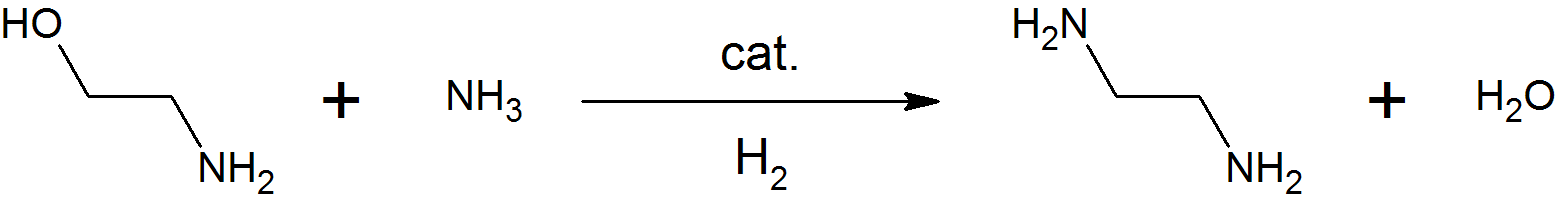|
Phosphorylethanolamine
Phosphorylethanolamine or phosphoethanolamine is an ethanolamine derivative that is used to construct two different categories of phospholipids. One category termed a glycerophospholipid and the other a sphingomyelin, or more specifically within the sphingomyelin class, a sphingophospholipid. Phosphorylethanolamine is a polyprotic acid with two pKa values at 5.61 and 10.39. Phosphorylethanolamine has been falsely promoted as a cancer treatment. Effectiveness As a potential drug, phosphorylethanolamine has undergone human clinical trials. These were halted when no evidence of benefit was found. Edzard Ernst has called Phosphorylethanolamine "the most peculiar case of Brazilian quackery". Legality There has been ongoing controversy and litigation in Brazil with regard to its use as a cancer treatment without approval by the National Health Surveillance Agency. For years, Gilberto Chierice, a Chemistry Professor at the São Carlos São Carlos (Saint Charles, in English, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanolamine
Ethanolamine (2-aminoethanol, monoethanolamine, ETA, or MEA) is an organic chemical compound with the formula or . The molecule is bifunctional, containing both a primary amine and a primary alcohol. Ethanolamine is a colorless, viscous liquid with an odor reminiscent of ammonia.. ETA molecules are a component in the formation of cellular membranes and are thus a molecular building block for life. It was thought to exist only on Earth and on certain asteroids, but in 2021 evidence was found that ETA molecules exist in interstellar space. Derivatives of ethanolamine are widespread in nature; e.g., lipids, as precursor of a variety of ''N''-acylethanolamines (NAEs), that modulate several animal and plant physiological processes such as seed germination, plant–pathogen interactions, chloroplast development and flowering, as well as precursor, combined with arachidonic acid 20: 4, ω-6), to form the endocannabinoid anandamide (AEA: ; 20:4, ω-6). The ethanolamines comprise a gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of São Paulo
The University of São Paulo ( pt, Universidade de São Paulo, USP) is a public university in the Brazilian state of São Paulo. It is the largest Brazilian public university and the country's most prestigious educational institution, the best university in Ibero-America, and holds a high reputation among world universities, being ranked 100 worldwide in reputation by the Times Higher Education World University Rankings. The USP is involved in teaching, research and university extension in all areas of knowledge, offering a broad range of courses. The university was founded in 1934, regrouping already existing schools in the state of São Paulo, such as the Faculdade de Direito do Largo de São Francisco (Faculty of Law), the Escola Politécnica (Engineering School) and the Escola Superior de Agricultura Luiz de Queiroz (College of Agriculture). The university's foundation is marked by the creation in 1934 of the Faculdade de Filosofia, Ciências e Letras (Faculty of Philoso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amines
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (). The substituent is called an amino group. Compounds with a nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl group, thus having the structure , are called amides and have different chemical properties from amines. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number of substituents on nitrogen. Aliphatic amines contain only H and alkyl substituents. Aromatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanolamine
Ethanolamine (2-aminoethanol, monoethanolamine, ETA, or MEA) is an organic chemical compound with the formula or . The molecule is bifunctional, containing both a primary amine and a primary alcohol. Ethanolamine is a colorless, viscous liquid with an odor reminiscent of ammonia.. ETA molecules are a component in the formation of cellular membranes and are thus a molecular building block for life. It was thought to exist only on Earth and on certain asteroids, but in 2021 evidence was found that ETA molecules exist in interstellar space. Derivatives of ethanolamine are widespread in nature; e.g., lipids, as precursor of a variety of ''N''-acylethanolamines (NAEs), that modulate several animal and plant physiological processes such as seed germination, plant–pathogen interactions, chloroplast development and flowering, as well as precursor, combined with arachidonic acid 20: 4, ω-6), to form the endocannabinoid anandamide (AEA: ; 20:4, ω-6). The ethanolamines comprise a gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid . The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosphoric acid by the removal of three protons . Removal of one or two protons gives the dihydrogen phosphate ion and the hydrogen phosphate ion ion, respectively. These names are also used for salts of those anions, such as ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and trisodium phosphate. File:3-phosphoric-acid-3D-balls.png, Phosphoricacid File:2-dihydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Dihydrogenphosphate File:1-hydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Hydrogenphosphate File:0-phosphate-3D-balls.png, Phosphate In organic chemistry, phosphate or orthophosphate is an organophosphate, an ester of orthophosphoric acid of the form where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups. An example is trimethyl phosphate, . The term also refers to the triv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoserine
Phosphoserine (abbreviated as SEP or J) is an ester of serine and phosphoric acid. Phosphoserine is a component of many proteins as the result of posttranslational modifications. The phosphorylation of the alcohol functional group in serine to produce phosphoserine is catalyzed by various types of kinases. Through the use of technologies that utilize an expanded genetic code, phosphoserine can also be incorporated into proteins during translation. It is a normal metabolite In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism. The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, c ... found in human biofluids. Phosphoserine has three potential coordination sites (carboxyl, amine and phosphate group) Determination of the mode of coordination between phosphorylated ligands and metal ions occurring in an organism is a first step to explain the fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphocholine
Phosphocholine is an intermediate in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine in tissues. Phosphocholine is made in a reaction, catalyzed by choline kinase, that converts ATP and choline into phosphocholine and ADP. Phosphocholine is a molecule found, for example, in lecithin. In nematodes and human placentas, phosphocholine is selectively attached to other proteins as a posttranslational modification to suppress an immune response by their hosts. It is also one of the binding targets of C-reactive protein (CRP). Thus, when a cell is damaged, CRP binds to phosphocholine, beginning the recognition and phagocytotic immunologic response. Phosphocholine is a natural constituent of hens' eggs (and many other eggs) often used in biomimetic membrane studies. See also * Alkylphosphocholines * Choline * Phosphoethanolamine Phosphorylethanolamine or phosphoethanolamine is an ethanolamine derivative that is used to construct two different categories of phospholipids. One category ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anvisa
Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency ( pt, Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária, links=no, italics=yes, ''Anvisa'', literally National Health Surveillance Agency) is a regulatory body of the Brazilian government, created in 1999 during President Fernando Henrique Cardoso's term of office. It is responsible for the regulation and approval of pharmaceutical drugs, sanitary standards and regulation of the food industry. The agency bills itself as "an independently administered, financially autonomous" regulatory body. It is administered by a five-member collegiate board of directors, who oversee five thematic directorates, assisted by a five-tier oversight structure. Since September 2018 the agency is headed by Antonio Barra Torres. Pesticide approvals and monitoring Brazil is the world's largest consumer of pesticides. They are primarily used in the production of soy and corn. The number of approved pesticides increased "rapidly" between 2015 and 2019. Tereza Cristina Tere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazilian Medical Association
The Brazilian Medical Association ( pt, Associação Médica Brasileira) founded in 1951, is the national class association of physicians in Brazil. With more than 140,000 associates, it is the second largest in the Americas The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. Along with th ..., just after the American Medical Association. Its official journal, ''Revista da Associação Médica Brasileira'' (), is published by Elsevier. External links Brazilian Medical Association References Medical associations based in Brazil Organizations established in 1951 1951 establishments in Brazil {{med-org-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
São Carlos
São Carlos (Saint Charles, in English, ; named after Saint Charles Borromeo) is a Brazilian municipality in the interior of the state of São Paulo, 254 kilometers from the city of São Paulo. With a population of 254,484 inhabitants, it is the 13th largest city in the state in terms of the number of residents, being almost in the center of the state of São Paulo. The municipality is formed by the headquarters and the districts of Água Vermelha, Bela Vista São-Carlense, Santa Eudóxia and Vila Nery. The city is an important regional industrial center, with the economy based on industrial activities and farming, such as the production of sugar cane, orange, milk and chicken. Served by road and rail systems, São Carlos houses several multinational companies. Given local and, in some ways, regional needs, there is a network of commerce and services distributed in street stores, convenience stores and a mall of the Iguatemi network. In the field of research, besides the univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycerophospholipid
Glycerophospholipids or phosphoglycerides are glycerol-based phospholipids. They are the main component of biological membranes. Two major classes are known: those for bacteria and eukaryotes and a separate family for archaea. Structures The term glycerophospholipid signifies any derivative of glycerophosphoric acid that contains at least one ''O''-acyl, or ''O''-alkyl, or ''O''-alk-1'-enyl residue attached to the glycerol moiety. The phosphate group forms an ester linkage to the glycerol. The long-chained hydrocarbons are typically attached through ester linkages in bacteria/eucaryotes and by ether linkages in archaea. In bacteria and procaryotes, the lipids consist of diesters commonly of C16 or C18 fatty acids. These acids are straight-chained and, especially for the C18 members, can be unsaturated. For archaea, the hydrocarbon chains have chain lengths of C10, C15, C20 etc. since they are derived from isoprene units. These chains are branched, with one methyl substitue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Health Surveillance Agency
Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency ( pt, Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária, links=no, italics=yes, ''Anvisa'', literally National Health Surveillance Agency) is a regulatory body of the Brazilian government, created in 1999 during President Fernando Henrique Cardoso's term of office. It is responsible for the regulation and approval of pharmaceutical drugs, sanitary standards and regulation of the food industry. The agency bills itself as "an independently administered, financially autonomous" regulatory body. It is administered by a five-member collegiate board of directors, who oversee five thematic directorates, assisted by a five-tier oversight structure. Since September 2018 the agency is headed by Antonio Barra Torres. Pesticide approvals and monitoring Brazil is the world's largest consumer of pesticides. They are primarily used in the production of soy and corn. The number of approved pesticides increased "rapidly" between 2015 and 2019. Tereza Cristina, the ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |