|
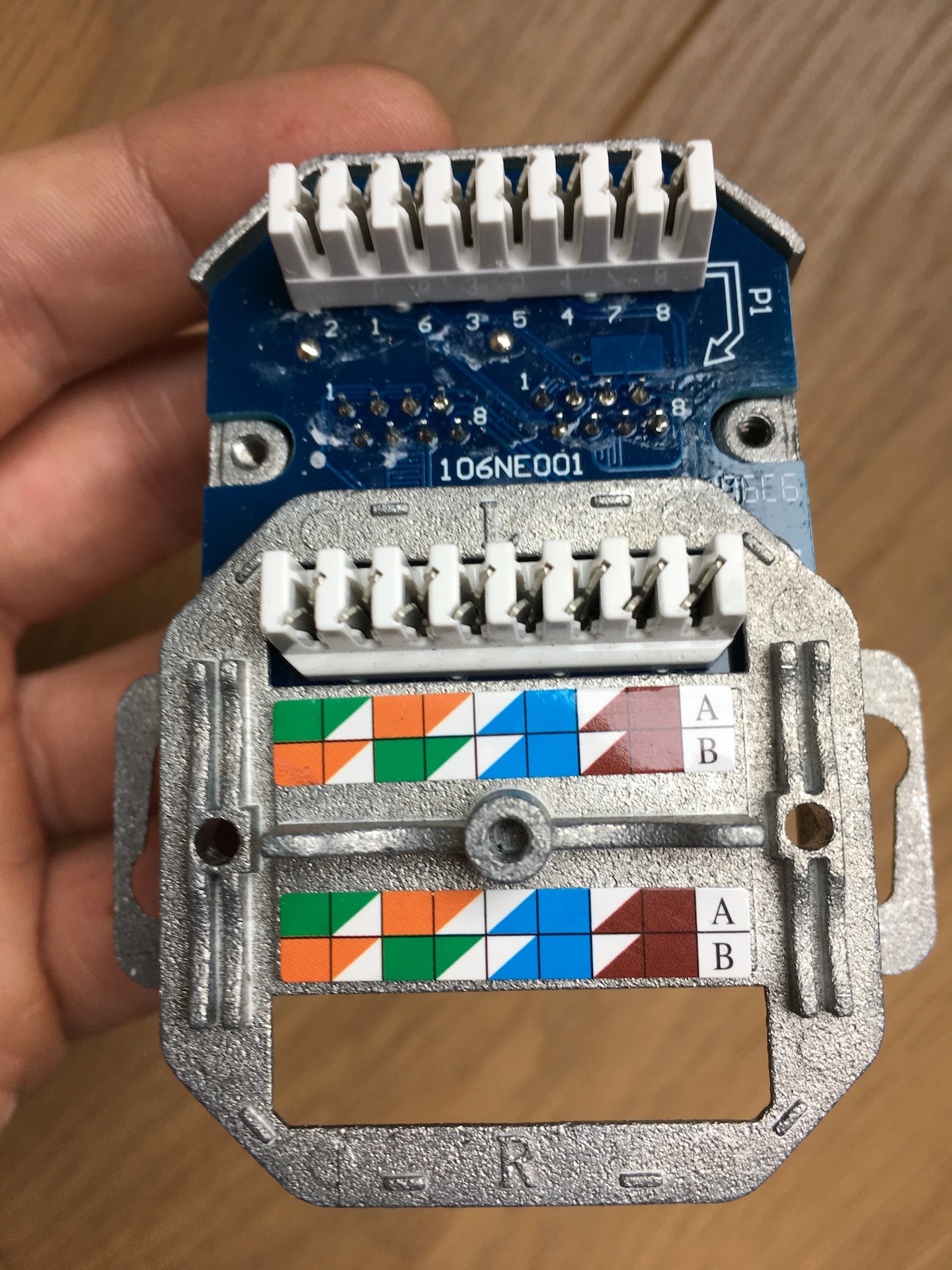
Pinout
In electronics, a pinout (sometimes written "pin-out") is a cross-reference between the contacts, or ''pins'', of an electrical connector or electronic component, and their functions. "Pinout" now supersedes the term "basing diagram" which was the standard terminology used by the manufacturers of vacuum tubes and the Radio Manufacturers Association (RMA). The RMA started its standardization in 1934, collecting and correlating tube data for registration at what was to become the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA), which now has many sectors reporting to it and sets what is known as EIA standards where all registered pinouts and registered jacks can be found. Purpose The functions of contacts in electrical connectors, be they power- or signaling-related, must be specified for connectors to be interchangeable. Each connector contact must mate with the contact on the other connector with the same function. If contacts of disparate functions are allowed to make contact, the connec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANSI/TIA-568
ANSI/TIA-568 is a technical standard for commercial building cabling for telecommunications products and services. The title of the standard is ''Commercial Building Telecommunications Cabling Standard'' and is published by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA), a body accredited by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). , the revision status of the standard is ''ANSI/TIA-568-E'', published 2020, which replaced ANSI/TIA-568-D of 2015, revision C of 2009, revision B of 2001, and revision A of 1995, and the initial issue of 1991, which are now obsolete. Perhaps the best-known features of ANSI/TIA-568 are the pin and pair assignments for eight-conductor 100-ohm balanced twisted pair cabling. These assignments are named ''T568A'' and ''T568B''. History ANSI/TIA-568 was developed through the efforts of more than 60 contributing organizations including manufacturers, end-users, and consultants. Work on the standard began with the Electronic Industries Alliance (EI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USB Type-A Receptacle White
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical interfaces, and communication protocols to and from ''hosts'', such as personal computers, to and from peripheral ''devices'', e.g. displays, keyboards, and mass storage devices, and to and from intermediate ''hubs'', which multiply the number of a host's ports. Introduced in 1996, USB was originally designed to standardize the connection of peripherals to computers, replacing various interfaces such as serial ports, parallel ports, game ports, and Apple Desktop Bus (ADB) ports. Early versions of USB became commonplace on a wide range of devices, such as keyboards, mice, cameras, printers, scanners, flash drives, smartphones, game consoles, and power banks. USB has since evolved into a standard to replace virtually all common ports on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Connectors
Components of an electrical circuit are electrically connected if an electric current can run between them through an electrical conductor. An electrical connector is an electromechanical device used to create an electrical connection between parts of an electrical circuit, or between different electrical circuits, thereby joining them into a larger circuit. The connection may be removable (as for portable equipment), require a tool for assembly and removal, or serve as a permanent electrical joint between two points. An adapter can be used to join dissimilar connectors. Most electrical connectors have a genderi.e. the male component, called a ''plug'', connects to the female component, or ''socket''. Thousands of configurations of connectors are manufactured for power, data, and audiovisual applications. Electrical connectors can be divided into four basic categories, differentiated by their function: * ''inline'' or ''cable'' connectors permanently attached to a cable, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LM741 Pinout Round
An operational amplifier (often op amp or opamp) is a DC-coupled electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input, a (usually) single-ended output, and an extremely high gain. Its name comes from its original use of performing mathematical operations in analog computers. By using negative feedback, an op amp circuit's characteristics (e.g. its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth, and functionality) can be determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or engineering tolerance in the op amp itself. This flexibility has made the op amp a popular building block in analog circuits. Today, op amps are used widely in consumer, industrial, and scientific electronics. Many standard integrated circuit op amps cost only a few cents; however, some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over . Op amps may be packaged as components or used as elements of more complex integrated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossover Cable
A crossover cable connects two devices of the same type, for example Data terminal equipment, DTE-DTE or Data circuit-terminating equipment, DCE-DCE, usually connected asymmetrically (DTE-DCE), by a modified electrical cable, cable called a crosslink. Such a distinction between devices was introduced by IBM. The crossing of wires in a cable or in a connector adaptor allows: * connecting two devices directly, output of one to input of the other, * letting two terminal (DTE) devices communicate without an interconnecting Ethernet hub, hub knot, i.e. Personal computer, PCs, * linking two or more hubs, Network switch, switches or Router (computing), routers (DCE) together, possibly to work as one wider device. In contrast, a straight-through cable uses direct wiring to connect complementary devices, e.g. a PC to a switch. Concept Straight-through cables are used for most applications, but crossover cables are required in others. In a straight-through cable, pins on one end corres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4000 Series
The 4000 series is a CMOS logic family of integrated circuits (ICs) first introduced in 1968 by RCA. It was slowly migrated into the 4000B buffered series after about 1975. It had a much wider supply voltage range than any contemporary logic family (3V to 18V recommended range for "B" series). Almost all IC manufacturers active during this initial era fabricated models for this series. Its naming convention is still in use today. History The 4000 series was introduced as the ''CD4000 COS/MOS'' series in 1968 by RCA as a lower power and more versatile alternative to the 7400 series of transistor-transistor logic (TTL) chips. The logic functions were implemented with the newly introduced Complementary Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor (CMOS) technology. While initially marketed with "COS/MOS" labeling by RCA (which stood for Complementary Symmetry Metal-Oxide Semiconductor), the shorter ''CMOS'' terminology emerged as the industry preference to refer to the technology. The first chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EIA Standards
This is a list of American Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) Standards. The EIA ceased operations on February 11, 2011, but the former sectors continue to serve the constituencies of EIA. EIA designated ECA to continue to develop standards for interconnect, passive and electro-mechanical (IP&E) electronic components under the ANSI-designation of EIA standards. All other electronic components standards are managed by their respective sectors. ECA is expected to merge with the National Electronic Distributors Association (NEDA) to form the Electronic Components Industry Association (ECIA). However, the EIA standards brand will continue for IP&E standards within ECIA. As currently authorized, any ANSI standard designated at ANSI EIA-xxx is developed and/or managed by ECA (and, in the future, ECIA). 1–199 * IS-41, TIA/EIA-41 Cellular Radiocommunications Intersystem Operations. * EIA/TIA/IS-55 Recommended Minimum Performance Standards of 800 MHz Dual Mode Mobile Stations * EIA/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Registered Jack
A registered jack (RJ) is a standardized telecommunication network interface device, network interface for connecting voice and data equipment to a computer service provided by a local exchange carrier or long distance carrier. Registered interfaces were first defined in the ''Universal Service Ordering Code'' (USOC) of the Bell System in the United States for complying with the registration program for customer-supplied telephone equipment mandated by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the 1970s. Subsequently, in 1980 they were codified in title 47 of the Code of Federal Regulations Part 68. Registered jack connections began to see use after their invention in 1973 by Bell Labs. The specification includes physical construction, wiring, and signal semantics. Accordingly, registered jacks are primarily named by the letters ''RJ'', followed by two digits that express the type. Additional letter suffixes indicate minor variations. For example, RJ11, RJ14, and RJ25 are th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Component
An electronic component is any basic discrete electronic device or physical entity part of an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singular form and are not to be confused with electrical elements, which are conceptual abstractions representing idealized electronic components and elements. A datasheet for an electronic component is a technical document that provides detailed information about the component's specifications, characteristics, and performance. Discrete circuits are made of individual electronic components that only perform one function each as packaged, which are known as discrete components, although strictly the term discrete component refers to such a component with semiconductor material such as individual transistors. Electronic components have a number of electrical terminals or leads. These leads connect to other electrical components, often over wire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
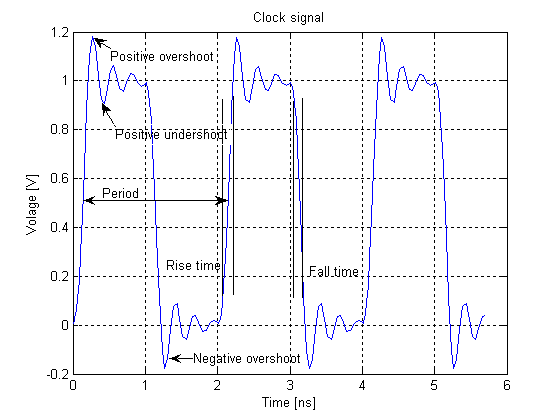
Clock Signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and is used like a metronome to synchronize actions of digital circuits. In a synchronous logic circuit, the most common type of digital circuit, the clock signal is applied to all storage devices, flip-flops and latches, and causes them all to change state simultaneously, preventing race conditions. A clock signal is produced by an electronic oscillator called a clock generator. The most common clock signal is in the form of a square wave with a 50% duty cycle. Circuits using the clock signal for synchronization may become active at either the rising edge, falling edge, or, in the case of double data rate, both in the rising and in the falling edges of the clock cycle. Digital circuits Most integrated circuits (ICs) of suffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schematic
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a designed representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the key information the schematic is intended to convey, and may include oversimplified elements in order to make this essential meaning easier to grasp, as well as additional organization of the information. For example, a subway map intended for passengers may represent a subway station with a dot. The dot is not intended to resemble the actual station at all but aims to give the viewer information without unnecessary visual clutter. A schematic diagram of a chemical process uses symbols in place of detailed representations of the vessels, piping, valves, pumps, and other equipment that compose the system, thus emphasizing the functions of the individual elements and the interconnections among them and suppresses their physical details. In an electronic circuit d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |