|
Phenoscape
Phenoscape is a project to develop a database of phenotype data for species across the Ostariophysi, a large group of teleost fish. The data is captured using annotations that combine terms from an anatomy ontology, an accompanying taxonomic ontology, and quality terms from the PATO ontology of phenotype qualities. Several other OBO ontologies are also used. The anatomy ontology was developed from the zebrafish anatomy ontology developed by the Zebrafish Information Network The Zebrafish Information NetworkZFIN is an online biological database of information about the zebrafish (''Danio rerio''). The zebrafish is a widely used model organism for Genetics, genetic, Genomics, genomic, and Developmental biology, developme .... References External links * https://phenoscape.org/ {{Database-stub Biological databases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases spans formal techniques and practical considerations, including data modeling, efficient data representation and storage, query languages, security and privacy of sensitive data, and distributed computing issues, including supporting concurrent access and fault tolerance. A database management system (DBMS) is the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS software additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an appli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostariophysi
Ostariophysi is the second-largest superorder of fish. Members of this superorder are called ostariophysians. This diverse group contains 10,758 species, about 28% of known fish species in the world and 68% of freshwater species, and are present on all continents except Antarctica. They have a number of common characteristics such as an alarm substance and a Weberian apparatus. Members of this group include fish important to people for food, sport, the aquarium industry, and research. Taxonomy The superorder is divided into two series, Anotophysi and Otophysi. However, in older literature, Ostariophysi was restricted only to the fish that are currently classified under Otophysi. Otophysi was coined in 1970 by Rosen and Greenwood to separate the traditional Ostariophysians from the added Gonorynchiformes. The superorder is classified below: *Series Anotophysi ** Gonorynchiformes, about 37 species *Series Otophysi (Euostariophysi) ** Cypriniformes (minnows and allies), about 4, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
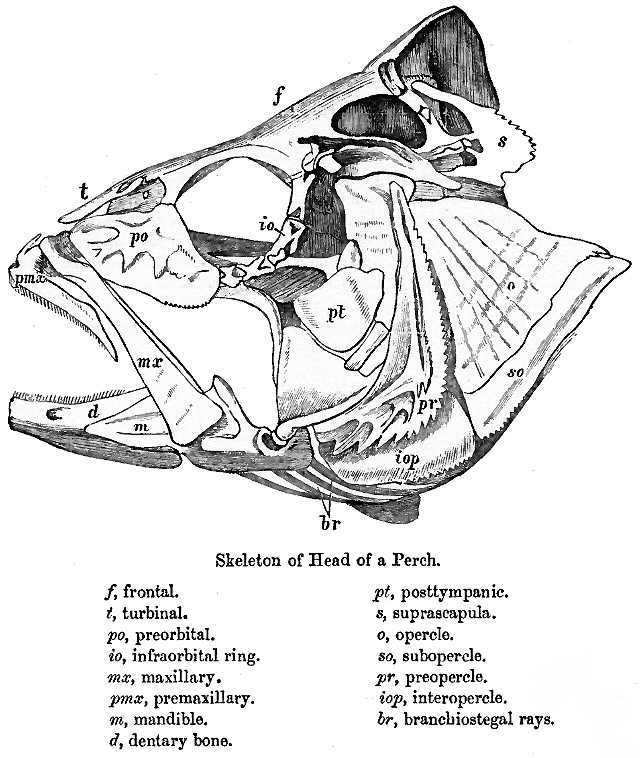
Teleost Fish
Teleostei (; Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts ), is, by far, the largest infraclass in the class Actinopterygii, the ray-finned fishes, containing 96% of all extant species of fish. Teleosts are arranged into about 40 orders and 448 families. Over 26,000 species have been described. Teleosts range from giant oarfish measuring or more, and ocean sunfish weighing over , to the minute male anglerfish ''Photocorynus spiniceps'', just long. Including not only torpedo-shaped fish built for speed, teleosts can be flattened vertically or horizontally, be elongated cylinders or take specialised shapes as in anglerfish and seahorses. The difference between teleosts and other bony fish lies mainly in their jaw bones; teleosts have a movable premaxilla and corresponding modifications in the jaw musculature which make it possible for them to protrude their jaws outwards from the mouth. This is of great advantage, enabling them to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PATO Ontology
', also called ' (, literally "duck game"), is a game played on horseback that combines elements from polo and basketball. Since 1953 it has been the national sport of Argentina. ' is Spanish for "duck", as early games used a live duck inside a basket instead of a ball. Accounts of early versions of ''pato'' have been written since 1610. The playing field would often stretch the distance between neighboring ' (ranches). The first team to reach its own ' (ranch house) with the duck would be declared the winner. ' was banned several times during its history because of the violence—not only to the duck; many gauchos were trampled underfoot, and many more died in knife fights started in the heat of the game. In 1796, a Catholic priest insisted that ' players who died in such a way should be denied Christian burial. Government ordinances forbidding the practice of ' were common throughout the 19th century. During the 1930s, ' was regulated through the efforts of ranch owner Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zebrafish Information Network
The Zebrafish Information NetworkZFIN is an online biological database of information about the zebrafish (''Danio rerio''). The zebrafish is a widely used model organism for Genetics, genetic, Genomics, genomic, and Developmental biology, developmental studies, and ZFIN provides an integrated interface for querying and displaying the large volume of data generated by this research. To facilitate use of the zebrafish as a model of human biology, ZFIN links these data to corresponding information about other model organisms (e.g., Mus musculus, mouse) and to human disease databases. Abundant links to external DNA sequence, sequence databases (e.g., GenBank) and to genome browsers are included. Gene product, gene expression, and phenotype data are annotated with terms from biomedical Ontology (computer science), ontologies. ZFIN is based at the University of Oregon in the United States, with funding provided by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Contents ZFIN consists of two prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |