|
Philosophical Essays On Freud
''Philosophical Essays on Freud'' is a 1982 anthology of articles about Sigmund Freud and psychoanalysis edited by the philosophers Richard Wollheim and James Hopkins. Published by Cambridge University Press, it includes an introduction from Hopkins and an essay from Wollheim, as well as selections from philosophers such as Ludwig Wittgenstein, Clark Glymour, Adam Morton, Stuart Hampshire, Brian O'Shaughnessy, Jean-Paul Sartre, Thomas Nagel, and Donald Davidson. The essays deal with philosophical questions raised by the work of Freud, including topics such as materialism, intentionality, and theories of the self's structure. They represent a range of different viewpoints, most of them from within the tradition of analytic philosophy. The book received a mixture of positive, mixed, and negative reviews. Commentators found the contributions included in the book to be of uneven value. Summary ''Philosophical Essays on Freud'' includes an introduction from James Hopkins and select ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Wollheim
Richard Arthur Wollheim (5 May 1923 − 4 November 2003) was a British philosopher noted for original work on mind and emotions, especially as related to the visual arts, specifically, painting. Wollheim served as the president of the British Society of Aesthetics from 1992 onwards until his death in 2003. Biography Richard Wollheim was the son of Eric Wollheim, a theatre impresario, and Constance (Connie) Mary Baker, an actress who used the stage name Constance Luttrell. He attended Westminster School, London, and Balliol College, Oxford (1941–2, 1945–8), interrupted by active military service in World War II. In 1949 he obtained a congratulatory first in Philosophy, Politics and Economics, and began teaching at University College London, where he became Grote Professor of Mind and Logic and Department Head from 1963 to 1982. He retired from that position to take up professorships, first, at Columbia University (1982–85) and then the University of California at Berk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytic Philosophy
Analytic philosophy is a branch and tradition of philosophy using analysis, popular in the Western world and particularly the Anglosphere, which began around the turn of the 20th century in the contemporary era in the United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and Scandinavia, and continues today. Analytic philosophy is often contrasted with continental philosophy, coined as a catch-all term for other methods prominent in Europe. Central figures in this historical development of analytic philosophy are Gottlob Frege, Bertrand Russell, G. E. Moore, and Ludwig Wittgenstein. Other important figures in its history include the logical positivists (particularly Rudolf Carnap), W. V. O. Quine, and Karl Popper. After the decline of logical positivism, Saul Kripke, David Lewis, and others led a revival in metaphysics. Elizabeth Anscombe, Peter Geach, Anthony Kenny and others brought analytic approach to Thomism. Analytic philosophy is characterized by an empha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defence Mechanisms
In psychoanalytic theory, a defence mechanism (American English: defense mechanism), is an unconscious psychological operation that functions to protect a person from anxiety-producing thoughts and feelings related to internal conflicts and outer stressors. The idea of defence mechanisms comes from psychoanalytic theory, a psychological perspective of personality that sees personality as the interaction between three components: id, ego, and super-ego. These psychological strategies may help people put distance between themselves and threats or unwanted feelings, such as guilt or shame. Defence mechanisms may result in healthy or unhealthy consequences depending on the circumstances and frequency with which the mechanism is used.Utah Psych. "Defense Mechanisms" 2010. Retrieved on 05 October 2013. Defence mechanisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Nature
Human nature is a concept that denotes the fundamental dispositions and characteristics—including ways of thinking, feeling, and acting—that humans are said to have naturally. The term is often used to denote the essence of humankind, or what it 'means' to be human. This usage has proven to be controversial in that there is dispute as to whether or not such an essence actually exists. Arguments about human nature have been a central focus of philosophy for centuries and the concept continues to provoke lively philosophical debate. While both concepts are distinct from one another, discussions regarding human nature are typically related to those regarding the comparative importance of genes and environment in human development (i.e., ' nature versus nurture'). Accordingly, the concept also continues to play a role in academic fields, such as the natural sciences, social sciences, history, and philosophy, in which various theorists claim to have yielded insight into hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
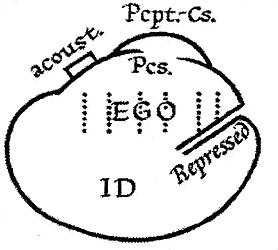
Id (psychology)
The id, ego, and super-ego are a set of three concepts in psychoanalytic theory describing distinct, interacting agents in the psychic apparatus (defined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche). The three agents are theoretical constructs that describe the activities and interactions of the mental life of a person. In the ego psychology model of the psyche, the id is the set of uncoordinated instinctual desires; the super-ego plays the critical and moralizing role; and the ego is the organized, realistic agent that mediates between the instinctual desires of the id and the critical super-ego; Freud explained that: The functional importance of the ego is manifested in the fact that, normally, control over the approaches to motility devolves upon it. Thus, in its relation to the id, he egois like a man on horseback, who has to hold in check the superior strength of the horse; with this difference, that the rider tries to do so with his own strength, while the ego uses b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat whereas the latter is defined as the emotional response to a real threat. It is often accompanied by nervous behavior such as pacing back and forth, somatic complaints, and rumination. Anxiety is a feeling of uneasiness and worry, usually generalized and unfocused as an overreaction to a situation that is only subjectively seen as menacing. It is often accompanied by muscular tension, restlessness, fatigue, inability to catch one's breath, tightness in the abdominal region, nausea, and problems in concentration. Anxiety is closely related to fear, which is a response to a real or perceived immediate threat (fight or flight response); anxiety involves the expectation of future threat including dread. People facing anxiety may withdraw fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repression (psychology)
Repression is a key concept of psychoanalysis, where it is understood as a defence mechanism that "ensures that what is unacceptable to the conscious mind, and would if recalled arouse anxiety, is prevented from entering into it." According to psychoanalytic theory, repression plays a major role in many mental illnesses, and in the psyche of the average person.Laplanche pp. 390, 392 There has been debate as to whether (or how often) memory repression really occurs and mainstream psychology holds that true memory repression occurs infrequently. American psychologists began to attempt to study repression in the experimental laboratory around 1930. However, psychoanalysts were at first uninterested in attempts to study repression in laboratory settings, and later came to reject them. Most psychoanalysts concluded that such attempts misrepresented the psychoanalytic concept of repression. Sigmund Freud's theory As Sigmund Freud moved away from hypnosis, and towards urging his patient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The International Journal Of Psychoanalysis
''The International Journal of Psychoanalysis'' is an academic journal in the field of psychoanalysis. The idea of the journal was proposed by Ernest Jones in a letter to Sigmund Freud dated 7 December 1918. The journal itself was established in 1920, with Jones serving as editor until 1939, the year of Freud's death. ''The International Journal of Psychoanalysis'' incorporates the ''International Review of Psycho-Analysis'', founded in 1974 by Joseph Sandler. It is run by the Institute of Psychoanalysis. For the last 95 years, the ''IJP'' has enjoyed its role as the main international vehicle for communication about psychoanalysis, enjoying a wide international readership from Europe, the Middle East, Africa, Asia-Pacific, North America, and Latin America. Past Editors of the ''International Journal'' have included Ernest Jones, James Strachey, Joseph Sandler, and David Tuckett. In 2015 the ''IJP'' had around 9000 subscribers. Dana Birksted-Breen is the current Editor in Chief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Popper
Sir Karl Raimund Popper (28 July 1902 – 17 September 1994) was an Austrian-British philosopher, academic and social commentator. One of the 20th century's most influential philosophers of science, Popper is known for his rejection of the classical inductivist views on the scientific method in favour of empirical falsification. According to Popper, a theory in the empirical sciences can never be proven, but it can be falsified, meaning that it can (and should) be scrutinised with decisive experiments. Popper was opposed to the classical justificationist account of knowledge, which he replaced with critical rationalism, namely "the first non-justificational philosophy of criticism in the history of philosophy". In political discourse, he is known for his vigorous defence of liberal democracy and the principles of social criticism that he believed made a flourishing open society possible. His political philosophy embraced ideas from major democratic political ideologies, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoscience
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or falsifiability, unfalsifiable claims; reliance on confirmation bias rather than rigorous attempts at refutation; lack of openness to Peer review, evaluation by other experts; absence of systematic practices when developing Hypothesis, hypotheses; and continued adherence long after the pseudoscientific hypotheses have been experimentally discredited. The demarcation problem, demarcation between science and pseudoscience has scientific, philosophical, and political implications. Philosophers debate the nature of science and the general criteria for drawing the line between scientific theory, scientific theories and pseudoscientific beliefs, but there is general agreement on examples such as ancient astronauts, climate change denial, dowsing, evolution denial, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Cioffi
: ''Frank L. Cioffi, of Baruch College is Frank Cioffi's nephew.''"There Is No Theory of Everything" Simon Critchley in "The Stone" blog in ''The New York Times'' September 12, 2015'' Frank Cioffi (11 January 1928 – 1 January 2012) was an American philosopher educated in New York and Oxford. Cioffi held posts at the University of Singapore, the University of Kent and the University of Essex, where he was a founding member of the Department of Philosophy. He wrote extensively on Sigmund Freud and psychoanalysis, Ludwig Wittgenstein, and behaviour and explanation. On 29 July 1989 he made an extended appearance on the British TV discussion programme ''After Dark (TV series), After Dark'', alongside, among others, Steven Rose, David Edward Jenkins, The Bishop of Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy Of Science
Philosophy of science is a branch of philosophy concerned with the foundations, methods, and implications of science. The central questions of this study concern what qualifies as science, the reliability of scientific theories, and the ultimate purpose of science. This discipline overlaps with metaphysics, ontology, and epistemology, for example, when it explores the relationship between science and truth. Philosophy of science focuses on metaphysical, epistemic and semantic aspects of science. Ethical issues such as bioethics and scientific misconduct are often considered ethics or science studies rather than the philosophy of science. There is no consensus among philosophers about many of the central problems concerned with the philosophy of science, including whether science can reveal the truth about unobservable things and whether scientific reasoning can be justified at all. In addition to these general questions about science as a whole, philosophers of science consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.png)
