and articulate with the ulna through Triangular fibrocartilage discManaster, B. J., Julia Crim "Imaging Anatomy: Musculoskeletal E-Book" Elsevier Health Sciences, 2016, p. 326. and ligament, which forming the part of the ulnocarpal joint capsule. It connects with the pisiform, hamate, and lunate bones. It is the 2nd most commonly fractured carpal bone. Structure The triquetral is one of the eight carpal bones of the hand. It is a three-faced bone found within the proximal row of carpal bones. Situated beneath the pisiform, it is one of the carpal bones that form the carpal arch, within which lies the carpal tunnel. The triquetral bone may be distinguished by i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisohamate Ligament
The pisohamate ligament is a ligament in the hand. It connects the pisiform to the hook of the hamate. It is a prolongation of the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris. It serves as part of the origin for the abductor digiti minimi. It also forms the floor of the ulnar canal, a canal that allows the ulnar nerve and ulnar artery The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the medial aspects of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins with the superficial branch of the radial ar ... into the hand. References Ligaments of the upper limb {{ligament-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisometacarpal Ligament
The pisometacarpal ligament joins the pisiform to the base of the fifth metacarpal bone. It is a continuation of the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris The flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) is a muscle of the forearm that flexes and adducts at the wrist joint. Structure Origin The flexor carpi ulnaris has two heads; a humeral head and ulnar head. The humeral head originates from the medial epicondyle o .... Additional images Image:Ligamentumpisometacarpeum.png, Ligaments of wrist. Anterior view. (Pisometacarpal labeled at right, second from bottom.) References External links * https://web.archive.org/web/20070806224310/http://classes.kumc.edu/sah/resources/handkines/ligaments/wvdpisometa.htm Ligaments of the upper limb {{ligament-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-_animation02.gif)