|
Phosphatidylglycerol
Phosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant and in the plasma membrane where it directly activates lipid-gated ion channels. The general structure of phosphatidylglycerol consists of a L-glycerol 3-phosphate backbone ester-bonded to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. The head group substituent glycerol is bonded through a phosphomonoester. It is the precursor of surfactant and its presence (>0.3) in the amniotic fluid of the newborn indicates fetal lung maturity. Approximately 98% of alveolar wall surface area is due to the presence of type I cells, with type II cells producing pulmonary surfactant covering around 2% of the alveolar walls. Once surfactant is secreted by the type II cells, it must be spread over the remaining type I cellular surface area. Phosphatidylglycerol is thought to be important in spreading of surfactant over the Type I cellular surface area. The major surfactant deficiency in premature infants r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphatidylglycerol
Phosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant and in the plasma membrane where it directly activates lipid-gated ion channels. The general structure of phosphatidylglycerol consists of a L-glycerol 3-phosphate backbone ester-bonded to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. The head group substituent glycerol is bonded through a phosphomonoester. It is the precursor of surfactant and its presence (>0.3) in the amniotic fluid of the newborn indicates fetal lung maturity. Approximately 98% of alveolar wall surface area is due to the presence of type I cells, with type II cells producing pulmonary surfactant covering around 2% of the alveolar walls. Once surfactant is secreted by the type II cells, it must be spread over the remaining type I cellular surface area. Phosphatidylglycerol is thought to be important in spreading of surfactant over the Type I cellular surface area. The major surfactant deficiency in premature infants r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiolipin Synthase
Cardiolipin (IUPAC name 1,3-bis(''sn''-3’-phosphatidyl)-''sn''-glycerol) is an important component of the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it constitutes about 20% of the total lipid composition. It can also be found in the membranes of most bacteria. The name "cardiolipin" is derived from the fact that it was first found in animal hearts. It was first isolated from beef heart in the early 1940s by Mary C. Pangburn. In mammalian cells, but also in plant cells, cardiolipin (CL) is found almost exclusively in the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it is essential for the optimal function of numerous enzymes that are involved in mitochondrial energy metabolism. Structure Cardiolipin (CL) is a kind of diphosphatidylglycerol lipid. Two phosphatidic acid moieties connect with a glycerol backbone in the center to form a dimeric structure. So it has four alkyl groups and potentially carries two negative charges. As there are four distinct alkyl chains in cardiolipin, the potent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiolipin
Cardiolipin (IUPAC name 1,3-bis(''sn''-3’-phosphatidyl)-''sn''-glycerol) is an important component of the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it constitutes about 20% of the total lipid composition. It can also be found in the membranes of most bacteria. The name "cardiolipin" is derived from the fact that it was first found in animal hearts. It was first isolated from beef heart in the early 1940s by Mary C. Pangburn. In mammalian cells, but also in plant cells, cardiolipin (CL) is found almost exclusively in the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it is essential for the optimal function of numerous enzymes that are involved in mitochondrial energy metabolism. Structure Cardiolipin (CL) is a kind of diphosphatidylglycerol lipid. Two phosphatidic acid moieties connect with a glycerol backbone in the center to form a dimeric structure. So it has four alkyl groups and potentially carries two negative charges. As there are four distinct alkyl chains in cardiolipin, the potenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiolipin
Cardiolipin (IUPAC name 1,3-bis(''sn''-3’-phosphatidyl)-''sn''-glycerol) is an important component of the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it constitutes about 20% of the total lipid composition. It can also be found in the membranes of most bacteria. The name "cardiolipin" is derived from the fact that it was first found in animal hearts. It was first isolated from beef heart in the early 1940s by Mary C. Pangburn. In mammalian cells, but also in plant cells, cardiolipin (CL) is found almost exclusively in the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it is essential for the optimal function of numerous enzymes that are involved in mitochondrial energy metabolism. Structure Cardiolipin (CL) is a kind of diphosphatidylglycerol lipid. Two phosphatidic acid moieties connect with a glycerol backbone in the center to form a dimeric structure. So it has four alkyl groups and potentially carries two negative charges. As there are four distinct alkyl chains in cardiolipin, the potenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Surfactant
Pulmonary surfactant is a surface-active complex of phospholipids and proteins formed by type II alveolar cells. The proteins and lipids that make up the surfactant have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water. Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, t ... regions. By adsorption, adsorbing to the air-water Interface (chemistry), interface of pulmonary alveolus, alveoli, with hydrophilic head groups in the water and the hydrophobic tails facing towards the air, the main lipid component of surfactant, dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), reduces surface tension. As a medication, Pulmonary surfactant (medication), pulmonary surfactant is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, the most important medications needed in a basic health system. Function * To increase pulmonary com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
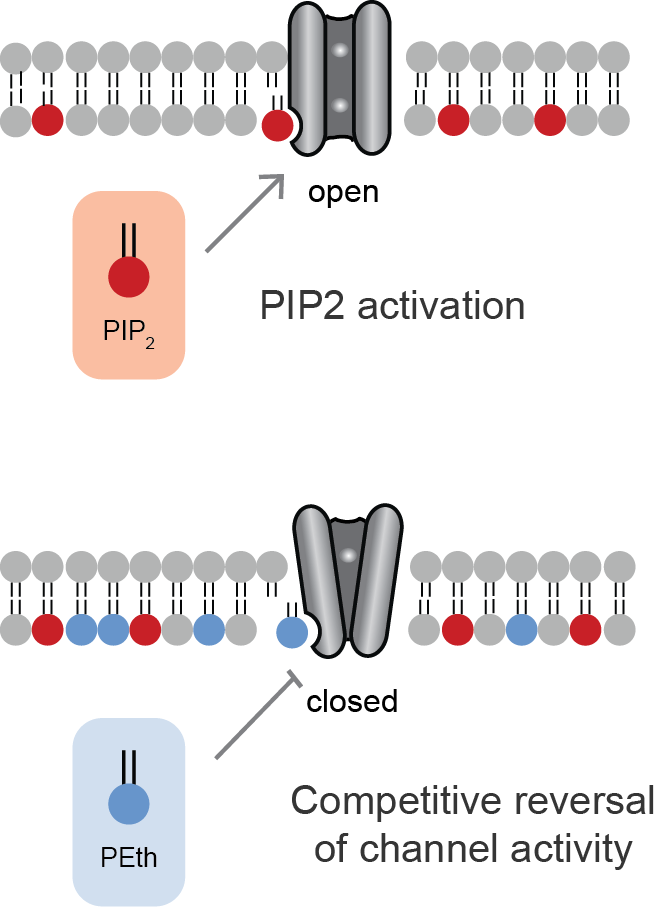
Lipid-gated Ion Channels
Lipid-gated ion channels are a class of ion channels whose conductance of ions through the membrane depends directly on lipids. Classically the lipids are membrane resident anionic signaling lipids that bind to the transmembrane domain on the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane with properties of a classic ligand. Other classes of lipid-gated channels include the mechanosensitive ion channels that respond to lipid tension, thickness, and hydrophobic mismatch. A lipid ligand differs from a lipid cofactor in that a ligand derives its function by dissociating from the channel while a cofactor typically derives its function by remaining bound. PIP2-gated channels Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) was the first and remains the best studied lipid to gate ion channels. PIP2 is a cell membrane lipid, and its role in gating ion channels represents a novel role for the molecule. Kir channels: PIP2 binds to and directly activates inwardly rectifying potassium channels (Kir) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid-gated Ion Channels
Lipid-gated ion channels are a class of ion channels whose conductance of ions through the membrane depends directly on lipids. Classically the lipids are membrane resident anionic signaling lipids that bind to the transmembrane domain on the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane with properties of a classic ligand. Other classes of lipid-gated channels include the mechanosensitive ion channels that respond to lipid tension, thickness, and hydrophobic mismatch. A lipid ligand differs from a lipid cofactor in that a ligand derives its function by dissociating from the channel while a cofactor typically derives its function by remaining bound. PIP2-gated channels Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) was the first and remains the best studied lipid to gate ion channels. PIP2 is a cell membrane lipid, and its role in gating ion channels represents a novel role for the molecule. Kir channels: PIP2 binds to and directly activates inwardly rectifying potassium channels (Kir) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycerophospholipid
Glycerophospholipids or phosphoglycerides are glycerol-based phospholipids. They are the main component of biological membranes. Two major classes are known: those for bacteria and eukaryotes and a separate family for archaea. Structures The term glycerophospholipid signifies any derivative of glycerophosphoric acid that contains at least one ''O''-acyl, or ''O''-alkyl, or ''O''-alk-1'-enyl residue attached to the glycerol moiety. The phosphate group forms an ester linkage to the glycerol. The long-chained hydrocarbons are typically attached through ester linkages in bacteria/eucaryotes and by ether linkages in archaea. In bacteria and procaryotes, the lipids consist of diesters commonly of C16 or C18 fatty acids. These acids are straight-chained and, especially for the C18 members, can be unsaturated. For archaea, the hydrocarbon chains have chain lengths of C10, C15, C20 etc. since they are derived from isoprene units. These chains are branched, with one methyl substitue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipase D
Phospholipase D (EC 3.1.4.4, lipophosphodiesterase II, lecithinase D, choline phosphatase, PLD; systematic name phosphatidylcholine phosphatidohydrolase) is an enzyme of the phospholipase superfamily that catalyses the following reaction : a phosphatidylcholine + H2O = choline + a phosphatidate Phospholipases occur widely, and can be found in a wide range of organisms, including bacteria, yeast, plants, animals, and viruses. Phospholipase D's principal substrate is phosphatidylcholine, which it hydrolyzes to produce the signal molecule phosphatidic acid (PA), and soluble choline in a cholesterol dependent process called substrate presentation. Plants contain numerous genes that encode various PLD isoenzymes, with molecular weights ranging from 90 to 125 kDa. Mammalian cells encode two isoforms of phospholipase D: PLD1 and PLD2. Phospholipase D is an important player in many physiological processes, including membrane trafficking, cytoskeletal reorganization, receptor-mediated e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosynthesis Of Phosphatidylglycerol, Phosphatidylserine, And Phosphatidylethanolamine
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism. The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytidine Triphosphate
Cytidine triphosphate (CTP) is a pyrimidine nucleoside triphosphate. CTP, much like ATP, consists of a ribose sugar, and three phosphate groups. The major difference between the two molecules is the base used, which in CTP is cytosine. CTP is a substrate in the synthesis of RNA. CTP is a high-energy molecule similar to ATP, but its role as an energy coupler is limited to a much smaller subset of metabolic reactions. CTP is a coenzyme in metabolic reactions like the synthesis of glycerophospholipids, where it is used for activation and transfer of diacylglycerol and lipid head groups, and glycosylation of proteins. CTP acts as an inhibitor of the enzyme aspartate carbamoyltransferase, which is used in pyrimidine biosynthesis.Blackburn, G. Michael. ''Nucleic Acids in Chemistry and Biology''. The Royal Society of Chemistry, 2006, p. 119-120. See also * CTP synthase * Cytidine * Cytosine Cytosine () ( symbol C or Cyt) is one of the four nucleobases found in DNA and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrophosphate
In chemistry, pyrophosphates are phosphorus oxyanions that contain two phosphorus atoms in a P–O–P linkage. A number of pyrophosphate salts exist, such as disodium pyrophosphate (Na2H2P2O7) and tetrasodium pyrophosphate (Na4P2O7), among others. Often pyrophosphates are called diphosphates. The parent pyrophosphates are derived from partial or complete neutralization of pyrophosphoric acid. The pyrophosphate bond is also sometimes referred to as a phosphoanhydride bond, a naming convention which emphasizes the loss of water that occurs when two phosphates form a new P–O–P bond, and which mirrors the nomenclature for anhydrides of carboxylic acids. Pyrophosphates are found in ATP and other nucleotide triphosphates, which are important in biochemistry. The term pyrophosphate is also the name of esters formed by the condensation of a phosphorylated biological compound with inorganic phosphate, as for dimethylallyl pyrophosphate. This bond is also referred to as a high-energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |