|
Phonological History Of The High Back Vowels
Most dialects of modern English have two close back vowels: the near-close near-back rounded vowel found in words like ''foot'', and the close back rounded vowel (realized as central in many dialects) found in words like ''goose''. The vowel , which historically was back, is often central as well. This article discusses the history of these vowels in various dialects of English, focusing in particular on phonemic splits and mergers involving these sounds. Historical development The Old English vowels included a pair of short and long close back vowels, and , both written (the longer vowel is often distinguished as in modern editions of Old English texts). There was also a pair of back vowels of mid-height, and , both of which were written (the longer vowel is often in modern editions). The same four vowels existed in the Middle English system. The short vowels were still written and , but long came to be spelt as , and as . Generally, the Middle English vowels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic (Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in the 8th and 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonological History Of English Close Front Vowels
The close and mid-height front vowels of English (vowels of ''i'' and ''e'' type) have undergone a variety of changes over time and often vary by dialect. Developments involving long vowels Until Great Vowel Shift Middle English had a long close front vowel , and two long mid front vowels: the close-mid and the open-mid . The three vowels generally correspond to the modern spellings , and respectively, but other spellings are also possible. The spellings that became established in Early Modern English are mostly still used today, but the qualities of the sounds have changed significantly. The and generally corresponded to similar Old English vowels, and came from Old English or . For other possible histories, see English historical vowel correspondences. In particular, the long vowels sometimes arose from short vowels by Middle English open syllable lengthening or other processes. For example, ''team'' comes from an originally-long Old English vowel, and ''eat'' com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labial Consonant
Labial consonants are consonants in which one or both lips are the active articulator. The two common labial articulations are bilabials, articulated using both lips, and labiodentals, articulated with the lower lip against the upper teeth, both of which are present in English. A third labial articulation is dentolabials, articulated with the upper lip against the lower teeth (the reverse of labiodental), normally only found in pathological speech. Generally precluded are linguolabials, in which the tip of the tongue contacts the posterior side of the upper lip, making them coronals, though sometimes, they behave as labial consonants. The most common distribution between bilabials and labiodentals is the English one, in which the nasal and the stops, , , and , are bilabial and the fricatives, , and , are labiodental. The voiceless bilabial fricative, voiced bilabial fricative, and the bilabial approximant do not exist as the primary realizations of any sounds in English, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Modern English
Early Modern English or Early New English (sometimes abbreviated EModE, EMnE, or ENE) is the stage of the English language from the beginning of the Tudor period to the English Interregnum and Restoration, or from the transition from Middle English, in the late 15th century, to the transition to Modern English, in the mid-to-late 17th century. Before and after the accession of James I to the English throne in 1603, the emerging English standard began to influence the spoken and written Middle Scots of Scotland. The grammatical and orthographical conventions of literary English in the late 16th century and the 17th century are still very influential on modern Standard English. Most modern readers of English can understand texts written in the late phase of Early Modern English, such as the '' King James Bible'' and the works of William Shakespeare, and they have greatly influenced Modern English. Texts from the earlier phase of Early Modern English, such as the late-15th-ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pembrokeshire
