|
Pierre-Mathurin Gillet
Pierre-Mathurin Gillet (sometimes referred to as 'René Mathurin Gillet') (28 June 1762, Lanrelas, near Broons - 4 November 1795, Paris) was a French politician. Before the French Revolution he was a lawyer at Rochefort-en-Terre. In 1790 the young Gillet was sent by the electors of Rochefort to the assembly of Pontivy and in May of the same year he was elected to a position in the administration of the newly-created département of Morbihan. On 5 September 1791 Gillet was elected as an alternate deputy to the National Legislative Assembly but he was never called on to take a seat. Seven days later he was appointed procureur-général-syndic of Morbihan, making him, at 25, the highest-ranking local political figure. On 9 September 1792 he was elected to the National Convention, coming sixth out of eight deputies elected. At just over 26 he was one of the youngest Convention members. He generally followed a moderate line, sitting with the Plain while having a number of Girondin a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanrelas
Lanrelas (; ) is a commune in the Côtes-d'Armor department of Brittany in northwestern France. Population Inhabitants of Lanrelas are called ''lanrelasiens'' in French. See also *Communes of the Côtes-d'Armor department Notable people *Pierre-Mathurin Gillet Pierre-Mathurin Gillet (sometimes referred to as 'René Mathurin Gillet') (28 June 1762, Lanrelas, near Broons - 4 November 1795, Paris) was a French politician. Before the French Revolution he was a lawyer at Rochefort-en-Terre. In 1790 the youn ... (1762-1795), revolutionary politician References External links Official website Communes of Côtes-d'Armor {{CôtesArmor-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War In The Vendée
The war in the Vendée (french: link=no, Guerre de Vendée) was a counter-revolution from 1793 to 1796 in the Vendée region of France during the French Revolution. The Vendée is a coastal region, located immediately south of the river Loire in Western France. Initially, the revolt was similar to the 14th-century Jacquerie peasant uprising, but the Vendée quickly became counter-revolutionary and Royalist. The revolt headed by the newly-formed Catholic and Royal Army was comparable to the Chouannerie, which took place in the area north of the Loire. While elsewhere in France the revolts against the were repressed, an insurgent territory, called the by historians, formed south of the Loire-Inférieure (Brittany), south-west of Maine-et-Loire (Anjou), north of Vendée and north-west of Deux-Sèvres ( Poitou). Gradually referred to as the "Vendeans", the insurgents established in April a " Catholic and Royal Army" which won a succession of victories in the spring and summ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1795 Deaths
Events January–June * January – Central England records its coldest ever month, in the CET records dating back to 1659. * January 14 – The University of North Carolina opens to students at Chapel Hill, becoming the first state university in the United States. * January 16 – War of the First Coalition: Flanders campaign: The French occupy Utrecht, Netherlands. * January 18 – Batavian Revolution in Amsterdam: William V, Prince of Orange, Stadtholder of the Dutch Republic (Republic of the Seven United Netherlands), flees the country. * January 19 – The Batavian Republic is proclaimed in Amsterdam, ending the Dutch Republic (Republic of the Seven United Netherlands). * January 20 – French troops enter Amsterdam. * January 23 – Flanders campaign: Capture of the Dutch fleet at Den Helder: The Dutch fleet, frozen in Zuiderzee, is captured by the French 8th Hussars. * February 7 – The Eleventh Amendment to the United S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1761 Births
Events January–March * January 14 – Third Battle of Panipat: Ahmad Shah Durrani and his coalition decisively defeat the Maratha Confederacy, and restore the Mughal Empire to Shah Alam II. * January 16 – Siege of Pondicherry (1760) ended: The British capture Pondichéry, India from the French. * February 8 – An earthquake in London breaks chimneys in Limehouse and Poplar. * March 8 – A second earthquake occurs in North London, Hampstead and Highgate. * March 31 – 1761 Portugal earthquake: A magnitude 8.5 earthquake strikes Lisbon, Portugal, with effects felt as far north as Scotland. April–June * April 1 – The Austrian Empire and the Russian Empire sign a new treaty of alliance. * April 4 – A severe epidemic of influenza breaks out in London and "practically the entire population of the city" is afflicted; particularly contagious to pregnant women, the disease causes an unusual number of miscarriages and prema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Five Hundred
The Council of Five Hundred (''Conseil des Cinq-Cents''), or simply the Five Hundred, was the lower house of the legislature of France under the Constitution of the Year III. It existed during the period commonly known (from the name of the executive branch during this time) as the Directory (''Directoire''), from 26 October 1795 until 9 November 1799: roughly the second half of the period generally referred to as the French Revolution. Role and function The Council of Five Hundred was established under the Constitution of Year III which was adopted by a referendum on 24 September 1795,Chronicle of the French Revolutions, Longman 1989 p.495 and constituted after the first elections which were held from 12–21 October 1795. Voting rights were restricted to citizens owning property bringing in income equal to 150 days of work. Each member elected had to be at least 30 years old, meet residency qualifications and pay taxes. To prevent them coming under the pressure of the san ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolt Of 1 Prairial Year III
The insurrection of 1 Prairial Year III was a popular revolt in Paris on 20 May 1795 against the policies of the Thermidorian Convention. It was the last and one of the most remarkable and stubborn popular revolts of the French Revolution. After their defeat in Prairial, the ''sans-culottes'' ceased to play any effective part until the next round of revolutions in the early nineteenth century. To a lesser extent, these movements are also important in that they mark the final attempt of the remnants of the Mountain and the Jacobins to recapture their political ascendancy in the Convention and the Paris Sections; this time, though they gave some political direction to the popular movement which arose in the first place in protest against worsening economic conditions, their intervention was timorous and halfhearted and doomed the movement to failure. Causes The abandonment of the controlled economy provoked a frightful economic catastrophe. Prices soared and the rate of exchange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Committee Of Public Safety
The Committee of Public Safety (french: link=no, Comité de salut public) was a committee of the National Convention which formed the provisional government and war cabinet during the Reign of Terror, a violent phase of the French Revolution. Supplementing the Committee of General Defence created after the execution of King Louis XVI in January 1793, the Committee of Public Safety was created in April 1793 by the National Convention. It was charged with protecting the new republic against its foreign and domestic enemies, fighting the First Coalition and the Vendée revolt. As a wartime measure, the committee was given broad supervisory and administrative powers over the armed forces, judiciary and legislature, as well as the executive bodies and ministers of the Convention. As the committee, restructured in July, raised the defense ('' levée en masse'') against the monarchist coalition of European nations and counter-revolutionary forces within France, it became more and more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermidorian Reaction
The Thermidorian Reaction (french: Réaction thermidorienne or ''Convention thermidorienne'', "Thermidorian Convention") is the common term, in the historiography of the French Revolution, for the period between the ousting of Maximilien Robespierre on 9 Thermidor II, or 27 July 1794, and the inauguration of the French Directory on 2 November 1795. The "Thermidorian Reaction" was named after Thermidor, the month in which the coup took place and was the latter part of the National Convention's rule of France. It was marked by the end of the Reign of Terror, decentralization of executive powers from the Committee of Public Safety and a turn from the radical Jacobin policies of the The Mountain, Montagnard Convention to more conservative positions. Economic and general populism, dechristianization, and harsh wartime measures were largely abandoned, as the members of the convention, disillusioned and frightened of the centralized government of the Terror, preferred a more stable polit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Fleurus (1794)
The Battle of Fleurus, on 26 June 1794, was an engagement during the War of the First Coalition, between the army of the First French Republic, under General Jean-Baptiste Jourdan, and the Coalition Army (Britain, Hanover, Dutch Republic, and Habsburg monarchy), commanded by Prince Josias of Coburg, in the most significant battle of the Flanders Campaign in the Low Countries during the French Revolutionary Wars. Both sides had forces in the area of around 80,000 men but the French were able to concentrate their troops and defeat the First Coalition. The Allied defeat led to the permanent loss of the Austrian Netherlands and to the destruction of the Dutch Republic. The battle marked a turning point for the French army, which remained ascendant for the rest of the War of the First Coalition. Background In May 1794, Jean-Baptiste Jourdan was given the command of approximately 96,000 men created by combining the Army of the Ardennes with portions of the Army of the North and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Hainaut
The County of Hainaut (french: Comté de Hainaut; nl, Graafschap Henegouwen; la, comitatus hanoniensis), sometimes spelled Hainault, was a territorial lordship within the medieval Holy Roman Empire that straddled what is now the border of Belgium and France. Its most important towns included Mons ( nl, Bergen), now in Belgium, and Valenciennes, now in France. The core of the county was named after the river Haine. It stretched southeast to include the ''Avesnois'' region and southwest to the Selle (Scheldt tributary). In the Middle Ages, it also gained control of part of the original ''pagus'' of Brabant to its north and the ''pagus'' of Oosterbant to the east, but they were not part of the old ''pagus'' of Hainaut. In modern terms, the original core of Hainaut consisted of the central part of the Belgian province of Hainaut, and the eastern part of the French ''département'' of Nord (the arrondissements of Avesnes-sur-Helpe and Valenciennes). Hainaut already appeared in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
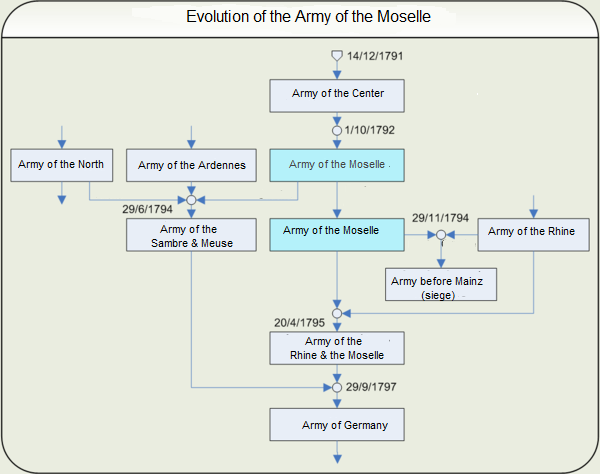
Army Of The Moselle
The Army of the Moselle (''Armée de la Moselle'') was a French Revolutionary Army from 1791 through 1795. It was first known as the ''Army of the Centre'' and it fought at Valmy. In October 1792 it was renamed and subsequently fought at Trier, First Arlon, Biesingen, Kaiserslautern, Froeschwiller and Second Wissembourg. In the spring of 1794 the left wing was detached and fought at Second Arlon, Lambusart and Fleurus before being absorbed by the ''Army of Sambre-et-Meuse''. In late 1794, the army captured Trier and initiated the Siege of Luxembourg. During the siege, the army was discontinued and its divisions were assigned to other armies. History Originally known as the ''Army of the Centre'', it was renamed by decree of the National Convention on 1 October 1792 and kept under that name in the decrees of 1 March and 30 April 1793. By the decree of 29 June 1794 its left wing joined with the ''Army of the Ardennes'' and the right wing of the ''Army of the North'' to form the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Carrier
Jean-Baptiste Carrier (, 16 March 1756 – 16 December 1794) was a French Revolutionary and politician most notable for his actions in the War in the Vendée during the Reign of Terror. While under orders to suppress a Royalist counter-revolution, he commanded the execution of 4,000 civilians, mainly priests, women and children in Nantes, some by drowning in the river Loire, which Carrier described as "the National Bathtub." After the fall of the Robespierre government, Carrier was tried for war crimes by the Revolutionary Tribunal, found guilty, and executed. Early life Carrier was born at Yolet, a village near Aurillac in upper Auvergne, as the fourth of six children born to Jean Carrier and Marguerite Puex. As the son of a middle class tenant farmer, Carrier and his family survived on income reaped from cultivating the land of a French nobleman. After attending a Jesuit school in Aurillac, he was able to pursue a wide variety of career interests. Carrier worked in a law off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |