|
Phyllodium Pulchellum
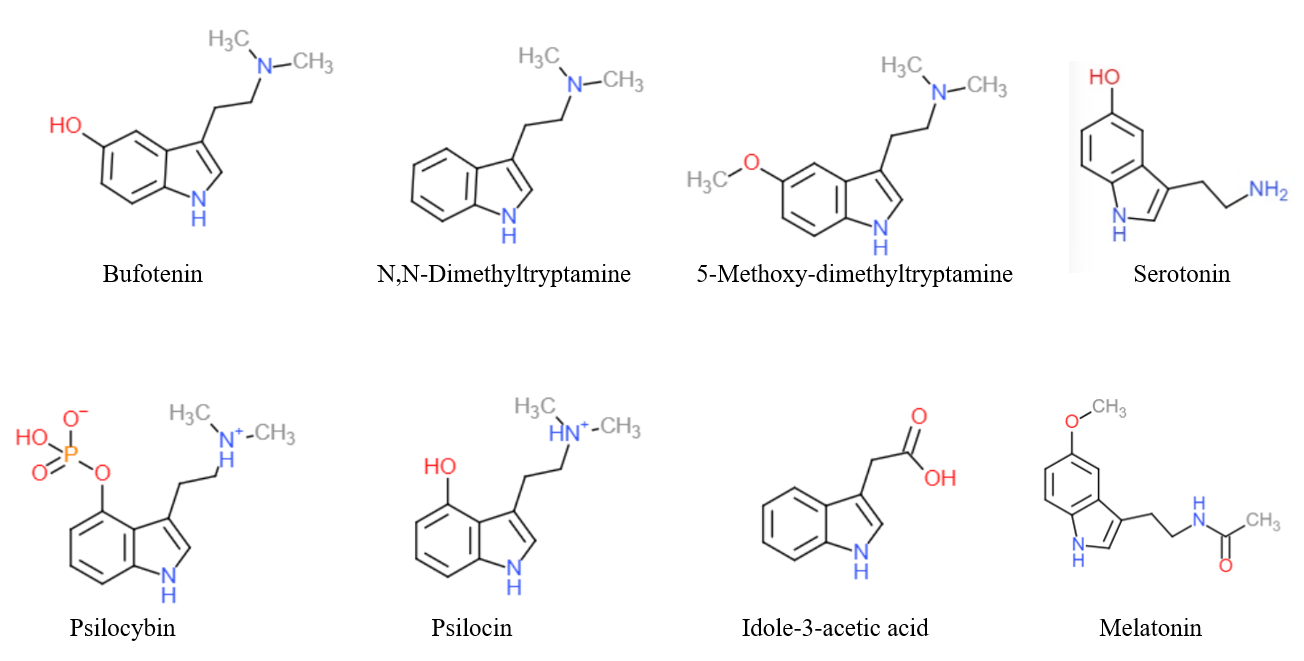
''Phyllodium pulchellum'' is a plant in the family Fabaceae. Medicinal Traditional In Bangladesh, a bark decoction is used for hemorrhage, diarrhea, poisoning and eye diseases. Flowers are used in biliousness. Chemical composition Plant: Bufotenin and its methyl ether, DMT and its oxides, two tryptamine derivatives, gramine, 15 indole-3-alkylamine, tryptophan bases, β-carbolines Seeds: Galactomannan, L-glucosyl rhamnoside of physcion Roots: Betulin, α-amyrin, β-sitosterol β-sitosterol (beta-sitosterol) is one of several phytosterols (plant sterols) with chemical structures similar to that of cholesterol. It is a white, waxy powder with a characteristic odor, and is one of the components of the food additive E499. ... The alkaloids are mainly of three broad structural types, i.e. indole-3-alkylamine, beta-carbolines, and tetrahydro-β-carboline. References Desmodieae {{medicinal-plant-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes (the archaea and bacteria). By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (Latin name for "green plants") which is sister of the Glaucophyta, and consists of the green algae and Embryophyta (land plants). The latter includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and their allies, hornworts, liverworts, and mosses. Most plants are multicellular organisms. Green plants obtain most of their energy from sunlight via photosynthesis by primary chloroplasts that are derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria. Their chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a and b, which gives them their green color. Some plants are parasitic or mycotrophic and have lost the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptamine
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid, tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole ─ a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic and glutamatergic systems. In the human gut, symbiotic bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptors and regulates gastrointestinal motility. Multiple tryptamine-derived drugs have been developed to treat migraines, while trace amine-associated receptors are being explored as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-Carboline
β-Carboline (9''H''- pyrido ,4-''b'' ndole) represents the basic chemical structure for more than one hundred alkaloids and synthetic compounds. The effects of these substances depend on their respective substituent. Natural β-carbolines primarily influence brain functions but can also exhibit antioxidant effects. Synthetically designed β-carboline derivatives have recently been shown to have neuroprotective, cognitive enhancing and anti-cancer properties. Pharmacology The pharmacological effects of specific β-carbolines are dependent on their substituents. For example, the natural β-carboline harmine has substituents on position 7 and 1. Thereby, it acts as a selective inhibitor of the DYRK1A protein kinase, a molecule necessary for neurodevelopment. It also exhibits various antidepressant-like effects in rats by interacting with serotonin receptor 2A. Furthermore, it increases levels of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in rat hippocampus. A decreased BDNF le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
β-sitosterol
β-sitosterol (beta-sitosterol) is one of several phytosterols (plant sterols) with chemical structures similar to that of cholesterol. It is a white, waxy powder with a characteristic odor, and is one of the components of the food additive E499. Phytosterols are hydrophobic and soluble in alcohols. Natural occurrences and food β-sitosterol is widely distributed in the plant kingdom. It is found in vegetable oil, nuts, avocados, and derived prepared foods such as salad dressings. Human research β-sitosterol is being studied for its potential to reduce benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and blood cholesterol levels. Genetic disorder While plant sterols are usually beneficial, there is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder phytosterolemia which causes over-absorption of phytosterols. Precursor of anabolic steroid boldenone Being a steroid, β-sitosterol is a precursor of anabolic steroid boldenone. Boldenone undecylenate is commonly used in veterinary medicine to induce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
α-amyrin
The amyrins are three closely related natural chemical compounds of the triterpene class. They are designated α-amyrin (ursane skeleton), β-amyrin (oleanane skeleton) and δ-amyrin. Each is a pentacyclic triterpenol with the chemical formula C30H50O. They are widely distributed in nature and have been isolated from a variety of plant sources such as epicuticular wax. In plant biosynthesis, α-amyrin is the precursor of ursolic acid and β-amyrin is the precursor of oleanolic acid. All three amyrins occur in the surface wax of tomato fruit. α-Amyrin is found in dandelion coffee. A study demonstrated that α,β-amyrin exhibits long-lasting antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory properties in 2 models of persistent nociception via activation of the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 and by inhibiting the production of cytokines and expression of NF-κB, CREB and cyclooxygenase 2 Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase) (The HUGO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betulin
Betulin is an abundant, naturally occurring triterpene. It is commonly isolated from the bark of birch trees. It forms up to 30% of the dry weight of silver birch bark. It is also found in birch sap. '' Inonotus obliquus'' and red alder also contain betulin. The compound in the bark gives the tree its white color which appears to protect the tree from mid-winter overheating by the sun. As a result, birches are some of the northernmost occurring deciduous trees. It can be converted to betulinic acid (the alcohol group replaced by a carboxylic acid group), which is biologically more active than betulin itself. History Betulin was discovered in 1788 by German-Russian chemist Johann Tobias Lowitz. Chemistry Chemically, betulin is a triterpenoid of lupane structure. It has a pentacyclic ring structure, and hydroxyl groups in positions C3 and C28. Biological activities Preliminary ''in vitro'' studies have shown that betulin demonstrates anti-cancer properties against a variety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parietin
Parietin is the predominant cortical pigment of lichens in the genus '' Caloplaca'', a secondary product of the lichen ''Xanthoria parietina'', and a pigment found in the roots of Curled Dock (''Rumex crispus''). It has an orangy-yellow color and absorbs blue light. It is also known as physcion. It has also been shown to protect lichens against UV-B light, at high altitudes in Alpine regions. The UV-B light stimulates production of parietin and the parietin protects the lichens from damage. Lichens in arctic regions such as Svarlbard retain this capability though they do not encounter damaging levels of UV-B, a capability that could help protect the lichens in case of Ozone layer thinning. It has also shown anti-fungal activity against barley powdery mildew and cucumber powdery mildew, more efficiently in the latter case than treatments with fenarimol and polyoxin B. It reacts with KOH to form a deep, reddish-magenta compound. Effect on human cancer cells Also found in rhu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactomannan
Galactomannans are polysaccharides consisting of a mannose backbone with galactose side groups, more specifically, a (1-4)-linked beta-D-mannopyranose backbone with branchpoints from their 6-positions linked to alpha-D-galactose, (i.e. 1-6-linked alpha-D-galactopyranose). In order of increasing number of mannose-to-galactose ratio: *fenugreek, fenugreek gum, mannose:galactose ~1:1 *guar gum, mannose:galactose ~2:1 *tara gum, mannose:galactose ~3:1 *locust bean gum or ''carob gum'', mannose:galactose ~4:1 *cassia gum, mannose:galactose ~5:1 Galactomannans are often used in food products to increase the viscosity of the water phase. Guar gum has been used to add viscosity to artificial tears, but is not as stable as Carboxymethyl cellulose, carboxymethylcellulose. Food use Galactomannans are used in foods as stabilizer (chemistry), stabilisers. Guar and locust bean gum (LBG) are commonly used in ice cream to improve texture and reduce ice cream meltdown. LBG is also used extensiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
15 Indole-3-alkylamine
Fifteen or 15 may refer to: *15 (number), the natural number following 14 and preceding 16 *one of the years 15 BC, AD 15, 1915, 2015 Music *Fifteen (band), a punk rock band Albums * ''15'' (Buckcherry album), 2005 * ''15'' (Ani Lorak album), 2007 * ''15'' (Phatfish album), 2008 * ''15'' (mixtape), a 2018 mixtape by Bhad Bhabie * ''Fifteen'' (Green River Ordinance album), 2016 * ''Fifteen'' (The Wailin' Jennys album), 2017 * ''Fifteen'', a 2012 album by Colin James Songs * "Fifteen" (song), a 2008 song by Taylor Swift *"Fifteen", a song by Harry Belafonte from the album '' Love Is a Gentle Thing'' *"15", a song by Rilo Kiley from the album ''Under the Blacklight'' *"15", a song by Marilyn Manson from the album ''The High End of Low'' *"The 15th", a 1979 song by Wire Other uses *Fifteen, Ohio, a community in the United States * ''15'' (film), a 2003 Singaporean film * ''Fifteen'' (TV series), international release name of ''Hillside'', a Canadian-American teen drama *Fif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gramine
Gramine (also called donaxine) is a naturally occurring indole alkaloid present in several plant species. Gramine may play a defensive role in these plants, since it is toxic to many organisms. Occurrence Gramine has been found in the giant reed, ''Arundo donax'', ''Acer saccharinum'' (Silver Maple), ''Hordeum'', (a grass genus that includes barley) and ''Phalaris'' (another grass genus). Effects and toxicity Gramine has been found to act as an agonist of the adiponectin receptor 1 Adiponectin receptor 1 (AdipoR1) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''ADIPOR1'' gene. It is a member of the progestin and adipoQ receptor (PAQR) family, and is also known as PAQR1. Structure Similar to G protein-coupled receptors (GP ... (AdipoR1). The LD50 of gramine is 44.6 mg/ kg iv in mice and 62.9 mg/ kg iv in rats. Numerous studies have been done on the toxicity in insects harmful to crops for use as a possible insecticide. References {{Reflist Adiponectin receptor a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N,N-dimethyltryptamine
''N'',''N''-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT or ''N'',''N''-DMT, SPL026) is a substituted tryptamine that occurs in many plants and animals, including human beings, and which is both a derivative and a structural analog of tryptamine. It is used as a psychedelic drug and prepared by various cultures for ritual purposes as an entheogen. DMT has a rapid onset, intense effects, and a relatively short duration of action. For those reasons, DMT was known as the "business trip" during the 1960s in the United States, as a user could access the full depth of a psychedelic experience in considerably less time than with other substances such as LSD or psilocybin mushrooms. DMT can be inhaled, ingested, or injected and its effects depend on the dose, as well as the mode of administration. When inhaled or injected, the effects last a short period of time: about five to 15 minutes. Effects can last three hours or more when orally ingested along with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), such as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |