|
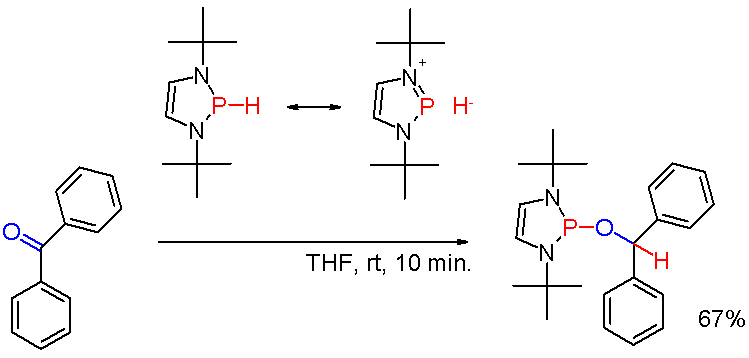
Phosphinous Acid
Phosphinous acid is the inorganic compound with the formula H2POH. It exists, fleetingly, as a mixture with its less stable tautomer H3PO (phosphine oxide). This mixture has been generated by low temperature oxidation of phosphine with ozone. H2POH is mainly of pedagogical interest. Organophosphinous acids are more prevalent than the parent H2POH. Organophosphinous acids Phosphinous acids exist mainly as minor tautomers of secondary phosphine oxides. For example diphenylphosphinous acid, which is not detectable directly, is invoked as the tautomer of diphenylphosphine oxide Diphenylphosphine oxide is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2P(O)H. It is a white solid that soluble in polar organic solvents. Synthesis Diphenylphosphine oxide can be prepared by the reaction of phosphonic esters, such as d .... Highly electron-withdrawing substituents stabilize the phosphinous acid tautomer as illustrated by (CF3)2POH.{{cite journal , doi=10.1002/chem.201102370, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting point of modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphine Oxide
Phosphine oxides are phosphorus compounds with the formula OPX3. When X = alkyl or aryl, these are organophosphine oxides. Triphenylphosphine oxide is an example. An inorganic phosphine oxide is phosphoryl chloride (POCl3). Structure and bonding Tertiary phosphine oxides Tertiary phosphine oxides are the most commonly encountered phosphine oxides. With the formula R3PO, they are tetrahedral compounds. They are usually prepared by oxidation of tertiary phosphines. The P-O bond is short and polar. According to molecular orbital theory, the short P–O bond is attributed to the donation of the lone pair electrons from oxygen p-orbitals to the antibonding phosphorus-carbon bonds. The nature of the P–O bond was once hotly debated. Some discussions invoked a role for phosphorus-centered d-orbitals in bonding, but this analysis is not supported by computational analyses. In terms of simple Lewis structure, the bond is more accurately represented as a dative bond, as is currently us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphine
Phosphine (IUPAC name: phosphane) is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic compound with the chemical formula , classed as a pnictogen hydride. Pure phosphine is odorless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphane (). With traces of present, is spontaneously flammable in air ( pyrophoric), burning with a luminous flame. Phosphine is a highly toxic respiratory poison, and is immediately dangerous to life or health at 50 ppm. Phosphine has a trigonal pyramidal structure. Phosphines are compounds that include and the organophosphines, which are derived from by substituting one or more hydrogen atoms with organic groups. They have the general formula . Phosphanes are saturated phosphorus hydrides of the form , such as triphosphane. Phosphine, PH3, is the smallest of the phosphines and the smallest of the phosphanes. History Philippe Gengembre (1764–1838), a student of Lavois ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lower atmosphere to (dioxygen). Ozone is formed from dioxygen by the action of ultraviolet (UV) light and electrical discharges within the Earth's atmosphere. It is present in very low concentrations throughout the latter, with its highest concentration high in the ozone layer of the stratosphere, which absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Ozone's odour is reminiscent of chlorine, and detectable by many people at concentrations of as little as in air. Ozone's O3 structure was determined in 1865. The molecule was later proven to have a bent structure and to be weakly diamagnetic. In standard conditions, ozone is a pale blue gas that condenses at cryogenic temperatures to a dark blue liquid and finally a violet-black soli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphinous Acids
