|
Pi Meson
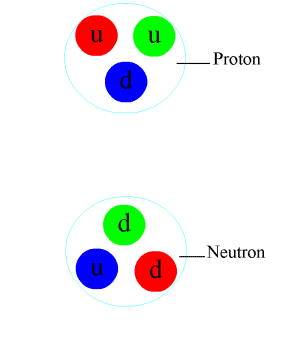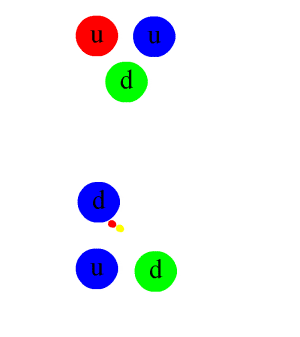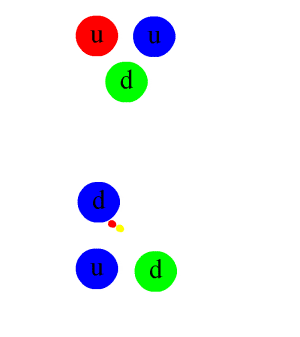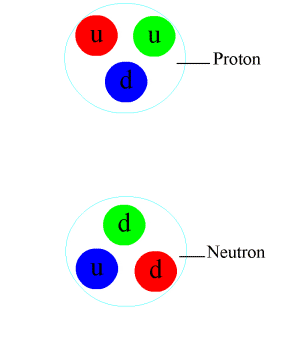
In particle physics, a pion (or a pi meson, denoted with the Greek letter pi: ) is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more generally, the lightest hadrons. They are unstable, with the charged pions and decaying after a mean lifetime of 26.033 nanoseconds ( seconds), and the neutral pion decaying after a much shorter lifetime of 85 attoseconds ( seconds). Charged pions most often decay into muons and muon neutrinos, while neutral pions generally decay into gamma rays. The exchange of virtual pions, along with vector, rho and omega mesons, provides an explanation for the residual strong force between nucleons. Pions are not produced in radioactive decay, but commonly are in high-energy collisions between hadrons. Pions also result from some matter–antimatter annihilation events. All types of pions are also produced in natural processes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boson
In particle physics, a boson ( ) is a subatomic particle whose spin quantum number has an integer value (0,1,2 ...). Bosons form one of the two fundamental classes of subatomic particle, the other being fermions, which have odd half-integer spin (,, ...). Every observed subatomic particle is either a boson or a fermion. Bosons are named after physicist Satyendra Nath Bose. Some bosons are elementary particles and occupy a special role in particle physics unlike that of fermions, which are sometimes described as the constituents of "ordinary matter". Some elementary bosons (for example, gluons) act as force carriers, which give rise to forces between other particles, while one (the Higgs boson) gives rise to the phenomenon of mass. Other bosons, such as mesons, are composite particles made up of smaller constituents. Outside the realm of particle physics, superfluidity arises because composite bosons (bose particles), such as low temperature helium-4 atoms, follow Bose� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiquark
A quark () is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. All commonly observable matter is composed of up quarks, down quarks and electrons. Owing to a phenomenon known as '' color confinement'', quarks are never found in isolation; they can be found only within hadrons, which include baryons (such as protons and neutrons) and mesons, or in quark–gluon plasmas. There is also the theoretical possibility of more exotic phases of quark matter. For this reason, much of what is known about quarks has been drawn from observations of hadrons. Quarks have various intrinsic properties, including electric charge, mass, color charge, and spin. They are the only elementary particles in the Standard Model of particle physics to experience all four fundamental interactions, also known as ''fundamental forces' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omega Meson
The omega meson () is a flavourless meson formed from a superposition of an up quark–antiquark and a down quark–antiquark pair. It is part of the vector meson nonet and mediates the nuclear force along with pions and rho mesons. Properties The most common decay mode for the ω meson is at 89.2±0.7%, followed by at 8.34±0.26%. The quark composition of the meson can be thought of as a mix between , and states, but it is very nearly a pure symmetric - state. This can be shown by deconstructing the wave function A wave function in quantum physics is a mathematical description of the quantum state of an isolated quantum system. The wave function is a complex-valued probability amplitude, and the probabilities for the possible results of measurements m ... of the into its component parts. We see that the and mesons are mixtures of the SU(3) wave functions as follows. : \omega = \psi_8 \sin\theta + \psi_1 \cos\theta, : \phi = \psi_8 \cos\theta - \psi_1 \s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rho Meson
Rho (uppercase Ρ, lowercase ρ or ; el, ρο or el, ρω, label=none) is the 17th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 100. It is derived from Phoenician letter res . Its uppercase form uses the same glyph, Ρ, as the distinct Latin letter P; the two letters have different Unicode encodings. Uses Greek Rho is classed as a liquid consonant (together with Lambda and sometimes the nasals Mu and Nu), which has important implications for morphology. In both Ancient and Modern Greek, it represents a alveolar trill , alveolar tap , or alveolar approximant . In polytonic orthography, a rho at the beginning of a word is written with a rough breathing, equivalent to ''h'' ( ''rh''), and a double rho within a word is written with a smooth breathing over the first rho and a rough breathing over the second ( ''rrh''). That apparently reflected an aspirated or voiceless pronunciation in Ancient Greek, which led to the various Greek- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Meson
In high energy physics, a vector meson is a meson with total spin 1 and odd parity (usually noted as ). Vector mesons have been seen in experiments since the 1960s, and are well known for their spectroscopic pattern of masses. The vector mesons contrast with the pseudovector mesons, which also have a total spin 1 but instead have even parity. The vector and pseudovector mesons are also dissimilar in that the spectroscopy of vector mesons tends to show nearly pure states of constituent quark flavors, whereas pseudovector mesons and scalar mesons tend to be expressed as composites of mixed states. Uniquely pure flavor states Since the development of the quark model by Murray Gell-Mann (and also independently by George Zweig), the vector mesons have demonstrated the spectroscopy of pure states. The fact that the rho meson (ρ) and omega meson (ω) have nearly equal mass centered on 770–, while the phi meson (φ) has a higher mass around , indicates that the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Particle
A virtual particle is a theoretical transient particle that exhibits some of the characteristics of an ordinary particle, while having its existence limited by the uncertainty principle. The concept of virtual particles arises in the perturbation theory of quantum field theory where interactions between ordinary particles are described in terms of exchanges of virtual particles. A process involving virtual particles can be described by a schematic representation known as a Feynman diagram, in which virtual particles are represented by internal lines. Virtual particles do not necessarily carry the same mass as the corresponding real particle, although they always conserve energy and momentum. The closer its characteristics come to those of ordinary particles, the longer the virtual particle exists. They are important in the physics of many processes, including particle scattering and Casimir forces. In quantum field theory, forces—such as the electromagnetic repulsion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically shorter than those of X-rays. With frequency, frequencies above 30 exahertz (), it imparts the highest photon energy. Paul Ulrich Villard, Paul Villard, a French chemist and physicist, discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation emitted by radium. In 1903, Ernest Rutherford named this radiation ''gamma rays'' based on their relatively strong penetration of matter; in 1900 he had already named two less penetrating types of decay radiation (discovered by Henri Becquerel) alpha particle, alpha rays and beta particle, beta rays in ascending order of penetrating power. Gamma rays from radioactive decay are in the energy range from a few kiloelectronvolts (keV) to approximately 8 megaelectronvolts (MeV), corres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muon Neutrino
The muon neutrino is an elementary particle which has the symbol () and zero electric charge. Together with the muon it forms the second generation of leptons, hence the name muon neutrino. It was discovered in 1962 by Leon Lederman, Melvin Schwartz and Jack Steinberger. The discovery was rewarded with the 1988 Nobel Prize in Physics. Discovery The muon neutrino or "neutretto" was hypothesized to exist by a number of physicists in the 1940s. The first paper on it may be Shoichi Sakata and Takesi Inoue's two-meson theory of 1942, which also involved two neutrinos. In 1962 Leon M. Lederman, Melvin Schwartz and Jack Steinberger proved the existence of the muon neutrino in an experiment at the Brookhaven National Laboratory. This earned them the 1988 Nobel Prize. Speed In September 2011 OPERA researchers reported that muon neutrinos were apparently traveling at faster than light speed. This result was confirmed again in a second experiment in November 2011. These resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muon
A muon ( ; from the Greek letter mu (μ) used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with an electric charge of −1 '' e'' and a spin of , but with a much greater mass. It is classified as a lepton. As with other leptons, the muon is not thought to be composed of any simpler particles; that is, it is a fundamental particle. The muon is an unstable subatomic particle with a mean lifetime of , much longer than many other subatomic particles. As with the decay of the non-elementary neutron (with a lifetime around 15 minutes), muon decay is slow (by subatomic standards) because the decay is mediated only by the weak interaction (rather than the more powerful strong interaction or electromagnetic interaction), and because the mass difference between the muon and the set of its decay products is small, providing few kinetic degrees of freedom for decay. Muon decay almost always produces at least three particles, which must include an electron o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Decay
In particle physics, particle decay is the spontaneous process of one unstable subatomic particle transforming into multiple other particles. The particles created in this process (the ''final state'') must each be less massive than the original, although the total invariant mass of the system must be conserved. A particle is unstable if there is at least one allowed final state that it can decay into. Unstable particles will often have multiple ways of decaying, each with its own associated probability. Decays are mediated by one or several fundamental forces. The particles in the final state may themselves be unstable and subject to further decay. The term is typically distinct from radioactive decay, in which an unstable atomic nucleus is transformed into a lighter nucleus accompanied by the emission of particles or radiation, although the two are conceptually similar and are often described using the same terminology. Probability of survival and particle lifetime Particle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attosecond
An attosecond (symbol as) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to 1×10−18 of a second (one quintillionth of a second). For comparison, an attosecond is to a second what a second is to about 31.71 billion years.Electron Motion Filmed 28 February 2008 The word "attosecond" is formed by the ''atto'' and the ''second''. ''Atto-'' was derived from the Danish word for eighteen (''atten''). Its symbol is as. An attosecond is equal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanosecond
A nanosecond (ns) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one billionth of a second, that is, of a second, or 10 seconds. The term combines the SI prefix ''nano-'' indicating a 1 billionth submultiple of an SI unit (e.g. nanogram, nanometre, etc.) and ''second'', the primary unit of time in the SI. A nanosecond is equal to 1000 picoseconds or microsecond. Time units ranging between 10 and 10 seconds are typically expressed as tens or hundreds of nanoseconds. Time units of this granularity are commonly found in telecommunications, pulsed lasers, and related aspects of electronics. Common measurements * 0.001 nanoseconds – one picosecond * 0.5 nanoseconds – the half-life of beryllium-13. * 0.96 nanoseconds – 100 Gigabit Ethernet Interpacket gap * 1.0 nanosecond – cycle time of an electromagnetic wave with a frequency of 1 GHz (1 hertz). * 1.0 nanosecond – electromagnetic wavelength of 1 light-nanosecond. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |