|
Philippe-Thomas Chabert De Joncaire
Philippe-Thomas Chabert de Joncaire (), also known as Nitachinon by the Iroquois, was a French army officer and interpreter in New France who established Fort Machault in the 18th century. During his career, he largely served as a diplomat with the indigenous nations rather than as a soldier. Early life Philippe-Thomas Chabert de Joncaire was the eldest son of Louis-Thomas Chabert de Joncaire (1670–1739) and Marie-Madeleine Le Gay. He was baptized in Montreal on January 9, 1707. He was the older brother of Daniel-Marie Chabert de Joncaire de Clausonne. Joncaire was given by his father to the Seneca at the age of 10 and was raised by the Iroquois. Career Early career Joncaire joined the colonial French army in 1726 and attained the rank of second ensign in 1727. On July 23, 1731, he married Madeleine Renaud Dubuisson. In 1735, Joncaire succeeded his father as the principal interpreter and political agent from New France to the Iroquois. His responsibilities included ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis-Thomas Chabert De Joncaire
Louis-Thomas Chabert de Joncaire (1670June 29, 1739), also known as Sononchiez by the Iroquois, was a French army officer and interpreter for New France who worked with the Iroquois tribes during the French and Indian Wars in the early 18th century. He helped negotiate the Great Peace of Montreal in 1701 and founded Fort Niagara in 1720. Early life Louis-Thomas Chabert de Joncaire was born in 1670 in Saint-Rémy-de-Provence, France, to esquire Antoine-Marie de Joncaire and Gabrielle Hardi. Joncaire came to Canada in approximately 1687 as a cavalry sergeant in the Governor General's Guard. Career as an interpreter Soon after his arrival in Canada, he was captured by members of the Seneca tribe. According to his son Daniel, Joncaire was tortured by the tribe and en route to execution at a stake, but was saved when a woman of the tribe adopted him. During Joncaire's captivity, a cordial relationship was established between him and the Iroquois which continued until his death. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Shawneetown
Lower Shawneetown, also known as Shannoah or Sonnontio, was an 18th-century Shawnee village located within the Lower Shawneetown Archeological District, near South Portsmouth in Greenup County, Kentucky and Lewis County, Kentucky. The population eventually occupied areas on both sides of the Ohio River, and along both sides of the Scioto River in what is now Scioto County, Ohio. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places on 28 April, 1983. It is near the Bentley site, a Madisonville Horizon settlement inhabited between 1400 CE and 1625 CE. Nearby, to the east, there are also four groups of Hopewell tradition mounds, built between 100 BCE and 500 CE, known as the Portsmouth Earthworks. Extensive archaelogical work has provided a clear picture of the town's appearance and activities, particularly the nature of trade, social organization, agriculture, and relationships with other Native American communities. Well-known British traders William Trent and George Croghan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
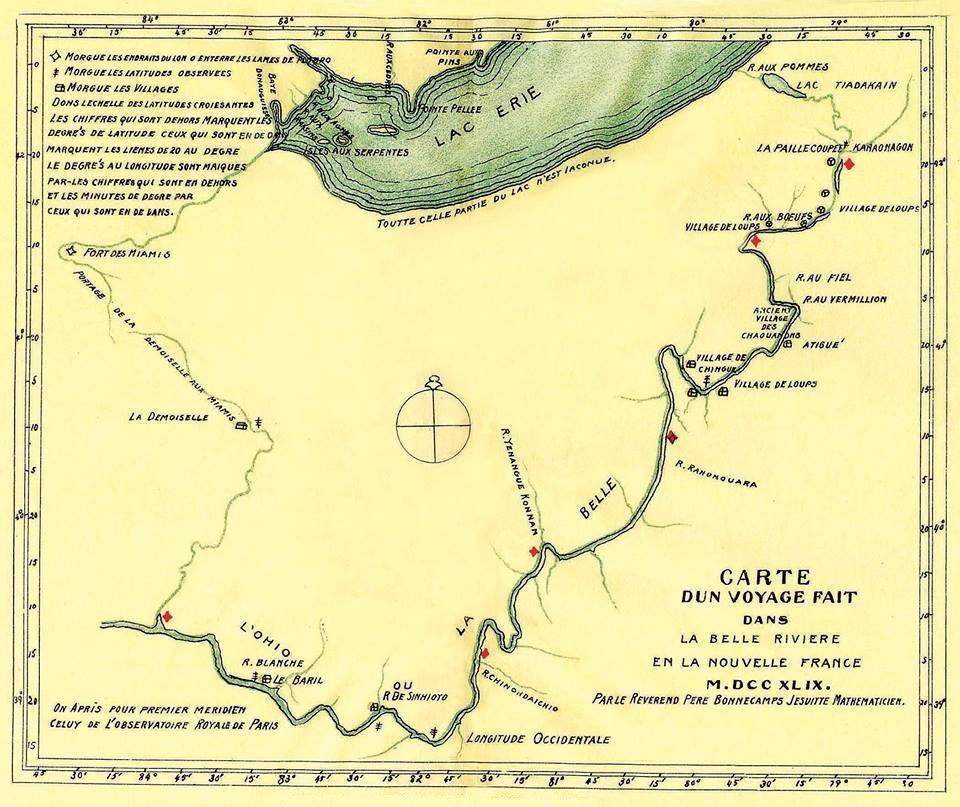
Fort LeBoeuf
Fort Le Bœuf (often referred to as Fort de la Rivière au Bœuf) was a fort established by the French during 1753 on a fork of French Creek (in the drainage area of the River Ohio), in present-day Waterford, in northwest Pennsylvania. The fort was part of a line that included Fort Presque Isle, Fort Machault, and Fort Duquesne. The fort was located about from the shores of Lake Erie, on the banks of LeBoeuf Creek, for which the fort was named. The French portaged supplies and trade goods from Lake Erie overland to Fort Le Bœuf. From there they traveled by raft and canoe down French Creek to the rivers Allegheny, Ohio and Mississippi. Today, the site of the fort is occupied by the Fort LeBoeuf Museum, operated by the Fort LeBoeuf Historical Society. History Captain Paul Marin de la Malgue began construction on 11 July 1753; Jacques Legardeur de Saint-Pierre began command of the fort on 3 December 1753. This fort was the second of a series of posts that the French built bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Washington In The French And Indian War
George Washington's military experience began in the French and Indian War with a commission as a major in the militia of the British Province of Virginia. In 1753 Washington was sent as an ambassador from the British crown to the French officials and Indians as far north as present-day Erie, Pennsylvania. The following year he led another expedition to the area to assist in the construction of a fort at present-day Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Before reaching that point, he and some of his men, along with Mingo allies led by Tanacharison, ambushed a French scouting party. Its leader was killed, although the exact circumstances of his death were disputed. This peacetime act of aggression is seen as one of the first military steps leading to the global Seven Years' War. The French responded by attacking fortifications Washington erected following the ambush, forcing his surrender. Released on parole, Washington and his troops returned to Virginia. In 1755 he participated as a vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of the Continental Army, Washington led the Patriot (American Revolution), Patriot forces to victory in the American Revolutionary War and served as the president of the Constitutional Convention (United States), Constitutional Convention of 1787, which created the Constitution of the United States and the American federal government. Washington has been called the "Father of the Nation, Father of his Country" for his manifold leadership in the formative days of the country. Washington's first public office was serving as the official Surveying, surveyor of Culpeper County, Virginia, from 1749 to 1750. Subsequently, he received his first military training (as well as a command with the Virginia Regiment) d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort D'Anjou
Fort Machault (, ) was a fort built by the French in 1754 near the confluence of French Creek with the Allegheny River, in northwest Pennsylvania. (Present-day Franklin developed here later.) The fort helped the French control these waterways, part of what was known as the Venango Path from Lake Erie to the Ohio River. It was one of four forts designed to protect French access to the Ohio Country and connections between its northern and southern colonies. From north to south the forts were Fort Presque Isle (at Lake Erie), Fort Le Boeuf (at the south end of the portage leading to the head of French Creek), Fort Machault (at the confluence noted), and Fort Duquesne, at the Forks of the Ohio. Description The fort was built on a hill, 60 yards west of the Allegheny River. The fort was in the form of a parallelogram, about 75 by . The curtain was made of hewed timber, stacked lengthwise. The four corners had bastions in the form of polygons. The bastions were built of sap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venango, Pennsylvania
Venango is a borough in Crawford County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 214 at the 2020 census, down from 239 at the 2010 census, down from 288 in 2000. Geography Venango is located in north-central Crawford County at (41.772815, -80.110813). It is bordered by Venango Township to the north, west, and south, and by Cambridge Township to the east, across French Creek. According to the United States Census Bureau, the borough has a total area of , all land. Venango is located on conjoined U.S. Route 6 and U.S. Route 19, with Cambridge Springs to the northeast and Meadville, the county seat, to the south. Interstate 79 passes to the west of Venango, but without any nearby exits. Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 288 people, 104 households, and 79 families residing in the borough. The population density was . There were 112 housing units at an average density of . The racial makeup of the borough was 96.53% White, 2.43% African American, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Creek (Allegheny River Tributary)
French Creek (also known as the Venango River) is a tributary of the Allegheny River in northwestern Pennsylvania and western New York in the United States. Name The stream has been sometimes called a river and sometimes a creek. It is thought that the stream's Seneca name, ''in nungash'', was modified over time to ''Venango''. The phrase ''in nungash'' may have derived from ''Onenga'', the Seneca word for mink, or it may have stemmed from ''Winingus'', the Delaware (Lenape) word for the same animal. Interpretations of ''Venango'' have included "crooked", and the Seneca chief Cornplanter suggested that ''in nungash'' referred to a particular carving on a tree along the stream. ''Venango'' was likewise the name of a native settlement at the creek's mouth, later the site of Franklin, Pennsylvania. In the 18th century, the stream was an important link between the Great Lakes and the Ohio River. The French built Fort Presque Isle and Fort Le Boeuf to control the portage from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean De Lauson
Jean de Lauzon or de Lauson (; 2 January 1586 – 16 February 1666) was the governor of New France from 1651 to 1657, one of the most challenging times for the new colony. He also was born into being the lord of Lirec. As a prominent lawyer in France, in 1613 Lauzon was appointed a counsellor in the Parliament. He served in several government positions, including president of the Grand Conseil, intendant of Provence, then of Guyenne, and of Dauphiné. Lauzon had been developing interests in the colony of New France. He was a founding member and became the director of the Compagnie des Cent-Associés. Lauzon used his influence within the company to obtain land for himself and his sons in the colony. By 1640, the Lauzons had become the biggest landowners in the colony. Their properties included the Island of Montreal and Île d'Orléans. Lauzon was appointed as governor in 1651. He moved with his three sons – including François, the eldest, who was a member of Parl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delaware People
The Lenape (, , or Lenape , del, Lënapeyok) also called the Leni Lenape, Lenni Lenape and Delaware people, are an indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands, who live in the United States and Canada. Their historical territory included present-day northeastern Delaware, New Jersey and eastern Pennsylvania along the Delaware River watershed, New York City, western Long Island, and the lower Hudson Valley. Today, Lenape people belong to the Delaware Nation and Delaware Tribe of Indians in Oklahoma; the Stockbridge–Munsee Community in Wisconsin; and the Munsee-Delaware Nation, Moravian of the Thames First Nation, and Delaware of Six Nations in Ontario. The Lenape have a matrilineal clan system and historically were matrilocal. During the last decades of the 18th century, most Lenape were removed from their homeland by expanding European colonies. The divisions and troubles of the American Revolutionary War and United States' independence pushed them farther west. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Marin De La Malgue
Paul Marin de la Malgue ( bap. 19 March 1692 – 29 October 1753) was the eldest son of Charles-Paul Marin de la Malgue and Catherine Niquet. He was born in Montreal and, as many of the prominent historical figures of his time, had a military career in the colonial regular troops. He was commissioned an ensign in May 1722, and in the same year he was given command of a post near Ashland, Wisconsin. His career was a military one with a significant amount of time spent south of New France in what is now part of the United States. His activities, which included the construction of Fort de la Rivière au Bœuf (''Fort Le Boeuf'') are significant in the attempts of the French to secure a sustainable foothold in the Ohio region. His military successes earned him the cross of Saint Louis but he died before learning of this honor. In 1730, he led the battle at the Siege of Little Butte des Mortes, in what is now Winnebago County, Wisconsin. He also fought in Nova Scotia in the Nava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captain (armed Forces)
The army rank of captain (from the French ) is a commissioned officer rank historically corresponding to the command of a company of soldiers. The rank is also used by some air forces and marine forces. Today, a captain is typically either the commander or second-in-command of a company or artillery battery (or United States Army cavalry troop or Commonwealth squadron). In the Chinese People's Liberation Army, a captain may also command a company, or be the second-in-command of a battalion. In some militaries, such as United States Army and Air Force and the British Army, captain is the entry-level rank for officer candidates possessing a professional degree, namely, most medical professionals (doctors, pharmacists, dentists) and lawyers. In the U.S. Army, lawyers who are not already officers at captain rank or above enter as lieutenants during training, and are promoted to the rank of captain after completion of their training if they are in the active component, or aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |