|
Philippe-Isidore Picot De Lapeyrouse
Philippe-Isidore Picot de Lapeyrouse or La Peirouse, Baron de Lapeyrouse (20 October 1744 in Toulouse – 18 October 1818 in château de Lapeyrouse, Haute-Garonne) was a French naturalist. He was particularly interested in the flora and fauna of the Pyrenees. After the revolution, he became the first professor of natural history in Toulouse and his collections, from 1796, were housed in the former Carmelite Monastery of Toulouse which went on to become the Muséum de l'Histoire Naturelle de Toulouse. In 1782 he was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. In 1800 he was mayor of Toulouse. The genus ''Lapeirousia'' in the family Iridaceae was named after him by his friend Pierre André Pourret, and ''not'', as is sometimes erroneously stated, after the French mariner, Jean-François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse Jean François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse (; variant spelling: ''La Pérouse''; 23 August 17411788?), often called simply Lap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lapeirousia
''Lapeirousia'' is a genus in the plant family Iridaceae. It is endemic to sub-Saharan Africa, about a third of the species occurring in fynbos. Origin of the generic name The genus ''Lapeirousia'' was described by Pierre André Pourret in Mém. Acad. Sci. Toulouse 3 : 79 (1788); Bak. In FC. 6 : 88 (1896) in part; Goldblatt in Contrib. Bol. Herb. 4 : 1 (1972); Sölch & Roessl. in FSWA. 155 : 6 (1969). Chasmatocallis Foster in Contrib. Gray Herb. 127 : 40 (1939).Dyer, R. Allen, “The Genera of Southern African Flowering Plants”. , 1975 He named the genus in honour of his friend, the botanist Philippe-Isidore Picot de Lapeyrouse. The inconsistent spellings of that name no doubt led to the original genus name being spelt "Lapeirousia" and contributed to various subsequent misspellings of the genus in various reference sources, notably "Lapeyrousia".Chittenden, Fred J. Ed., Royal Horticultural Society Dictionary of Gardening, Oxford 1951 There also has been confusion leading to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Ornithologists
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to France ** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents ** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with France ** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices Fortnite French places Arts and media * The French (band), a British rock band * "French" (episode), a live-action episode of ''The Super Mario Bros. Super Show!'' * ''Française'' (film), 2008 * French Stewart (born 1964), American actor Other uses * French (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) * French (tunic), a particular type of military jacket or tunic used in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union * French's, an American brand of mustard condiment * French catheter scale, a unit of measurement of diameter * French Defence, a chess opening * French kiss, a type of kiss involving the tongue See also * France (other) * Franch, a surname * Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century French Botanists
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium. The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1818 Deaths
Events January–March * January 1 ** Battle of Koregaon: Troops of the British East India Company score a decisive victory over the Maratha Empire. ** Mary Shelley's ''Frankenstein'' is published anonymously in London. * January 2 – The British Institution of Civil Engineers is founded. * January 3 (21:52 UTC) – Venus occults Jupiter. It is the last occultation of one planet by another before November 22, 2065. * January 6 – The Treaty of Mandeswar brings an end to the Third Anglo-Maratha War, ending the dominance of Marathas, and enhancing the power of the British East India Company, which controls territory occupied by 180 million Indians. * January 11 – Percy Bysshe Shelley's '' Ozymandias'' is published pseudonymously in London. * January 12 – The Dandy horse (''Laufmaschine'' bicycle) is invented by Karl Drais in Mannheim. * February 3 – Jeremiah Chubb is granted a British patent for the Chubb detector lock. * February 5 – Upon his death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
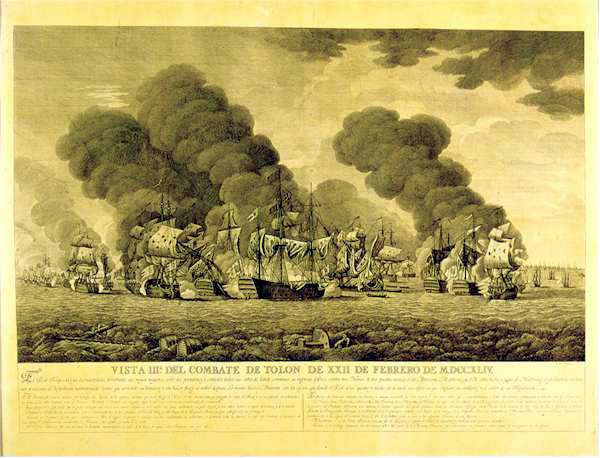
1744 Births
Events January–March * January 6 – The Royal Navy ship ''Bacchus'' engages the Spanish Navy privateer ''Begona'', and sinks it; 90 of the 120 Spanish sailors die, but 30 of the crew are rescued. * January 24 – The Dagohoy rebellion in the Philippines begins, with the killing of Father Giuseppe Lamberti. * February – Violent storms frustrate a planned French invasion of Britain. * February 22– 23 – Battle of Toulon: The British fleet is defeated by a joint Franco-Spanish fleet. * March 1 (approximately) – The Great Comet of 1744, one of the brightest ever seen, reaches perihelion. * March 13 – The British ship ''Betty'' capsizes and sinks off of the Gold Coast (modern-day Ghana) near Anomabu. More than 200 people on board die, although there are a few survivors. * March 15 – France declares war on Great Britain. April–June * April – '' The Female Spectator'' (a monthly) is founded by Eliza Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-François De Galaup, Comte De Lapérouse
Jean François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse (; variant spelling: ''La Pérouse''; 23 August 17411788?), often called simply Lapérouse, was a French naval officer and explorer. Having enlisted at the age of 15, he had a successful naval career and in 1785 was appointed to lead a scientific expedition around the world. His ships stopped in Chile, Hawaii, Alaska, California, Mauritius, Reunion, Macau, Japan, Russia, and Australia, before wrecking on the reefs of Vanikoro in the Solomon Islands. Early career Jean-François de Galaup was born near Albi, France. His family was ennobled in 1558. Lapérouse studied in a Jesuit college, and joined the Navy as a Garde-Marine in Brest on 19 November 1756. In 1757 he was appointed to the French ship ''Célèbre'' and participated in a supply expedition to the fort of Louisbourg in New France. Lapérouse also took part in a second supply expedition in 1758 to Louisbourg, but as this was in the early years of the Seven Years' War, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre André Pourret
Pierre André Pourret (1754–1818) was a French abbot and botanist who did research and teaching in France and Spain. He described and collected large amounts of plant species, especially from the Mediterranean, and amassed many species in his botanical garden and herbarium for his research. Pourret was also a pioneer user of binomial nomenclature, first developed by Carl Linnaeus. Career Pierre André Pourret was a clergyman, but started his botanical career earlier, working in the regions around his hometown, Narbonne. His given parish, however, was Saint-Jacob in Provence. He sent manuscripts of documented research to the ''Académie des sciences, inscriptions et belles-lettres de Toulouse''. During the French Revolution in 1789, Pourret was exiled to Spain. He did botanical work in Barcelona, Madrid, and ultimately the city of Ourense in Galicia. Due to xenophobia to the French during Napoleon's Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iridaceae
Iridaceae is a family of plants in order Asparagales, taking its name from the irises, meaning rainbow, referring to its many colours. There are 66 accepted genera with a total of c. 2244 species worldwide (Christenhusz & Byng 2016). It includes a number of other well known cultivated plants, such as freesias, gladioli and crocuses. Members of this family are perennial plants, with a bulb, corm or rhizome. The plants grow erect, and have leaves that are generally grass-like, with a sharp central fold. Some examples of members of this family are the blue flag and yellow flag. Name and history The family name is based on the genus '' Iris'', the largest and best known genus in Europe. This genus dates from 1753, when it was coined by Swedish botanist, Carl Linnaeus. Its name derives from the Greek goddess, Iris, who carried messages from Olympus to earth along a rainbow, whose colours were seen by Linnaeus in the multi-hued petals of many of the species. The family is cur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (taxonomy)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opinion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz Chloriteux UPS MIN PL 208b
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth's continental crust, behind feldspar. Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at . Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold. There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classified as gemstones. Since antiquity, varieties of quartz have been the most commonly used minerals in the making of jewelry and hardstone carvings, especially in Eurasia. Quartz is the mineral defining the valu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |