|
Pine-oak Gall Rust
''Cronartium quercuum'', also known as pine-oak gall rust is a fungal disease of pine (''Pinus'' spp.) and oak (''Quercus'' spp.) trees. Similar to pine-pine gall rust, this disease is found on pine trees but its second host is an oak tree rather than another pine. Hosts and symptoms The pathogen requires pine and oak trees to complete its life cycle. Aecial hosts in North America are two- and three-needled ''Pinus'' spieces. ''Pinus'' hosts include Austrian ('' P. nigra''), Jack pine ('' P. banksiana''), Mugo pine ('' P. mugo''), Red pine ('' P. resinosa''), Ponderosa pine ('' P. ponderosa''), and Scots pine ('' P. sylvestris''). Telial hosts are ''Quercus'' species. ''Quercus'' hosts are generally made up of the red oak group and include Northern pin oak ('' Q. ellipsoidalis''), Bur oak ('' Q. macrocarpa''), Pin oak ('' Q. palustris''), and Northern red oak (''Q. rubra''). Galls start to form as slight, rounded swelling on the tree stem, then grow to become spherical and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family (biology), family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden accepts 187 species names of pines as current, together with more synonyms. The American Conifer Society (ACS) and the Royal Horticultural Society accept 121 species. Pines are commonly found in the Northern Hemisphere. ''Pine'' may also refer to the lumber derived from pine trees; it is one of the more extensively used types of lumber. The pine family is the largest conifer family and there are currently 818 named cultivars (or Trinomial nomenclature, trinomials) recognized by the ACS. Description Pine trees are evergreen, coniferous resinous trees (or, rarely, shrubs) growing tall, with the majority of species reaching tall. The smallest are Siberian dwarf pine and Potosi pinyon, and the tallest is an tall ponderosa pine lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quercus Rubra
''Quercus rubra'', the northern red oak, is an oak tree in the red oak group (''Quercus'' section ''Lobatae''). It is a native of North America, in the eastern and central United States and southeast and south-central Canada. It has been introduced to small areas in Western Europe, where it can frequently be seen cultivated in gardens and parks. It prefers good soil that is slightly acidic. Often simply called red oak, northern red oak is so named to distinguish it from southern red oak (''Q. falcata''), also known as the Spanish oak. Northern Red Oak is sometimes called champion oak. Description In many forests, this deciduous tree grows straight and tall, to , exceptionally to tall, with a trunk of up to in diameter. Open-grown trees do not get as tall, but can develop a stouter trunk, up to in diameter. It has stout branches growing at right angles to the stem, forming a narrow round-topped head. Under optimal conditions and full sun, northern red oak is fast growin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
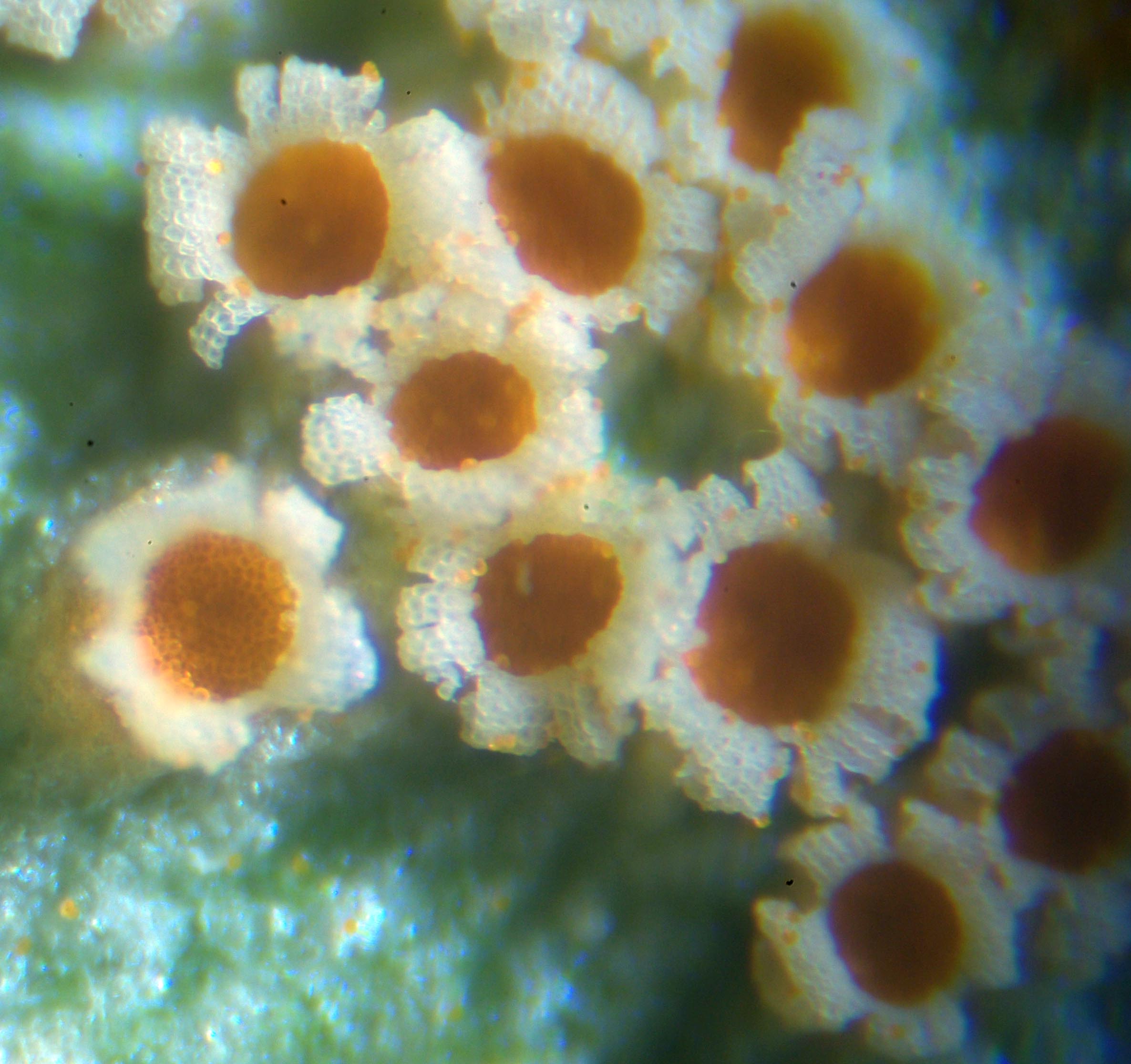
Basidiospore
A basidiospore is a reproductive spore produced by Basidiomycete fungi, a grouping that includes mushrooms, shelf fungi, rusts, and smuts. Basidiospores typically each contain one haploid nucleus that is the product of meiosis, and they are produced by specialized fungal cells called basidia. Typically, four basidiospores develop on appendages from each basidium, of which two are of one strain and the other two of its opposite strain. In gills under a cap of one common species, there exist millions of basidia. Some gilled mushrooms in the order Agaricales have the ability to release billions of spores. The puffball fungus '' Calvatia gigantea'' has been calculated to produce about five trillion basidiospores. Most basidiospores are forcibly discharged, and are thus considered ballistospores. These spores serve as the main air dispersal units for the fungi. The spores are released during periods of high humidity and generally have a night-time or pre-dawn peak concentration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teliospore