Pembrokeshire ( ; cy, Sir Benfro ) is a Local government in Wales#Principal areas, county in the South West Wales, south-west of Wales. It is bordered by Carmarthenshire to the east, Ceredigion to the northeast, and the rest by sea. The county is home to Pembrokeshire Coast National Park. The Park occupies more than a third of the area of the county and includes the Preseli Hills in the north as well as the Pembrokeshire Coast Path. Historically, mining and fishing were important activities, while industry nowadays is focused on agriculture (86 per cent of land use), oil and gas, and tourism; Pembrokeshire's beaches have won many awards. The county has a diverse geography with a wide range of geological features, habitats and wildlife. Its prehistory and modern history have been extensively studied, from tribal occupation, through Roman times, to Welsh, Irish, Norman, English, Scandinavian and Flemish influences. Pembrokeshire County Council's headquarters are in the county ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
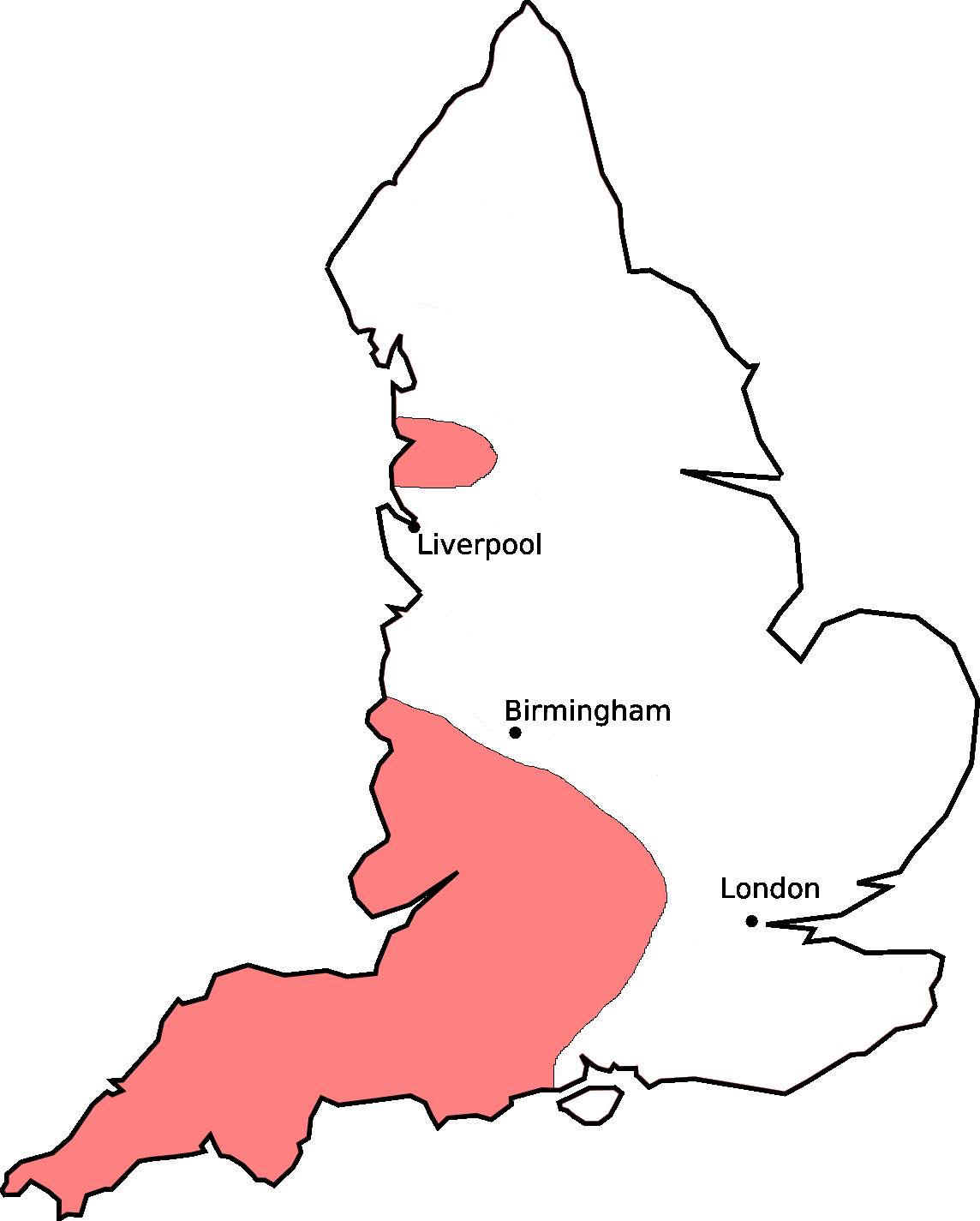
Cheshire Dialect
Cheshire ( ) is a ceremonial and historic county in North West England, bordered by Wales to the west, Merseyside and Greater Manchester to the north, Derbyshire to the east, and Staffordshire and Shropshire to the south. Cheshire's county town is the cathedral city of Chester, while its largest town by population is Warrington. Other towns in the county include Alsager, Congleton, Crewe, Ellesmere Port, Frodsham, Knutsford, Macclesfield, Middlewich, Nantwich, Neston, Northwich, Poynton, Runcorn, Sandbach, Widnes, Wilmslow, and Winsford. Cheshire is split into the administrative districts of Cheshire West and Chester, Cheshire East, Halton, and Warrington. The county covers and has a population of around 1.1 million as of 2021. It is mostly rural, with a number of towns and villages supporting the agricultural and chemical industries; it is primarily known for producing chemicals, Cheshire cheese, salt, and silk. It has also had an impact on popular culture, producing notabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scouse
Scouse (; formally known as Liverpool English or Merseyside English) is an Accent (dialect), accent and dialect of English language, English associated with Liverpool and the surrounding county of Merseyside. The Scouse accent is highly distinctive; having been influenced heavily by Irish, Norwegian, and Welsh immigrants who arrived via the Liverpool docks, it has little in common with the accents of its neighbouring regions or the rest of England. Scouse is also a general term for this pan-ethnic community or Liverpool, Liverpudlians in general. The accent is named after Scouse (food), scouse, a stew eaten by sailors and locals. The development of Liverpool since the 1950s has spread the accent into nearby areas such as the towns of Runcorn and Skelmersdale. Variations within Scouse have been noted: the accent of Liverpool's Liverpool city centre, city centre and northern neighbourhoods is usually described as fast, harsh, and nasal, while the accent found in the southern s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welsh English
Welsh English ( cy, Saesneg Gymreig) comprises the dialects of English spoken by Welsh people. The dialects are significantly influenced by Welsh grammar and often include words derived from Welsh. In addition to the distinctive words and grammar, a variety of accents are found across Wales, including those of North Wales, the Cardiff dialect, the South Wales Valleys and West Wales. Accents and dialects in the west of Wales have been more heavily influenced by the Welsh language while dialects in the east have been influenced more by dialects in England. In the east and south east, it has been influenced by West Country and West Midland dialects while in north east Wales and parts of the North Wales coast, it has been influenced by Merseyside English. A colloquial portmanteau word for Welsh English is Wenglish. It has been in use since 1985. Pronunciation Vowels Short monophthongs * The vowel of ''cat'' is pronounced either as an open front unrounded vowel or a mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiberno-English
