|
Photoelectrolysis Of Water
Photoelectrolysis of water, also known as photoelectrochemical water splitting, occurs in a photoelectrochemical cell when light is used as the energy source for the electrolysis of water, producing dihydrogen which can be used as a fuel. This process is one route to a "hydrogen economy", in which hydrogen fuel is produced efficiently and inexpensively from natural sources without using fossil fuels. In contrast, steam reforming usually or always uses a fossil fuel to obtain hydrogen. Photoelectrolysis is sometimes known colloquially as the ''hydrogen holy grail'' for its potential to yield a viable alternative to petroleum as a source of energy; such an energy source would supposedly come without the sociopolitically undesirable effects of extracting and using petroleum. Some researchers have practiced photoelectrolysis by means of a nanoscale process. Nanoscale photoelectrolysis of water could someday reach greater efficiency than that of "traditional" photoelectrolysis. Semicon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Splitting
Water splitting is the chemical reaction in which water is broken down into oxygen and hydrogen: :2 H2O → 2 H2 + O2 Efficient and economical water splitting would be a technological breakthrough that could underpin a hydrogen economy, based on green hydrogen. A version of water splitting occurs in photosynthesis, but hydrogen is not produced. The reverse of water splitting is the basis of the hydrogen fuel cell. Electrolysis Electrolysis of water is the decomposition of water (H2O) into oxygen (O2) and hydrogen (H2) due to an electric current being passed through the water. : * Vion, , "Improved method of using atmospheric electricity", June 1860. In power-to-gas production schemes, the excess power or off peak power created by wind generators or solar arrays is used for load balancing of the energy grid by storing and later injecting the hydrogen into the natural gas grid. Production of hydrogen from water is energy intensive. Potential electrical energy supplies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoscopic Scale
The nanoscopic scale (or nanoscale) usually refers to structures with a length scale applicable to nanotechnology, usually cited as 1–100 nanometers (nm). A nanometer is a billionth of a meter. The nanoscopic scale is (roughly speaking) a lower bound to the mesoscopic scale for most solids. For technical purposes, the nanoscopic scale is the size at which fluctuations in the averaged properties (due to the motion and behavior of individual particles) begin to have a significant effect (often a few percent) on the behavior of a system, and must be taken into account in its analysis. The nanoscopic scale is sometimes marked as the point where the properties of a material change; above this point, the properties of a material are caused by 'bulk' or 'volume' effects, namely which atoms are present, how they are bonded, and in what ratios. Below this point, the properties of a material change, and while the type of atoms present and their relative orientations are still importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
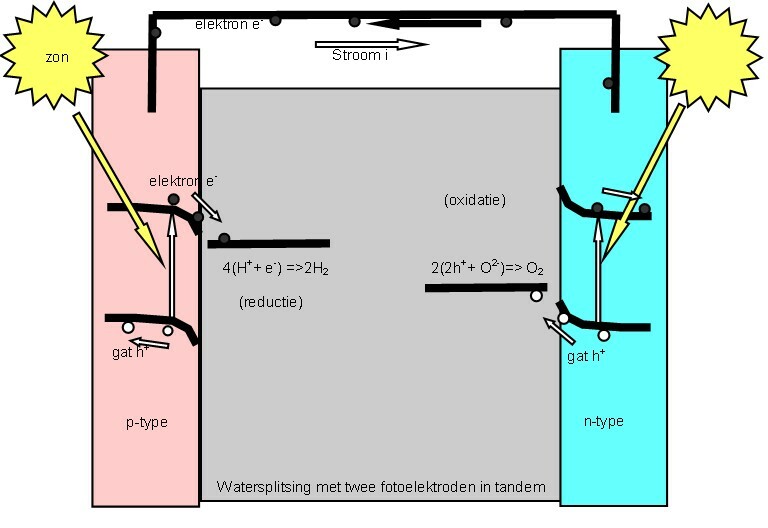
Photocatalytic Water Splitting
Photocatalytic water splitting is an artificial photosynthesis process using photocatalysis for the dissociation of water (H2O) into hydrogen () and oxygen (). Only light energy (photons), water, and a catalyst(s) are needed, since this is what naturally occurs in natural photosynthetic oxygen production and CO2 fixation. Hydrogen fuel production using water and light (photocatalytic water splitting), instead of petroleum, is an important renewable energy strategy. Concepts 2 mol is split into 1 mol and 2 mol using light in the process shown below. : \begin\\ \ce\\ \end The process of water-splitting is a highly endothermic process (Δ''H'' > 0). Water splitting occurs naturally in photosynthesis when the energy of four photons is absorbed and converted into chemical energy through a complex biochemical pathway (Dolai's or Kok's S-state diagrams). O–H bond homolysis in water requires energy of 6.5 - 6.9 eV (UV photon). Infrared light has sufficient energy to mediat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrolysis Of Water
Electrolysis of water, also known as electrochemical water splitting, is the process of using electricity to decompose water into oxygen and hydrogen gas by electrolysis. Hydrogen gas released in this way can be used as hydrogen fuel, or remixed with the oxygen to create oxyhydrogen gas, which is used in welding and other applications. Electrolysis of water requires a minimum potential difference of 1.23 volts, though at that voltage external heat is required. E lectrolysis is rarely used in industrial applications since hydrogen can be produced less expensively from fossil fuels. History In 1789, Jan Rudolph Deiman and Adriaan Paets van Troostwijk used an electrostatic machine to make electricity that was discharged on gold electrodes in a Leyden jar with water. In 1800 Alessandro Volta invented the voltaic pile, and a few weeks later English scientists William Nicholson and Anthony Carlisle used it to electrolyse water. In 1806 Humphry Davy reported the results of ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoelectrochemistry
Photoelectrochemistry is a subfield of study within physical chemistry concerned with the interaction of light with electrochemical systems. It is an active domain of investigation. One of the pioneers of this field of electrochemistry was the German electrochemist Heinz Gerischer. The interest in this domain is high in the context of development of renewable energy conversion and storage technology. Historical approach Photoelectrochemistry has been intensively studied in the 1970-80s because of the first peak oil crisis. Because fossil fuels are non-renewable, it is necessary to develop processes to obtain renewable resources and use clean energy. Artificial photosynthesis, photoelectrochemical water splitting and regenerative solar cells are of special interest in this context. The photovoltaic effect was discovered by Alexandre Edmond Becquerel. Heinz Gerischer, H. Tributsch, AJ. Nozik, AJ. Bard, A. Fujishima, K. Honda, PE. Laibinis, K. Rajeshwar, TJ Meyer, PV. Kamat, N.S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoelectrochemical Reduction Of CO2
Photoelectrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide, also known as photoelectrolysis of carbon dioxide, is a chemical process whereby carbon dioxide is reduced to carbon monoxide or hydrocarbons by the energy of incident light. This process requires catalysts, most of which are semiconductor, semiconducting materials. The feasibility of this chemical reaction was first theorised by Giacomo Luigi Ciamician, an Italian photochemist. Already in 1912 he stated that "[b]y using suitable catalyzers, it should be possible to transform the mixture of water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and methane, or to cause other endo-energetic processes." Furthermore, the reduced chemical species, species may prove to be a valuable feedstock for other processes. If the incident light utilized is solar energy, solar then this process also potentially represents energy routes which combine renewable energy with CO2 reduction. Thermodynamics Thermodynamic potentials for the reduction of CO2 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrochemiluminescence
Electrochemiluminescence or electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) is a kind of luminescence produced during electrochemical reactions in solutions. In electrogenerated chemiluminescence, electrochemically generated intermediates undergo a highly exergonic reaction to produce an electronically excited state that then emits light upon relaxation to a lower-level state. This wavelength of the emitted photon of light corresponds to the energy gap between these two states. ECL excitation can be caused by energetic electron transfer (redox) reactions of electrogenerated species. Such luminescence excitation is a form of chemiluminescence where one/all reactants are produced electrochemically on the electrodes. ECL is usually observed during application of potential (several volts) to electrodes of electrochemical cell that contains solution of luminescent species (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, metal complexes, Quantum Dots or Nanoparticles ) in aprotic organic solvent (ECL compos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Photosynthesis
Artificial photosynthesis is a chemical process that biomimics the natural process of photosynthesis to convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and oxygen. The term artificial photosynthesis is commonly used to refer to any scheme for capturing and storing the energy from sunlight in the chemical bonds of a fuel (a solar fuel). Photocatalytic water splitting converts water into hydrogen and oxygen and is a major research topic of artificial photosynthesis. Light-driven carbon dioxide reduction is another process studied that replicates natural carbon fixation. Research on this topic includes the design and assembly of devices for the direct production of solar fuels, photoelectrochemistry and its application in fuel cells, and the engineering of enzymes and photoautotrophic microorganisms for microbial biofuel and biohydrogen production from sunlight. Overview The photosynthetic reaction can be divided into two half-reactions of oxidation and redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogenase
A hydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyses the reversible oxidation of molecular hydrogen (H2), as shown below: Hydrogen uptake () is coupled to the reduction of electron acceptors such as oxygen, nitrate, sulfate, carbon dioxide (), and fumarate. On the other hand, proton reduction () is coupled to the oxidation of electron donors such as ferredoxin (FNR), and serves to dispose excess electrons in cells (essential in pyruvate fermentation). Both low-molecular weight compounds and proteins such as FNRs, cytochrome ''c''3, and cytochrome ''c''6 can act as physiological electron donors or acceptors for hydrogenases. Structural classification It has been estimated that 99% of all organisms utilize hydrogen, H2. Most of these species are microbes and their ability to use H2 as a metabolite arises from the expression of metalloenzymes known as hydrogenases. Hydrogenases are sub-classified into three different types based on the active site metal content: iron-iron hydrogenase, ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronvolt
In physics, an electronvolt (symbol eV, also written electron-volt and electron volt) is the measure of an amount of kinetic energy In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion. It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acc ... gained by a single electron accelerating from rest through an Voltage, electric potential difference of one volt in vacuum. When used as a Units of energy, unit of energy, the numerical value of 1 eV in joules (symbol J) is equivalent to the numerical value of the Electric charge, charge of an electron in coulombs (symbol C). Under the 2019 redefinition of the SI base units, this sets 1 eV equal to the exact value Historically, the electronvolt was devised as a standard unit of measure through its usefulness in Particle accelerator#Electrostatic particle accelerators, electrostatic particle accel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sociopolitical
Political sociology is an Interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary field of study concerned with exploring how governance and society interact and influence one another at the micro to macro Level of analysis, levels of analysis. Interested in the social causes and consequences of how power is distributed and changes throughout and amongst societies, political sociology's focus ranges across Family, individual families to the State (polity), State as sites of social and political conflict and power contestation. Introduction Political sociology was conceived as an Interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary sub-field of sociology and politics in the early 1930s throughout the social and political disruptions that took place through the rise of Communism, Fascism, and World War II. This new area drawing upon works by Alexis de Tocqueville, James Bryce, 1st Viscount Bryce, James Bryce, Robert Michels, Max Weber, Émile Durkheim, and Karl Marx to understand an integral theme of political ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoelectrochemical Cell
A "photoelectrochemical cell" is one of two distinct classes of device. The first produces electrical energy similarly to a dye-sensitized photovoltaic cell, which meets the standard definition of a photovoltaic cell. The second is a photoelectrolytic cell, that is, a device which uses light incident on a photosensitizer, semiconductor, or aqueous metal immersed in an electrolytic solution to directly cause a chemical reaction, for example to produce hydrogen via the electrolysis of water. Both types of device are varieties of solar cell, in that a photoelectrochemical cell's function is to use the photoelectric effect (or, very similarly, the photovoltaic effect) to convert electromagnetic radiation (typically sunlight) either directly into electrical power, or into something which can itself be easily used to produce electrical power (hydrogen, for example, can be burned to create electrical power, see photohydrogen). Two principles The standard photovoltaic effect, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)