Teliospore (sometimes called teleutospore) is the thick-walled resting spore of some fungi (rusts and smuts), from which the basidium arises. Development They develop in '' telia'' (sing. ''telium'' or ''teliosorus''). The telial host is the primary host in heteroecious rusts. The aecial host is the alternate host (look for pycnia and aecia). These terms apply when two hosts are required by a heteroecious rust fungus to complete its life cycle. Morphology Teliospores consist of one, two or more dikaryote cells. Teliospores are often dark-coloured and thick-walled, especially in species where they overwinter (acting as chlamydospores). Two-celled teliospores formerly defined the genus ''Puccinia''. Here the wall is particularly thick at the tip of the terminal cell which extends into a beak in some species. Teliospores consist of dikaryote cells. As the teliospore cells germinate, the nuclei undergo karyogamy and thereafter meiosis, giving rise to a four-celled basidium wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telium
Telium, plural telia, are structures produced by rust fungi as part of the reproductive cycle. They are typically yellow or orange drying to brown or black and are exclusively a mechanism for the release of teliospores which are released by wind or water to infect the alternate host in the rust life-cycle. The telial stage provides an overwintering strategy in the life cycle of a parasitic heteroecious fungus by producing teliospores; this occurs on cedar trees. A primary aecial stage is spent parasitizing a separate host plant which is a precursor in the life cycle of heteroecious fungi. Teliospores are released from the telia in the spring. The spores can spread many kilometers through the air, however most are spread near the host plant. Host plants There are a number of plants that can be infected by the telial stage. Therefore, the telial stage is considered a pathogen to those plants. A few specific plant pathogenic species are listed here with their hosts. # ''Puccinia gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeciospore
Aeciospores are one of several different types of spores formed by Rusts. They each have two nuclei and are typically seen in chain-like formations in the aecium An aecium (plural aecia) is a specialised reproductive structure found in some plant pathogenic rust Rust is an iron oxide, a usually reddish-brown oxide formed by the reaction of iron and oxygen in the catalytic presence of water or air mo .... References Fungal morphology and anatomy {{mycology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aecium
An aecium (plural aecia) is a specialised reproductive structure found in some plant pathogenic rust Rust is an iron oxide, a usually reddish-brown oxide formed by the reaction of iron and oxygen in the catalytic presence of water or air moisture. Rust consists of hydrous iron(III) oxides (Fe2O3·nH2O) and iron(III) oxide-hydroxide (FeO(OH), ... fungi that produce aeciospores. Aecia may also be referred to as "cluster cups". The term aecidium (plural aecidia) is used interchangeably but is not preferred. In some rust fungi such as '' Phragmidium'', aecia lack an outer wall structure (a peridium) but instead produce a diffuse aecium called a caeoma.''Fungi''. Lilian E Hawker, 1966, Hutchinson University Library In some species of rust fungi with a life cycle including two different host plants, the binucleate spores produced in the aecia cannot infect the current plant host, but must infect a different plant species. References Fungal morphology and anatomy Repro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pycnia
Pycniospores are a type of spore in fungi. They are produced in special cup-like structures called pycnia or pynidia. Almost all fungi reproduce asexually with the production of spores. Spores may be colorless, green, yellow, orange, red, brown or black. Other types of spore ;Sporangiospores Sporangiospores (spore:spore, angion:sac) are spores formed inside the sporangium which is a spore sac. ;Conidia Conidia (singular: conidium) are spores produced at the tip of special branches called conidiophores. ;Oidia Oidia (singular: oidium). In several fungi, the hyphae is often divided into a large number of short pieces by transverse walls. Each piece is able to germinate into a new body. These pieces are called oidia (small egg). ;Chlamydospores Chlamydospore A chlamydospore is the thick-walled large resting spore of several kinds of fungi, including Ascomycota such as '' Candida'', Basidiomycota such as '' Panus'', and various Mortierellales species. It is the life-stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypha
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium. Structure A hypha consists of one or more cells surrounded by a tubular cell wall. In most fungi, hyphae are divided into cells by internal cross-walls called "septa" (singular septum). Septa are usually perforated by pores large enough for ribosomes, mitochondria, and sometimes nuclei to flow between cells. The major structural polymer in fungal cell walls is typically chitin, in contrast to plants and oomycetes that have cellulosic cell walls. Some fungi have aseptate hyphae, meaning their hyphae are not partitioned by septa. Hyphae have an average diameter of 4–6 µm. Growth Hyphae grow at their tips. During tip growth, cell walls are extended by the external assembly and polymerization of cell wall components, and the internal production of new cell membran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gall
Galls (from the Latin , 'oak-apple') or ''cecidia'' (from the Greek , anything gushing out) are a kind of swelling growth on the external Tissue (biology), tissues of plants, fungi, or animals. Plant galls are abnormal outgrowths of plant tissues, similar to benign tumors or warts in animals. They can be caused by various parasites, from viruses, fungi and bacteria, to other plants, insects and mites. Plant galls are often highly organized structures so that the cause of the gall can often be determined without the actual agent being identified. This applies particularly to some insect and mite plant galls. The study of plant galls is known as cecidology. In human pathology, a gall is a raised sore on the skin, usually caused by chafing or rubbing. Causes of plant galls Insects and mites Insect galls are the highly distinctive plant structures formed by some Herbivore, herbivorous insects as their own microhabitats. They are plant tissue which is controlled by the insect. Gal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quercus Palustris
''Quercus palustris'', the pin oak or swamp Spanish oak, is a tree in the red oak section (''Quercus'' sect. ''Lobatae'') of the genus ''Quercus''. Pin oak is one of the most commonly used landscaping oaks in its native range due to its ease of transplant, relatively fast growth, and pollution tolerance. Description Pin oak is a medium-sized deciduous tree growing to tall, with a trunk up to in diameter. It has an spread. A 10-year-old tree grown in full sun will be about tall. Young trees have a straight, columnar trunk with smooth bark and a pyramidal canopy. By the time the tree is 40 years old, it develops more rough bark with a loose, spreading canopy. This canopy is considered one of the most distinctive features of the pin oak: the upper branches point upwards, the middle branches are at right angles to the trunk, and the lower branches droop downwards. The leaves are long and broad, lobed, with five or seven lobes. Each lobe has five to seven bristle-tipped tee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pine-pine Gall Rust
Pine-pine gall rust, also known as western gall rust, is a fungal disease of pine trees. It is caused by ''Endocronartium harknessii'' (asexual name is ''Peridermium harknessii''), an autoecious, endocyclic, rust fungus that grows in the vascular cambium of the host. The disease is found on pine trees (''Pinus'' spp.) with two or three needles, such as ponderosa pine, jack pine and scots pine.Peterson, Roger S. "Western Gall Rust on Hard Pines." U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service (1960): n. pag. Web. It is very similar to pine-oak gall rust, but its second host is another ''Pinus'' species. The fungal infection results in gall formation on branches or trunks of infected hosts. Gall formation is typically not detrimental to old trees, but has been known to kill younger, less stable saplings. Galls can vary from small growths on branch extremities to grapefruit-sized galls on trunks. Hosts and symptoms The hosts of the aecial stage of the fungus includes two and three ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(27)_(17008356190).jpg)