|
Phrases
In syntax and grammar, a phrase is a group of words or singular word acting as a grammatical unit. For instance, the English expression "the very happy squirrel" is a noun phrase which contains the adjective phrase "very happy". Phrases can consist of a single word or a complete sentence. In theoretical linguistics, phrases are often analyzed as units of syntactic structure such as a constituent. Common and technical use There is a difference between the common use of the term ''phrase'' and its technical use in linguistics. In common usage, a phrase is usually a group of words with some special idiomatic meaning or other significance, such as "all rights reserved", "economical with the truth", "kick the bucket", and the like. It may be a euphemism, a saying or proverb, a fixed expression, a figure of speech, etc.. In linguistics, these are known as phrasemes. In theories of syntax, a phrase is any group of words, or sometimes a single word, which plays a particular role within t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic (Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in the 8th and 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun Phrase
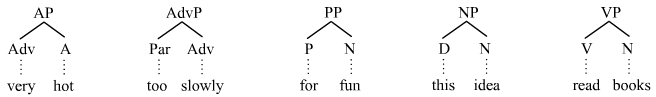
In linguistics, a noun phrase, or nominal (phrase), is a phrase that has a noun or pronoun as its head or performs the same grammatical function as a noun. Noun phrases are very common cross-linguistically, and they may be the most frequently occurring phrase type. Noun phrases often function as verb subjects and objects, as predicative expressions and as the complements of prepositions. Noun phrases can be embedded inside each other; for instance, the noun phrase ''some of his constituents'' contains the shorter noun phrase ''his constituents''. In some more modern theories of grammar, noun phrases with determiners are analyzed as having the determiner as the head of the phrase, see for instance Chomsky (1995) and Hudson (1990). Identification Some examples of noun phrases are underlined in the sentences below. The head noun appears in bold. ::This election-year's politics are annoying for many people. ::Almost every sentence contains at least one noun phrase. ::Current ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun Phrase
In linguistics, a noun phrase, or nominal (phrase), is a phrase that has a noun or pronoun as its head or performs the same grammatical function as a noun. Noun phrases are very common cross-linguistically, and they may be the most frequently occurring phrase type. Noun phrases often function as verb subjects and objects, as predicative expressions and as the complements of prepositions. Noun phrases can be embedded inside each other; for instance, the noun phrase ''some of his constituents'' contains the shorter noun phrase ''his constituents''. In some more modern theories of grammar, noun phrases with determiners are analyzed as having the determiner as the head of the phrase, see for instance Chomsky (1995) and Hudson (1990). Identification Some examples of noun phrases are underlined in the sentences below. The head noun appears in bold. ::This election-year's politics are annoying for many people. ::Almost every sentence contains at least one noun phrase. ::Current ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proverb
A proverb (from la, proverbium) is a simple and insightful, traditional saying that expresses a perceived truth based on common sense or experience. Proverbs are often metaphorical and use formulaic speech, formulaic language. A proverbial phrase or a proverbial expression is a type of a conventional saying similar to proverbs and transmitted by oral tradition. The difference is that a proverb is a fixed expression, while a proverbial phrase permits alterations to fit the grammar of the context. Collectively, they form a folklore genre, genre of folklore. Some proverbs exist in more than one language because people borrow them from languages and cultures with which they are in contact. In the West, the Bible (including, but not limited to the Book of Proverbs) and medieval Latin (aided by the work of Erasmus) have played a considerable role in distributing proverbs. Not all Biblical proverbs, however, were distributed to the same extent: one scholar has gathered evidence to show ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntactic Category
A syntactic category is a syntactic unit that theories of syntax assume. Word classes, largely corresponding to traditional parts of speech (e.g. noun, verb, preposition, etc.), are syntactic categories. In phrase structure grammars, the ''phrasal categories'' (e.g. noun phrase, verb phrase, prepositional phrase, etc.) are also syntactic categories. Dependency grammars, however, do not acknowledge phrasal categories (at least not in the traditional sense). Word classes considered as syntactic categories may be called ''lexical categories'', as distinct from phrasal categories. The terminology is somewhat inconsistent between the theoretical models of different linguists. However, many grammars also draw a distinction between ''lexical categories'' (which tend to consist of content words, or phrases headed by them) and ''functional categories'' (which tend to consist of function words or abstract functional elements, or phrases headed by them). The term ''lexical category'' therefore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saying
A saying is any concisely written or spoken expression that is especially memorable because of its meaning or style. Sayings are categorized as follows: * Aphorism: a general, observational truth; "a pithy expression of wisdom or truth". ** Adage, proverb, or saw: a widely known or popular aphorism that has gained credibility by long use or tradition. ** Apothegm: "an edgy, more cynical aphorism; such as, 'Men are generally more careful of the breed of their horses and dogs than of their children.'" * Axiom: a proposition that commends itself to general acceptance; a well-established or universally conceded principle; a maxim, rule, or law.''Oxford English Dictionary'' Online, accessed 2012-04-28 * Cliché or bromide: an unoriginal and overused saying. ** Platitude: a cliché that is unsuccessfully presented as though it were meaningful, original, or effective. * Epigram: a clever and often poetic written saying that comments on a specific person, idea, or thing; it especially den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adverb Phrase
In linguistics, an ''adverbial phrase'' ("AdvP") is a multi-word expression operating adverbially: its syntactic function is to modify other expressions, including verbs, adjectives, adverbs, adverbials, and sentences. Adverbial phrases can be divided into two types: complement adverbs and modifier adverbs. For example, in the sentence ''She sang very well'', the expression ''very well'' is an adverbial phrase, as it modifies the verb ''to sing''. More specifically, the adverbial phrase ''very well'' contains two adverbs, ''very'' and ''well'': while ''well'' modifies the verb to convey information about the manner of singing (for example, ''She sang well'' versus ''She sang badly''), ''very'' is a degree modifier that conveys information about the degree to which the action of singing well was accomplished (for example, ''Not only did she sing well, she sang very well''). Types The following examples illustrate some of the most common types of adverbial phrases. All adverbial phras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Determiner Phrase
In linguistics, a determiner phrase (DP) is a type of phrase headed by a determiner such as ''many''. Controversially, many approaches, take a phrase like ''not very many apples'' to be a DP, headed, in this case, by the determiner ''many''. This is called the DP analysis or the DP hypothesis. Others reject this analysis in favor of the more traditional NP (noun phrase or nominal phrase) analysis where ''apples'' would be the head of the phrase in which the DP ''not very many'' is merely a dependent. Thus, there are competing analyses concerning heads and dependents in nominal groups. The DP analysis developed in the late 1970s and early 1980s, and it is the majority view in generative grammar today. In the example determiner phrases below, the determiners are in boldface: * a little dog, the little dogs (indefinite or definite articles) * my little dog, your little dogs (possessives) * this little dog, those little dogs (demonstratives) * every little dog, each little dog, no dog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parse Tree
A parse tree or parsing tree or derivation tree or concrete syntax tree is an ordered, rooted tree that represents the syntactic structure of a string according to some context-free grammar. The term ''parse tree'' itself is used primarily in computational linguistics; in theoretical syntax, the term ''syntax tree'' is more common. Concrete syntax trees reflect the syntax of the input language, making them distinct from the abstract syntax trees used in computer programming. Unlike Reed-Kellogg sentence diagrams used for teaching grammar, parse trees do not use distinct symbol shapes for different types of constituents. Parse trees are usually constructed based on either the constituency relation of constituency grammars (phrase structure grammars) or the dependency relation of dependency grammars. Parse trees may be generated for sentences in natural languages (see natural language processing), as well as during processing of computer languages, such as programming languages. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The House At The End Of The Street
''House at the End of the Street'' is a 2012 American psychological thriller film directed by Mark Tonderai that stars Jennifer Lawrence. The film's plot revolves around a teenage girl, Elissa, who along with her newly divorced mother Sarah, moves to a new neighborhood only to discover that the house at the end of the street was the site of a gruesome double homicide committed by a thirteen-year-old girl named Carrie Anne who had disappeared without a trace four years prior. Elissa then starts a relationship with Carrie Anne's older brother Ryan, who lives in the same house, but nothing is as it appears to be. Although filming had been completed in 2010, the film was not released until 2012 by Relativity Media. Despite a negative response from critics, the film was a moderate commercial success. Plot Newly divorced medical doctor Sarah Cassidy (Elisabeth Shue) and her 17-year-old daughter Elissa ( Jennifer Lawrence) move to a small, upscale suburb. They are disturbed to discover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constituent (linguistics)
In syntactic analysis, a constituent is a word or a group of words that function as a single unit within a hierarchical structure. The constituent structure of sentences is identified using ''tests for constituents''. These tests apply to a portion of a sentence, and the results provide evidence about the constituent structure of the sentence. Many constituents are phrases. A phrase is a sequence of one or more words (in some theories two or more) built around a head lexical item and working as a unit within a sentence. A word sequence is shown to be a phrase/constituent if it exhibits one or more of the behaviors discussed below. The analysis of constituent structure is associated mainly with phrase structure grammars, although dependency grammars also allow sentence structure to be broken down into constituent parts. Tests for constituents in English Tests for constituents are diagnostics used to identify sentence structure. There are numerous tests for constituents that are co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase Structure Grammar
The term phrase structure grammar was originally introduced by Noam Chomsky as the term for grammar studied previously by Emil Post and Axel Thue (Post canonical systems). Some authors, however, reserve the term for more restricted grammars in the Chomsky hierarchy: context-sensitive grammars or context-free grammars. In a broader sense, phrase structure grammars are also known as ''constituency grammars''. The defining trait of phrase structure grammars is thus their adherence to the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation of dependency grammars. Constituency relation In linguistics, phrase structure grammars are all those grammars that are based on the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation associated with dependency grammars; hence, phrase structure grammars are also known as constituency grammars. Any of several related theories for the parsing of natural language qualify as constituency grammars, and most of them have been develope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_abbatiale_1.jpg)


.png)