Phosphinous acids are usually organophosphorus compounds with the formula R2POH. They are pyramidal in structure. Phosphorus is in the oxidation state III. Most phosphinous acids rapidly convert to the corresponding phosphine oxide, which are tetrahedral and are assigned oxidation state V. Synthesis Only one example is known, bis(trifluoromethyl)phosphinous acid, (CF3)2POH. It is prepared in several steps from phosphorus trichloride (Et = ethyl): :PCl3 + 2 Et2NH → PCl2NEt2 + Et2NH2Cl :2 P(NEt2)3 + PCl2NEt2 + 2 CF3Br → P(CF3)2NEt2 + 2 BrClP(NEt2)3 :P(CF3)2NEt2 + H2O → P(CF3)2OH + HNEt2 Reactions With the lone exception of the bis(trifluoromethyl) derivative, the dominant reaction of phosphinous acids is tautomerization: :PR2OH → OPR2H Even the pentafluorophenyl compound P(C6F5)2OH is unstable with respect to the phosphine oxide. Although phosphinous acids are rare, their P-bonded coordination complexes are well established, e.g. Mo(CO)5P(OH)3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Phosphine Oxide
Phosphine oxides are phosphorus compounds with the formula OPX3. When X = alkyl or aryl, these are organophosphine oxides. Triphenylphosphine oxide is an example. An inorganic phosphine oxide is phosphoryl chloride (POCl3). Structure and bonding Tertiary phosphine oxides Tertiary phosphine oxides are the most commonly encountered phosphine oxides. With the formula R3PO, they are tetrahedral compounds. They are usually prepared by oxidation of tertiary phosphines. The P-O bond is short and polar. According to molecular orbital theory, the short P–O bond is attributed to the donation of the lone pair electrons from oxygen p-orbitals to the antibonding phosphorus-carbon bonds. The nature of the P–O bond was once hotly debated. Some discussions invoked a role for phosphorus-centered d-orbitals in bonding, but this analysis is not supported by computational analyses. In terms of simple Lewis structure, the bond is more accurately represented as a dative bond, as is currently u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphenylphosphine Oxide
Diphenylphosphine oxide is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2P(O)H. It is a white solid that soluble in polar organic solvents. Synthesis Diphenylphosphine oxide can be prepared by the reaction of phosphonic esters, such as diethylphosphite, with Grignard reagents followed by acid workup: :(C2H5O)2P(O)H + 3C6H5MgBr → (C6H5)2P(O)MgBr + C2H5OMgBr :(C6H5)2P(O)MgBr + HCl → (C6H5)2P(O)H + MgBrCl Alternatively, it may be prepared by the partial hydrolysis of chlorodiphenylphosphine or diphenylphosphine. Reactions Diphenylphosphine oxide exists in equilibrium with its minor tautomer diphenylphosphinous acid, ((C6H5)2POH: : Diphenylphosphine oxide is used in Buchwald-Hartwig coupling reactions to introduce diphenylphosphino substituents. Thionyl chloride converts diphenylphosphine oxide to chlorodiphenylphosphine. Organophosphinous acids are deoxygenated with DIBAH. The resulting secondary phosphines are precursors to phosphine ligand A metal-phos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Groups
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis. A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a functional group are linked to each other and to the rest of the molecule by covalent bonds. For repeating units of polymers, functional groups attach to their nonpolar core of carbon atoms and thus add chemical character to carbon chains. Functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organophosphine Oxides
Organophosphines are organophosphorus compounds with the formula PR''n''H3−''n'', where R is an organic substituent. These compounds can be classified according to the value of ''n'': primary phosphines (''n'' = 1), secondary phosphines (''n'' = 2), tertiary phosphines (''n'' = 3). All adopt pyramidal structures. Organophosphines are generally colorless, lipophilic liquids or solids. The parent of the organophosphines is phosphine (PH3). Annette Schier and Hubert Schmidbaur"P-Donor Ligands" in Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry 2006, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. 1° vs 2° vs 3° phosphines Organophophines are classified according to the number of organic substituents. Primary phosphines Primary (1°) phosphines, with the formula RPH2, are typically prepared by alkylation of phosphine. Simple alkyl derivatives such as methylphosphine (CH3PH2) are prepared by alkylation of alkali metal derivatives MPH2 (M is Li, Na, or K). Another synthetic route in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |