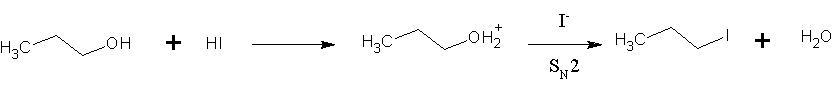|
Phosphorus Triiodide
Phosphorus triiodide (PI3) is an inorganic compound with the formula PI3. A red solid, it is a common misconception that PI3 is too unstable to be stored; it is, in fact, commercially available. It is widely used in organic chemistry for converting alcohols to alkyl iodides. It is also a powerful reducing agent. Note that phosphorus also forms a lower iodide, P2I4, but the existence of PI5 is doubtful at room temperature. Properties PI3 has a low dipole moment in carbon disulfide solution, because the P-I bond has almost no dipole. The P-I bond is also weak; PI3 is much less stable than PBr3 and PCl3, with a standard enthalpy of formation for PI3 of only −46 kJ/ mol (solid). The phosphorus atom has an NMR chemical shift of 178 ppm (downfield of H3PO4). Reactions Phosphorus triiodide reacts vigorously with water, producing phosphorous acid (H3PO3) and hydroiodic acid (HI), along with smaller amounts of phosphine and various P-P-containing compounds. Alcohols likewis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon ( graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroiodic Acid
Hydroiodic acid (or hydriodic acid) is an aqueous solution of hydrogen iodide (HI). It is a strong acid, one that is ionized completely in an aqueous solution. It is colorless. Concentrated solutions are usually 48% to 57% HI. Reactions Hydroiodic acid reacts with oxygen in air to give iodine: :4 HI + O2 → 2 + 2 I2 Like other hydrogen halides, hydroiodic acid adds to alkenes to give alkyl iodides. It can also be used as a reducing agent, for example in the reduction of aromatic nitro compounds to anilines. Cativa process The Cativa process is a major end use of hydroiodic acid, which serves as a co-catalyst for the production of acetic acid by the carbonylation of methanol. Illicit uses Hydroiodic acid is listed as a U.S. Federal DEA List I Chemical, owing to its use as a reducing agent related to the production of methamphetamine from ephedrine or pseudoephedrine Pseudoephedrine (PSE) is a sympathomimetic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grignard Reaction
The Grignard reaction () is an organometallic chemical reaction in which alkyl, allyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides ( Grignard reagent) is added to a carbonyl group in an aldehyde or ketone. This reaction is important for the formation of carbon–carbon bonds. The reaction of an organic halide with magnesium is ''not'' a Grignard reaction, but provides a Grignard reagent. : Grignard reactions and reagents were discovered by and are named after the French chemist François Auguste Victor Grignard ( University of Nancy, France), who published it in 1900 and was awarded the 1912 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work. Reaction mechanism Because carbon is more electronegative than magnesium, the carbon attached to magnesium functions as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon atom that is present within the polar bond of a carbonyl group. The addition of the Grignard reagent to the carbonyl typically proceeds through a six-membered ring transition state. Based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
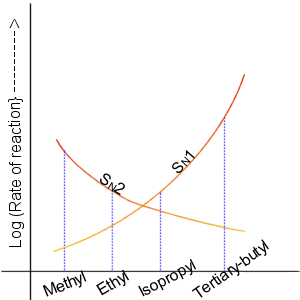
Nucleophilic Substitution
In chemistry, a nucleophilic substitution is a class of chemical reaction A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and break ...s in which an electron-rich chemical species (known as a nucleophile) replaces a functional group within another electron-deficient molecule (known as the electrophile). The molecule that contains the electrophile and the leaving functional group is called the Substrate (chemistry), substrate. The most general form of the reaction may be given as the following: :\text\mathbf + \ce + \text\mathbf The electron pair (:) from the nucleophile (Nuc) wiktionary:attack#Verb, attacks the substrate () and bonds with it. Simultaneously, the leaving group (LG) departs with an electron pair. The principal product in this case is . The nucleophile may be electricall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodomethane
Iodomethane, also called methyl iodide, and commonly abbreviated "MeI", is the chemical compound with the formula CH3I. It is a dense, colorless, volatile liquid. In terms of chemical structure, it is related to methane by replacement of one hydrogen atom by an atom of iodine. It is naturally emitted by rice plantations in small amounts. It is also produced in vast quantities estimated to be greater than 214,000 tons annually by algae and kelp in the world's temperate oceans, and in lesser amounts on land by terrestrial fungi and bacteria. It is used in organic synthesis as a source of methyl groups. Preparation and handling Iodomethane is formed via the exothermic reaction that occurs when iodine is added to a mixture of methanol with red phosphorus. The iodinating reagent is phosphorus triiodide that is formed ''in situ:'' :3 CH3OH + PI3 → 3 CH3I + H2PO3H Alternatively, it is prepared from the reaction of dimethyl sulfate with potassium iodide in the presence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a light, volatile, colourless, flammable liquid with a distinctive alcoholic odour similar to that of ethanol (potable alcohol). A polar solvent, methanol acquired the name wood alcohol because it was once produced chiefly by the destructive distillation of wood. Today, methanol is mainly produced industrially by hydrogenation of carbon monoxide. Methanol consists of a methyl group linked to a polar hydroxyl group. With more than 20 million tons produced annually, it is used as a precursor to other commodity chemicals, including formaldehyde, acetic acid, methyl tert-butyl ether, methyl benzoate, anisole, peroxyacids, as well as a host of more specialised chemicals. Occurrence Small amounts of methanol are present in normal, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for polar molecules and the most common solvent used by living things; all the ions and proteins in a cell are dissolved in water within the cell. The quantity of solute that can dissolve in a specific volume of solvent varies with temperature. Major uses of solvents are in paints, paint removers, inks, and dry cleaning. Specific uses for organic Organic may refer to: * Organic, of or relating to an organism, a living entity * Organic, of or relating to an anatomical organ Chemistry * Organic matter, matter that has come from a once-living organism, is capable of decay or is the product ... solvents are in dry cleaning (e.g. tetrachloroethylene); as paint thinners ( toluene, turpentine); as nail polish removers and solvents of glue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Iodide
Hydrogen iodide () is a diatomic molecule and hydrogen halide. Aqueous solutions of HI are known as hydroiodic acid or hydriodic acid, a strong acid. Hydrogen iodide and hydroiodic acid are, however, different in that the former is a gas under standard conditions, whereas the other is an aqueous solution of the gas. They are interconvertible. HI is used in organic and inorganic synthesis as one of the primary sources of iodine and as a reducing agent. Properties of hydrogen iodide HI is a colorless gas that reacts with oxygen to give water and iodine. With moist air, HI gives a mist (or fumes) of hydroiodic acid. It is exceptionally soluble in water, giving hydroiodic acid. One liter of water will dissolve 425 liters of HI gas, the most concentrated solution having only four water molecules per molecule of HI. Hydroiodic acid Hydroiodic acid is not pure hydrogen iodide, but a mixture containing it. Commercial "concentrated" hydroiodic acid usually contains 48–57% HI by mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Phosphorus
Elemental phosphorus can exist in several allotropes, the most common of which are white and red solids. Solid violet and black allotropes are also known. Gaseous phosphorus exists as diphosphorus and atomic phosphorus. White phosphorus White phosphorus, yellow phosphorus or simply tetraphosphorus () exists as molecules made up of four atoms in a tetrahedral structure. The tetrahedral arrangement results in ring strain and instability. The molecule is described as consisting of six single P–P bonds. Two crystalline forms are known. The α form is defined as the standard state of the element, but is actually metastable under standard conditions. It has a body-centered cubic crystal structure, and transforms reversibly into the β form at 195.2 K. The β form is believed to have a hexagonal crystal structure. White phosphorus is a translucent waxy solid that quickly becomes yellow when exposed to light. For this reason it is also called yellow phosphorus. It glows greenis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a violet gas at . The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek 'violet-coloured'. Iodine occurs in many oxidation states, including iodide (I−), iodate (), and the various periodate anions. It is the least abundant of the stable halogens, being the sixty-first most abundant element. As the heaviest essential mineral nutrient, iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities. The dominant producers of iodine today are Chile and Japan. Due to its high atomic number and ease of attachment to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1-iodobutane
Butyl iodide (1-iodobutane) is an organic compound which is an iodo derivative of butane. It is used as an alkylating agent Alkylation is the transfer of an alkyl group from one molecule to another. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting .... Isomer The compound isobutyl iodide AKA 1-iodo-2-methylpropane is isomeric to butyl iodide. References Alkylating agents Iodoalkanes {{Organohalide-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thioether
In organic chemistry, an organic sulfide (British English sulphide) or thioether is an organosulfur functional group with the connectivity as shown on right. Like many other sulfur-containing compounds, volatile sulfides have foul odors. A sulfide is similar to an ether except that it contains a sulfur atom in place of the oxygen. The grouping of oxygen and sulfur in the periodic table suggests that the chemical properties of ethers and sulfides are somewhat similar, though the extent to which this is true in practice varies depending on the application. Nomenclature Sulfides are sometimes called thioethers, especially in the old literature. The two organic substituents are indicated by the prefixes. (CH3)2S is called dimethylsulfide. Some sulfides are named by modifying the common name for the corresponding ether. For example, C6H5SCH3 is methyl phenyl sulfide, but is more commonly called thioanisole, since its structure is related to that for anisole, C6H5OCH3. The modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |