|
Physics Of Whistles
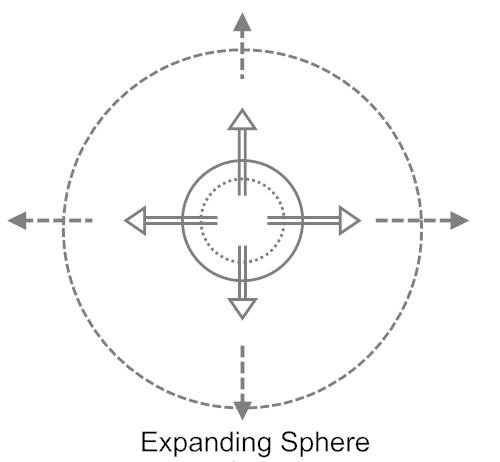
A whistle is a device that makes sound from forced air. The physical theory of the sound-making process is an example of the application of fluid dynamics or hydrodynamics. By understanding the geometry, dimensions, and fluid properties of the whistle, one can predict its properties and find hydrostatic equilibrium. The principles relevant to whistle operation also have applications in other areas, such as fluid flow measurement. Types Wilson, et al., in their study of human whistling (see below), pointed out the importance of including the symmetry or asymmetry of the unstable flow in addition to the feedback classes listed below. Because of the close relationship of flow symmetry to the sound field generated, their concept was included here as part of the sound source description (monopolesymmetric and dipoleasymmetric). Monopole Whistles that generate sound through fluctuations of mass flow across a boundary are called monopole-like sources. The figure on the right is an exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whistle
A whistle is an instrument which produces sound from a stream of gas, most commonly air. It may be mouth-operated, or powered by air pressure, steam, or other means. Whistles vary in size from a small slide whistle or nose flute type to a large multi-piped church organ. Whistles have been around since early humans first carved out a gourd or branch and found they could make sound with it. In prehistoric Egypt, small shells were used as whistles. Many present day wind instruments are inheritors of these early whistles. With the rise of more mechanical power, other forms of whistles have been developed. One characteristic of a whistle is that it creates a pure, or nearly pure, tone. The conversion of flow energy to sound comes from an interaction between a solid material and a fluid stream. The forces in some whistles are sufficient to set the solid material in motion. Classic examples are Aeolian tones that result in galloping power lines, or the Tacoma Narrows Bridge (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity quantifies the internal frictional force between adjacent layers of fluid that are in relative motion. For instance, when a viscous fluid is forced through a tube, it flows more quickly near the tube's axis than near its walls. Experiments show that some stress (such as a pressure difference between the two ends of the tube) is needed to sustain the flow. This is because a force is required to overcome the friction between the layers of the fluid which are in relative motion. For a tube with a constant rate of flow, the strength of the compensating force is proportional to the fluid's viscosity. In general, viscosity depends on a fluid's state, such as its temperature, pressure, and rate of deformation. However, the dependence on some of these properties is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Whistle
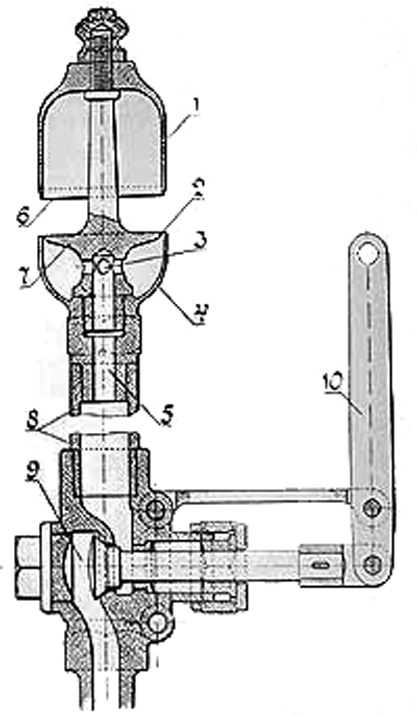
A steam whistle is a device used to produce sound in the form of a whistle using live steam, which creates, projects, and amplifies its sound by acting as a vibrating system (compare to train horn). Operation The whistle consists of the following main parts, as seen on the drawing: the whistle bell (1), the steam orifice or aperture (2), and the valve (9). When the lever (10) is actuated (usually via a pull cord), the valve opens and lets the steam escape through the orifice. The steam will alternately compress and rarefy in the bell, creating the sound. The pitch, or tone, is dependent on the length of the bell; and also how far the operator has opened the valve. Some locomotive engineers invented their own distinctive style of whistling. Uses of steam whistles Steam whistles were often used in factories, and similar places to signal the start or end of a shift, etc. steam-powered railway locomotives, traction engines, and steam ships have traditionally been fitted wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shock Wave
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a medium but is characterized by an abrupt, nearly discontinuous, change in pressure, temperature, and density of the medium. For the purpose of comparison, in supersonic flows, additional increased expansion may be achieved through an expansion fan, also known as a Prandtl–Meyer expansion fan. The accompanying expansion wave may approach and eventually collide and recombine with the shock wave, creating a process of destructive interference. The sonic boom associated with the passage of a supersonic aircraft is a type of sound wave produced by constructive interference. Unlike solitons (another kind of nonlinear wave), the energy and speed of a shock wave alone dissipates relatively quickly with distance. When a shock wave passes through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concorde
The Aérospatiale/BAC Concorde () is a retired Franco-British supersonic airliner jointly developed and manufactured by Sud Aviation (later Aérospatiale) and the British Aircraft Corporation (BAC). Studies started in 1954, and France and the UK signed a treaty establishing the development project on 29 November 1962, as the programme cost was estimated at £70 million (£ in ). Construction of the six prototypes began in February 1965, and the first flight took off from Toulouse on 2 March 1969. The market was predicted for 350 aircraft, and the manufacturers received up to 100 option orders from many major airlines. On 9 October 1975, it received its French Certificate of Airworthiness, and from the UK CAA on 5 December. Concorde is a tailless aircraft design with a narrow fuselage permitting a 4-abreast seating for 92 to 128 passengers, an ogival delta wing and a droop nose for landing visibility. It is powered by four Rolls-Royce/Snecma Olympus 593 turbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmholtz Resonator
Helmholtz resonance or wind throb is the phenomenon of air resonance in a cavity, such as when one blows across the top of an empty bottle. The name comes from a device created in the 1850s by Hermann von Helmholtz, the ''Helmholtz resonator'', which he used to identify the various frequencies or musical pitches present in music and other complex sounds.Helmholtz, Hermann von (1885), ''On the sensations of tone as a physiological basis for the theory of music'' Second English Edition, translated by Alexander J. Ellis. London: Longman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vortex Ring
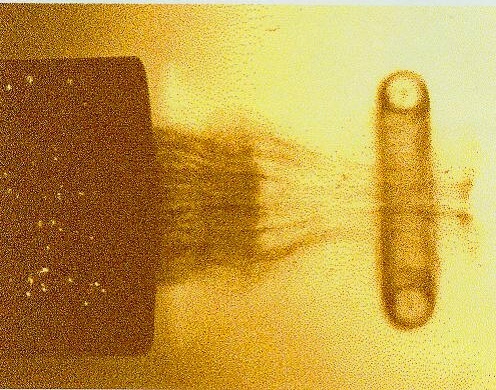
A vortex ring, also called a toroidal vortex, is a torus-shaped vortex in a fluid; that is, a region where the fluid mostly spins around an imaginary axis line that forms a closed loop. The dominant flow in a vortex ring is said to be toroidal, more precisely poloidal. Vortex rings are plentiful in turbulent flows of liquids and gases, but are rarely noticed unless the motion of the fluid is revealed by suspended particles—as in the smoke rings which are often produced intentionally or accidentally by smokers. Fiery vortex rings are also a commonly produced trick by fire eaters. Visible vortex rings can also be formed by the firing of certain artillery, in mushroom clouds, and in microbursts. A vortex ring usually tends to move in a direction that is perpendicular to the plane of the ring and such that the inner edge of the ring moves faster forward than the outer edge. Within a stationary body of fluid, a vortex ring can travel for relatively long distance, carrying the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |