|
Pisces–Cetus Supercluster Complex
The Pisces–Cetus Supercluster Complex is a galaxy filament. It includes the Laniakea Supercluster which contains the Virgo Supercluster lobe which in turn contains the Local Group, the galaxy cluster that includes the Milky Way. This filament is adjacent to the Perseus–Pegasus Filament. Discovery Astronomer R. Brent Tully of the University of Hawaii’s Institute of Astronomy identified the Complex in 1987. Extent The Pisces–Cetus Supercluster Complex is estimated to be about 1.0 billion light-years (Gly) long and 150 million light years (Mly) wide. It is one of the largest structures known in the observable universe, but is exceeded by the Sloan Great Wall (1.3 Gly), Clowes–Campusano LQG (2.0 Gly), U1.11 LQG (2.5 Gly), Huge-LQG (4.0 Gly), and Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall (10 Gly), respectively. The complex comprises about 60 clusters and is estimated to have a total mass of 10 . According to the discoverer, the complex is composed of 5 parts: # The Pisce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy Filament
In cosmology, galaxy filaments (subtypes: supercluster complexes, galaxy walls, and galaxy sheets) Boris V. Komberg, Andrey V. Kravtsov, Vladimir N. Lukash; "The search and investigation of the Large Groups of Quasars" ; ;R.G. Clowes; "Large Quasar Groups - A Short Review"; ''The New Era of Wide Field Astronomy'', ASP Conference Series, vol. 232.; 2001; Astronomical Society of the Pacific; ; are the largest known structures in the universe, consisting of walls of gravitationally bound galaxy superclusters. These massive, thread-like formations can reach 80 parsec#Megaparsecs and gigaparsecs, megaparsecs ''h''−1 (or of the order of 160 to 260 million light-years) and form the boundaries between large void (astronomy), voids. Formation In the Lambda-CDM model, standard model of the evolution of the universe, galactic filaments form along and follow web-like strings of dark matter—also referred to as the galactic web or cosmic web. It is thought that this dark matter dictates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perseus–Pisces Supercluster
The Perseus–Pisces Supercluster (SCl 40) is one of the largest known structures in the universe. Even at a distance of 250 million light-years, this chain of galaxy clusters extends more than 40° across the northern winter sky. The Perseus-Pisces Supercluster is one of two dominant concentrations of galaxies (the other being the Local supercluster) in the nearby universe (within 300 million light years). This supercluster also borders a prominent void, the Taurus Void, and is part of the Perseus–Pegasus Filament which stretches for roughly a billion light years.'Astrophysical Journal', Part 1 (), vol. 299, Dec. 1, 1985, p. 5-14. "A possible 300 megaparsec filament of clusters of galaxies in Perseus-Pegasus" ''12/1985'' Clusters The main clusters of the Perseus–Pisces Supercluster are Abell 262, Abell 347, and Abell 426. See also * Abell catalogue * Large-scale structure of the universe * List of Abell clusters * Supercluster A supercluster is a large group of smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Galaxy Groups And Clusters
This article lists some galaxy groups and galaxy clusters. Defining the limits of galaxy clusters is imprecise as many clusters are still forming. In particular, clusters close to the Milky Way tend to be classified as galaxy clusters even when they are much smaller than more distant clusters. Clusters exhibiting strong evidence of dark matter Some clusters exhibiting strong evidence of dark matter. Named groups and clusters This is a list of galaxy groups and clusters that are well known by something other than an entry in a catalog or list, or a set of coordinates, or a systematic designation. Clusters Groups The major nearby groups and clusters are generally named after the constellation they lie in. Many groups are named after the leading galaxy in the group. This represents an ad hoc systematic naming system. Groups and clusters visible to the unaided eye The Local Group contains the largest number of visible galaxies with the naked eye. However, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observable Universe
The observable universe is a ball-shaped region of the universe comprising all matter that can be observed from Earth or its space-based telescopes and exploratory probes at the present time, because the electromagnetic radiation from these objects has had time to reach the Solar System and Earth since the beginning of the cosmological expansion. There may be 2 trillion galaxies in the observable universe, although that number was reduced in 2021 to only several hundred billion based on data from ''New Horizons''. Assuming the universe is isotropic, the distance to the edge of the observable universe is roughly the same in every direction. That is, the observable universe is a spherical region centered on the observer and is unique for every unique observational position. The word ''observable'' in this sense does not refer to the capability of modern technology to detect light or other information from an object, or whether there is anything to be detected. It refers to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intracluster Medium
In astronomy, the intracluster medium (ICM) is the superheated plasma that permeates a galaxy cluster. The gas consists mainly of ionized hydrogen and helium and accounts for most of the baryonic material in galaxy clusters. The ICM is heated to temperatures on the order of 10 to 100 megakelvins, emitting strong X-ray radiation. Composition The ICM is composed primarily of ordinary baryons, mainly ionised hydrogen and helium. This plasma is enriched with heavier elements, including iron. The average amount of heavier elements relative to hydrogen, known as metallicity in astronomy, ranges from a third to a half of the value in the sun. Studying the chemical composition of the ICMs as a function of radius has shown that cores of the galaxy clusters are more metal rich than at larger radii. In some clusters (e.g. the Centaurus cluster) the metallicity of the gas can rise to above that of the sun. Due to the gravitational field of clusters, metal-enriched gas ejected from supernova ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Orientation
Galactic clusters are gravitationally bound large-scale structures of multiple galaxies. The evolution of these aggregates is determined by time and manner of formation and the process of how their structures and constituents have been changing with time. Gamow (1952) and Weizscker (1951) showed that the observed rotations of galaxies are important for cosmology. They postulated that the rotation of galaxies might be a clue of physical conditions under which these systems formed. Thus, understanding the distribution of spatial orientations of the spin vectors of galaxies is critical to understanding the origin of the angular momenta of galaxies. There are mainly three scenarios for the origin of galaxy clusters and superclusters. These models are based on different assumptions of the primordial conditions, so they predict different spin vector alignments of the galaxies. The three hypotheses are the ''pancake model'', the ''hierarchy model'', and the ''primordial vorticity theory''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy Cluster
A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. They are the second-largest known gravitationally bound structures in the universe after galaxy filaments and were believed to be the largest known structures in the universe until the 1980s, when superclusters were discovered. One of the key features of clusters is the intracluster medium (ICM). The ICM consists of heated gas between the galaxies and has a peak temperature between 2–15 keV that is dependent on the total mass of the cluster. Galaxy clusters should not be confused with ''galactic clusters'' (also known as open clusters), which are star clusters ''within'' galaxies, or with globular clusters, which typically orbit galaxies. Small aggregates of galaxies are referred to as galaxy groups rather than clusters of galaxies. The galaxy groups a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy Group
A galaxy group or group of galaxies (GrG) is an aggregation of galaxies comprising about 50 or fewer gravitationally bound members, each at least as luminous as the Milky Way (about 1010 times the luminosity of the Sun); collections of galaxies larger than groups that are first-order clustering are called galaxy clusters. The groups and clusters of galaxies can themselves be clustered, into superclusters of galaxies. The Milky Way galaxy is part of a group of galaxies called the Local Group. Characteristics Groups of galaxies are the smallest aggregates of galaxies. They typically contain no more than 50 galaxies in a diameter of 1 to 2 megaparsecs (Mpc).see 1022 m for distance comparisons Their mass is approximately 1013 solar masses. The spread of velocities for the individual galaxies is about 150 km/s. However, this definition should be used as a guide only, as larger and more massive galaxy systems are sometimes classified as galaxy groups. Groups are the most common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the microscopic description of nature in statistical physics, and to the principles of information theory. It has found far-ranging applications in chemistry and physics, in biological systems and their relation to life, in cosmology, economics, sociology, weather science, climate change, and information systems including the transmission of information in telecommunication. The thermodynamic concept was referred to by Scottish scientist and engineer William Rankine in 1850 with the names ''thermodynamic function'' and ''heat-potential''. In 1865, German physicist Rudolf Clausius, one of the leading founders of the field of thermodynamics, defined it as the quotient of an infinitesimal amount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
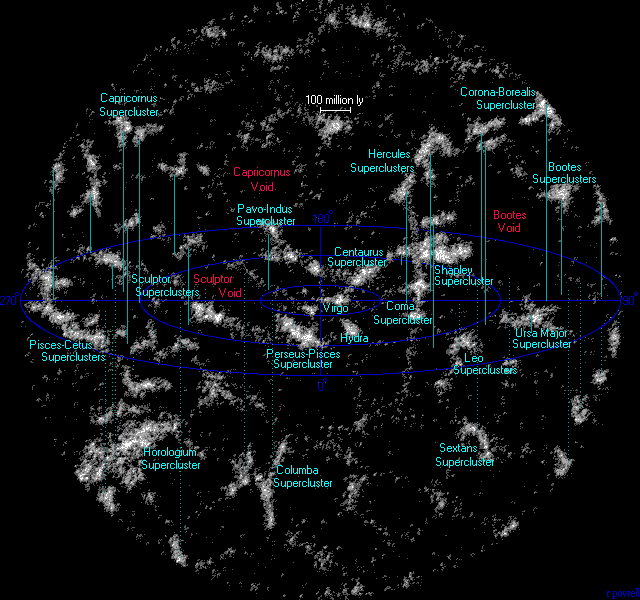
Superclusters Atlasoftheuniverse
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn is part of the Virgo Supercluster, which is part of the Laniakea Supercluster."Earth's new address: 'Solar System, Milky Way, Laniakea ''Nature (journal), Nature'' The large size and low density of superclusters means that they, unlike clusters, expand with the Hubble expansion. The number of superclusters in the observable universe is estimated to be 10 million. Existence [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |