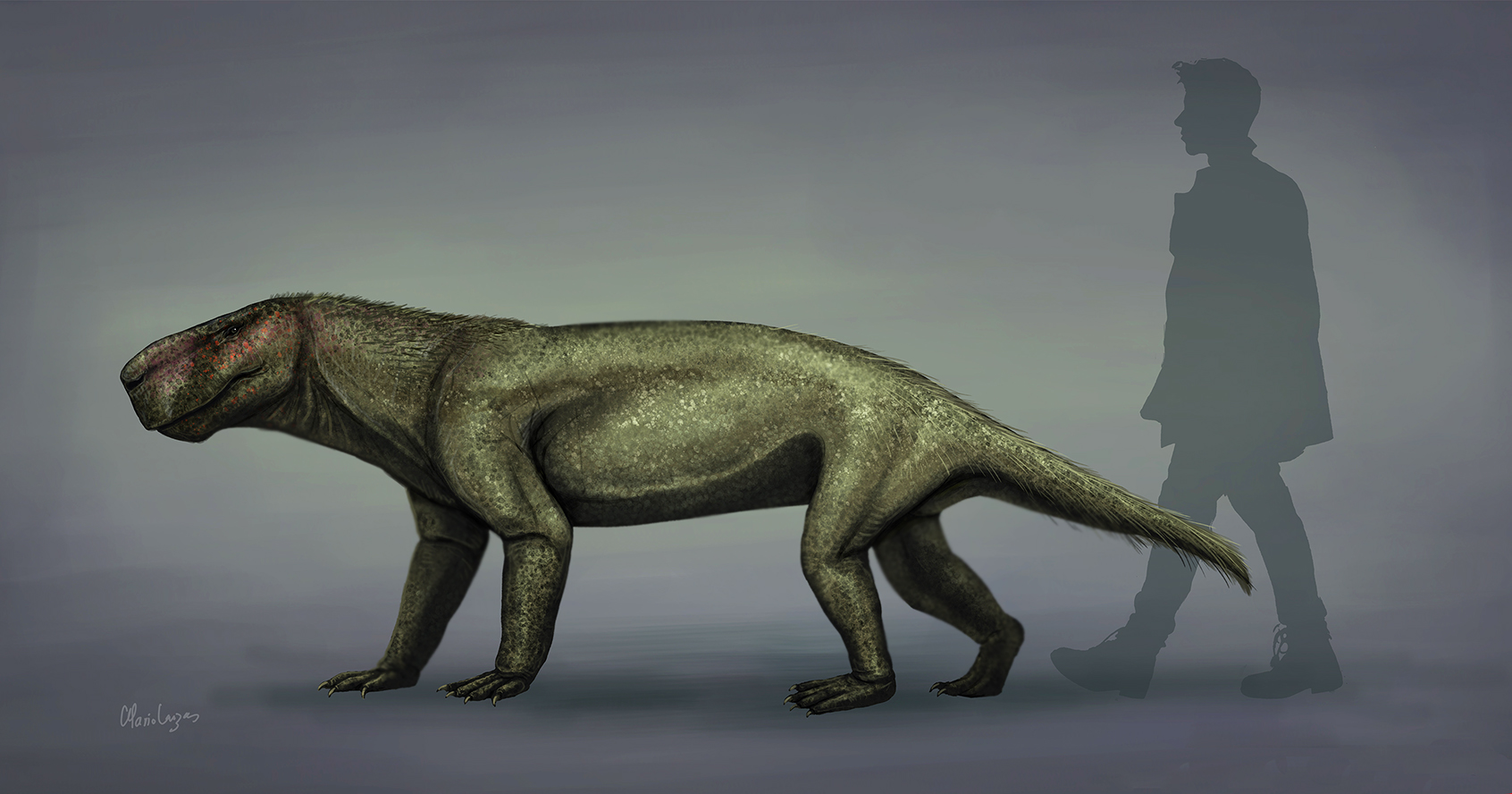|
Phthinosuchia
Phthinosuchia is an extinct group of therapsids including two poorly known species, ''Phthinosuchus discors'' and ''Phthinosaurus borrisiaki'', from the Middle Permian of Russia. ''Phthinthosuchus'' is known a partial crushed skull and ''Phthinosaurus'' is known from an isolated lower jaw. The two species have traditionally been grouped together based on their shared primitive characteristics, but more recent studies have proposed that they are more distantly related. ''Phthinosuchus'' is either a carnivorous gorgonopsian relative or an anteosaurian dinocephalian while ''Phthinosaurus'' is either a herbivorous rhopalodont dinocephalian or a therocephalian. Phthinosuchia was named by American paleontologist Everett C. Olson in 1961, who considered it the most primitive infraorder within Therapsida. A year later Olson named the new infraorder Eotheriodontia and reclassified Phthinosuchia as a subgroup of eotheriodonts, along with the families Biarmosuchidae and Brithopodidae. Each s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phthinosaurus Borrisiaki
''Phthinosaurus'' is an extinct genus of therapsids from the Middle Permian of Russia. The type species ''Phthinosaurus borrisiaki'' was named by Soviet paleontologist Ivan Yefremov in 1940 on the basis of an isolated lower jaw. Because this jaw provides few distinguishing characteristics, the evolutionary relationships of ''Phthinosaurus'' are poorly known. Yefremov named the family Phthinosuchidae in 1954 to include ''Phthinosaurus'' and the newly named '' Phthinosuchus'', which was described on the basis of a crushed partial skull. American paleontologist Everett C. Olson placed both of these therapsids in the larger infraorder Phthinosuchia in 1961. In 1974 Leonid Tatarinov named the family Phthinosauridae to include ''Phthinosaurus'' alone, retaining ''Phthinosuchus'' within Phthinosuchidae. ''Phthinosaurus'' differs from ''Phthinosuchus'' in that it has a small coronoid process near where the lower jaw would attach to the rest of the skull. Tatarinov classified ''Phthinosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgonopsia
Gorgonopsia (from the Greek Gorgon, a mythological beast, and 'aspect') is an extinct clade of sabre-toothed therapsids from the Middle to Upper Permian roughly 265 to 252 million years ago. They are characterised by a long and narrow skull, as well as elongated upper and sometimes lower canine teeth and incisors which were likely used as slashing and stabbing weapons. Postcanine teeth are generally reduced or absent. For hunting large prey, they possibly used a bite-and-retreat tactic, ambushing and taking a debilitating bite out of the target, and following it at a safe distance before its injuries exhausted it, whereupon the gorgonopsian would grapple the animal and deliver a killing bite. They would have had an exorbitant gape, possibly in excess of 90°, without having to unhinge the jaw. They markedly increased in size as time went on, growing from small skull lengths of in the Middle Permian to bear-like proportions of up to in the Upper Permian. The latest gorgonopsia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phthinosuchidae
''Phthinosuchus'' is an extinct genus of therapsids from the Middle Permian of Russia. ''Phthinosuchus'' is the sole member of the family Phthinosuchidae. ''Phthinosuchus'' may have been one of the most primitive therapsids, meaning that its ancestors may have branched off early from the main therapsid line. Discovery ''Phthinosuchus'' was named in 1954 by Ivan Yefremov. It is currently only known from the back of the skull, as the front of the skull was lost after description. Two species, ''P. discors'' and ''P. horissiaki'', have been described. Description ''Phthinosuchus'' was 1.5 m (5 ft) long with a 20 cm skull, and looked much like the Sphenacodontids, such as ''Dimetrodon'' and ''Sphenacodon''. Its temporal fenestrae were larger than those of the Sphenacodontids. Its jaw was slender, unlike other predatory therapsids, but like the other early therapsids, it was probably sprawling and carnivorous. Classification ''Phthinosuchus'' is a member of the subor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phthinosuchus Discors
''Phthinosuchus'' is an extinct genus of therapsids from the Middle Permian of Russia. ''Phthinosuchus'' is the sole member of the family Phthinosuchidae. ''Phthinosuchus'' may have been one of the most primitive therapsids, meaning that its ancestors may have branched off early from the main therapsid line. Discovery ''Phthinosuchus'' was named in 1954 by Ivan Yefremov. It is currently only known from the back of the skull, as the front of the skull was lost after description. Two species, ''P. discors'' and ''P. horissiaki'', have been described. Description ''Phthinosuchus'' was 1.5 m (5 ft) long with a 20 cm skull, and looked much like the Sphenacodontids, such as ''Dimetrodon'' and ''Sphenacodon''. Its temporal fenestrae were larger than those of the Sphenacodontids. Its jaw was slender, unlike other predatory therapsids, but like the other early therapsids, it was probably sprawling and carnivorous. Classification ''Phthinosuchus'' is a member of the subor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Permian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0.5 – 259.1 ± 0.4 Mya. The series saw the rise of the therapsids, a minor extinction event called Olson's Extinction and a significant mass extinction called the end-Capitanian extinction event. The Guadalupian was previously known as the Middle Permian. Name and background The Guadalupian is the second and middle series or epoch of the Permian. Previously called Middle Permian, the name of this epoch is part of a revision of Permian stratigraphy for standard global correlation. The name "Guadalupian" was first proposed in the early 1900s, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. References to the Middle Permian still exist. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biarmosuchidae
Biarmosuchidae is a family of biarmosuchian therapsids Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented mor ... from Russia. References Biarmosuchians Prehistoric therapsid families Fossil taxa described in 1962 {{Paleo-Therapsid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonid Tatarinov
Leonid (russian: Леонид ; uk, Леонід ; be, Леанід, Ljeaníd ) is a Slavic version of the given name Leonidas. The French version is Leonide. People with the name include: * Leonid Andreyev (1871–1919), Russian playwright and short-story writer who led the Expressionist movement in the national literature *Leonid Brezhnev (1906–1982), leader of the USSR from 1964 to 1982 *Leonid Buryak (b. 1953), USSR/Ukraine-born Olympic-medal-winning soccer player and coach * Leonid Bykov (1928–1979), Soviet and Ukrainian actor, film director, and script writer * Leonid Desyatnikov (b. 1955), Soviet and Russian opera and film composer *Leonid Feodorov (1879–1935), a bishop and Exarch for the Russian Catholic Church, and survivor of the Gulag * Leonid Filatov (1946–2003), Soviet and Russian actor, director, poet, and pamphleteer * Leonid Gaidai, (1923–1993), Soviet comedy film director *Leonid Geishtor (b. 1936), USSR (Belarus)-born Olympic champion Canadian pairs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Yefremov
Ivan Antonovich (real patronymic Antipovich) Yefremov ( ru , Ива́н Анто́нович (Анти́пович) Ефре́мов; April 23, 1908 – October 5, 1972; last name sometimes transliterated as Efremov) was a Soviet paleontologist, science-fiction author and social thinker. He founded taphonomy, the study of fossilization patterns. Biography He was born in the village of Vyritsa in Saint Petersburg Governorate on April 23, 1908. His parents divorced during the Russian Revolution. His mother married a Red Army commander and left the children in Kherson to be cared for by an aunt who soon died of typhus. Yefremov survived on his own for some time, after which he joined a Red Army unit as a "son of the regiment" and went to Perekop with it. In 1921, he was discharged and went to Petrograd (today's Saint Petersburg) to study. He completed his education there while combining his studies with a variety of odd jobs. He later commented that "the Revolution was als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brithopodidae
''Brithopus'' is an extinct genus of dinocephalian therapsids. It contains a single species, ''Brithopus priscus'', known from fragmentary remains found in the Copper Sandstones near Isheevo, Russia. Description ''Brithopus'' was fairly large, reaching a length of 2.5–3 m (8–10 ft). The skull was similar to ''Titanophoneus'', but more massive and heavily built.Olson, E.C. (1962). "Late Permian terrestrial vertebrates, U.S.A. and U.S.S.R." ''Transactions of the American Philosophical Society'', New Series, 52: 1–224. Classification ''B. priscus'' was first named in 1838 and was traditionally classified in the Anteosauria, a group of carnivorous dinocephalians. ''Brithopus'' served as the basis for the family Brithopodidae, which once included many anteosaurian species. Because it is based on fragmentary material, ''Brithopus'' is regarded as a ''nomen dubium'' by some researchers. ''Brithopus'' was later considered a possible estemmenosuchid,Kammerer, C. F. 2010. Syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Everett C
Everett may refer to: Places Canada * Everett, Ontario, a community in Adjala–Tosorontio, Simcoe County * Everett Mountains, a range on southern Baffin Island in Nunavut United States * Everett, Massachusetts, in Middlesex County, Massachusetts north of Boston * Everett, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Everett, Nebraska, an unincorporated community * Everett, New Jersey, an unincorporated community * Everett, Ohio, an unincorporated community * Everett, Pennsylvania, in Bedford County, Pennsylvania ** Everett Area School District, a public school district in Bedford Country. * Everett, Washington, the county seat and largest city in Washington state's Snohomish County ** Everett Massacre, an armed confrontation between local authorities and members of the Industrial Workers of the World union ** Boeing Everett Factory, an airplane assembly building owned by Boeing * Everett Township (other), a list of townships named Everett Elsewhere * Everett Range, Ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eotheriodontia
Synapsids + (, 'arch') > () "having a fused arch"; synonymous with ''theropsids'' (Greek, "beast-face") are one of the two major groups of animals that evolved from basal amniotes, the other being the sauropsids, the group that includes reptiles and birds. The group includes mammals and every animal more closely related to mammals than to sauropsids. Unlike other amniotes, synapsids have a single temporal fenestra, an opening low in the skull roof behind each eye orbit, leaving a bony arch beneath each; this accounts for their name. The distinctive temporal fenestra developed about 318 million years ago during the Late Carboniferous period, when synapsids and sauropsids diverged, but was subsequently merged with the orbit in early mammals. Traditionally, non-mammalian synapsids were believed to have evolved from reptiles, and therefore described as mammal-like reptiles in classical systematics, and primitive synapsids were also referred to as pelycosaurs, or pelycosaur- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |