|
Pioneer 2
Pioneer 2 (also known as Able 3) was the last of the three project Able space probes designed to probe lunar and cislunar space. The launch took place at 07:30:21 GMT on 8 November 1958. After Pioneer 1 had failed due to guidance system deficiencies, the guidance system was modified with a Doppler command system to ensure more accurate commands and minimize trajectory errors. Once again, the first and second stage portion of the flight was uneventful, but the third stage of the launch vehicle failed to ignite, making it impossible for Pioneer 2 to achieve orbital velocity. An attempt to fire the vernier engines on the probe was unsuccessful and the spacecraft attained a maximum altitude of before reentering Earth's atmosphere at 28.7° N, 1.9° E over NW Africa. A small amount of data was obtained during the short flight, including evidence that the equatorial region around Earth has higher flux and higher energy radiation than previously considered and that the micrometeorite d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each synodic period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propellant
A propellant (or propellent) is a mass that is expelled or expanded in such a way as to create a thrust or other motive force in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, and "propel" a vehicle, projectile, or fluid payload. In vehicles, the engine that expels the propellant is called a reaction engine. Although technically a propellant is the reaction mass used to create thrust, the term "propellant" is often used to describe a substance which is contains both the reaction mass and the fuel that holds the energy used to accelerate the reaction mass. For example, the term "propellant" is often used in chemical rocket design to describe a combined fuel/propellant, although the propellants should not be confused with the fuel that is used by an engine to produce the energy that expels the propellant. Even though the byproducts of substances used as fuel are also often used as a reaction mass to create the thrust, such as with a chemical rocket engine, propellant and fuel are two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Launched In 1958
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geomagnetic Meridian Planes
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic field is generated by electric currents due to the motion of convection currents of a mixture of molten iron and nickel in Earth's outer core: these convection currents are caused by heat escaping from the core, a natural process called a geodynamo. The magnitude of Earth's magnetic field at its surface ranges from . As an approximation, it is represented by a field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 11° with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were an enormous bar magnet placed at that angle through the center of Earth. The North geomagnetic pole actually represents the South pole of Earth's magnetic field, and conversely the South geomagnetic pole corresponds to the north pole of Earth's magnetic field ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin-stabilized Satellite
Spacecraft attitude control is the process of controlling the orientation of a spacecraft (vehicle/satellite) with respect to an inertial frame of reference or another entity such as the celestial sphere, certain fields, and nearby objects, etc. Controlling vehicle attitude requires sensors to measure vehicle orientation, actuators to apply the torques needed to orient the vehicle to a desired attitude, and algorithms to command the actuators based on (1) sensor measurements of the current attitude and (2) specification of a desired attitude. The integrated field that studies the combination of sensors, actuators and algorithms is called guidance, navigation and control (GNC). Overview A spacecraft's attitude must typically be stabilized and controlled for a variety of reasons. It is often needed so that the spacecraft high-gain antenna may be accurately pointed to Earth for communications, so that onboard experiments may accomplish precise pointing for accurate collection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury Battery
A mercury battery (also called mercuric oxide battery, mercury cell, button cell, or Ruben-Mallory) is a non-rechargeable electrochemical battery, a primary cell. Mercury batteries use a reaction between mercuric oxide and zinc electrodes in an alkaline electrolyte. The voltage during discharge remains practically constant at 1.35 volts, and the capacity is much greater than that of a similarly sized zinc-carbon battery. Mercury batteries were used in the shape of button cells for watches, hearing aids, cameras and calculators, and in larger forms for other applications. For a time during and after World War II, batteries made with mercury became a popular power source for portable electronic devices. Due to the content of toxic mercury and environmental concerns about its disposal, the sale of mercury batteries is now banned in many countries. Both ANSI and IEC have withdrawn their standards for mercury batteries. History The mercury oxide-zinc battery system was kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver-oxide Battery
A silver-oxide battery (IEC code: S) is a primary cell using silver oxide as the cathode material and zinc for the anode. These cells maintain a nearly constant nominal voltage during discharge until fully depleted. They are available in small sizes as button cells, where the amount of silver used is minimal and not a prohibitively expensive contributor to the overall product cost. Silver-oxide primary batteries account for 30% of all primary battery sales in Japan (64 out of 212 million in February 2020). Silver-oxide batteries were used on Apollo program lunar missions for the lunar module and lunar rover power supplies because of their high energy-to-weight ratio.Lyons, Pete; "10 Best Ahead-of-Their-Time Machines", ''Car and Driver'', Jan. 1988, p.78 Chemistry A silver-oxide battery uses silver(I) oxide as the positive electrode (cathode), zinc as the negative electrode (anode), plus an alkaline electrolyte, usually sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, and are created by electric currents such as those used in electromagnets, and by electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function assigning a vector to each point of space, cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, one that measures the direction of an ambient magnetic field, in this case, the Earth's magnetic field. Other magnetometers measure the magnetic dipole moment of a magnetic material such as a ferromagnet, for example by recording the effect of this magnetic dipole on the induced current in a coil. The first magnetometer capable of measuring the absolute magnetic intensity at a point in space was invented by Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1833 and notable developments in the 19th century included the Hall effect, which is still widely used. Magnetometers are widely used for measuring the Earth's magnetic field, in geophysical surveys, to detect magnetic anomalies of various types, and to determine the dipole moment of magnetic materials. In an air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionization Chamber
The ionization chamber is the simplest type of gas-filled radiation detector, and is widely used for the detection and measurement of certain types of ionizing radiation, including X-rays, gamma rays, and beta particles. Conventionally, the term "ionization chamber" refers exclusively to those detectors which collect all the charges created by ''direct ionization'' within the gas through the application of an electric field. It only uses the discrete charges created by each interaction between the incident radiation and the gas. Gaseous ionization detectors include ionization chambers and devices that use gas multiplication, namely the proportional counter and the Geiger counter. Ion chambers have a good uniform response to radiation over a wide range of energies and are the preferred means of measuring high levels of gamma radiation. They are widely used in the nuclear power industry, research labs, radiography, radiobiology, and environmental monitoring. Principle of operation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
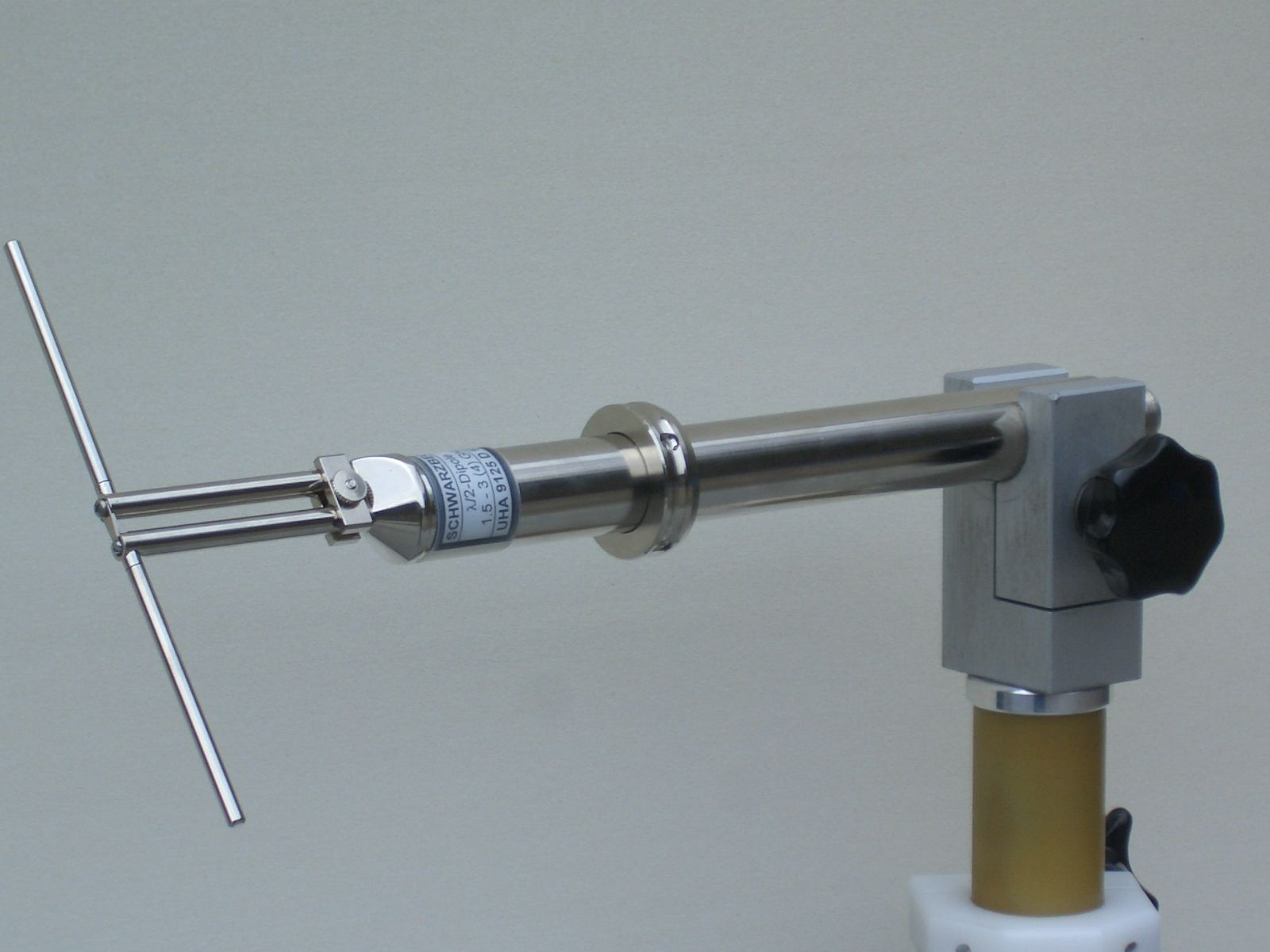
Dipole Antenna
In radio and telecommunications a dipole antenna or doublet is the simplest and most widely used class of antenna. The dipole is any one of a class of antennas producing a radiation pattern approximating that of an elementary electric dipole with a radiating structure supporting a line current so energized that the current has only one node at each end. A dipole antenna commonly consists of two identical conductive elements such as metal wires or rods. The driving current from the transmitter is applied, or for receiving antennas the output signal to the receiver is taken, between the two halves of the antenna. Each side of the feedline to the transmitter or receiver is connected to one of the conductors. This contrasts with a monopole antenna, which consists of a single rod or conductor with one side of the feedline connected to it, and the other side connected to some type of ground. A common example of a dipole is the "rabbit ears" television antenna found on broadcast telev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)