Hiberno-English (from Latin ''Hibernia'': "Ireland"), and in ga, Béarla na hÉireann. or Irish English, also formerly Anglo-Irish, is the set of English dialects native to the island of Ireland (including both the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland). In the Republic of Ireland, English is one of two official languages, along with the Irish language, and is the country's working language. Irish English's writing standards, such as its spelling, align with British English. However, Irish English's diverse accents and some of its grammatical structures and vocabulary are unique, with some influences deriving from the Irish language and some notably conservative phonological features: features no longer common in the accents of England or North America. Phonologists today often divide Irish English into four or five overarching dialects or accents:Hickey, Raymond. ''A Sound Atlas of Irish English'', Volume 1. Walter de Gruyter: 2004pp. 57–60. Ulster English, Ulster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language In England
The English language spoken and written in England encompasses a diverse range of accents and dialects. The language forms part of the broader British English, along with other varieties in the United Kingdom. Terms used to refer to the English language spoken and written in England include: English English and Anglo-English. The related term ''British English'' has many ambiguities and tensions in the word ''British'', so it can be used and interpreted in multiple ways, but it is usually reserved to describe the features common to Anglo-English, Welsh English and Scottish English (England, Wales and Scotland are the three traditional countries on the island of Great Britain; the main dialect of the fourth country of the United Kingdom, Northern Ireland, is Ulster English, which is generally considered a dialect of Hiberno-English). General features There are many different accents and dialects throughout England and people are often very proud of their local accent or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language In Northern England
The English language in Northern England has been shaped by the region's history of settlement and migration, and today encompasses a group of related dialects known as Northern England English (or, simply, Northern English in the United Kingdom). The strongest influence on the modern varieties of the English language spoken in Northern England is the Northumbrian dialect of Middle English, but also contact with Old Norse during the Viking Age, with Irish English following the Great Famine and particularly in Lancashire and the south of Yorkshire, with midlands dialects since the industrial revolution, have produced new and distinctive styles of speech. Some "Northern" traits can be found further south than others: only conservative Northumbrian dialects retain the pre-Great Vowel Shift pronunciation of words such as ''town'' (, ), but all northern accents lack the FOOT–STRUT split, and this trait extends a significant distance into the Midlands. There are traditional di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English period. Scholarly opinion varies, but the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' specifies the period when Middle English was spoken as being from 1150 to 1500. This stage of the development of the English language roughly followed the High to the Late Middle Ages. Middle English saw significant changes to its vocabulary, grammar, pronunciation, and orthography. Writing conventions during the Middle English period varied widely. Examples of writing from this period that have survived show extensive regional variation. The more standardized Old English language became fragmented, localized, and was, for the most part, being improvised. By the end of the period (about 1470) and aided by the invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in 14 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |