|
Phase Space Method
In applied mathematics, the phase space method is a technique for constructing and analyzing solutions of dynamical systems, that is, solving time-dependent differential equations. The method consists of first rewriting the equations as a system of differential equations that are first-order in time, by introducing additional variables. The original and the new variables form a vector in the phase space. The solution then becomes a curve in the phase space, parametrized by time. The curve is usually called a trajectory or an orbit. The (vector) differential equation is reformulated as a geometrical description of the curve, that is, as a differential equation in terms of the phase space variables only, without the original time parametrization. Finally, a solution in the phase space is transformed back into the original setting. The phase space method is used widely in physics. It can be applied, for example, to find traveling wave solutions of reaction–diffusion systems. A. Kolm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applied Mathematics
Applied mathematics is the application of mathematical methods by different fields such as physics, engineering, medicine, biology, finance, business, computer science, and industry. Thus, applied mathematics is a combination of mathematical science and specialized knowledge. The term "applied mathematics" also describes the professional specialty in which mathematicians work on practical problems by formulating and studying mathematical models. In the past, practical applications have motivated the development of mathematical theories, which then became the subject of study in pure mathematics where abstract concepts are studied for their own sake. The activity of applied mathematics is thus intimately connected with research in pure mathematics. History Historically, applied mathematics consisted principally of applied analysis, most notably differential equations; approximation theory (broadly construed, to include representations, asymptotic methods, variational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamical System
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a Function (mathematics), function describes the time dependence of a Point (geometry), point in an ambient space. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, fluid dynamics, the flow of water in a pipe, the Brownian motion, random motion of particles in the air, and population dynamics, the number of fish each springtime in a lake. The most general definition unifies several concepts in mathematics such as ordinary differential equations and ergodic theory by allowing different choices of the space and how time is measured. Time can be measured by integers, by real number, real or complex numbers or can be a more general algebraic object, losing the memory of its physical origin, and the space may be a manifold or simply a Set (mathematics), set, without the need of a Differentiability, smooth space-time structure defined on it. At any given time, a dynamical system has a State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Equations
In mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more unknown functions and their derivatives. In applications, the functions generally represent physical quantities, the derivatives represent their rates of change, and the differential equation defines a relationship between the two. Such relations are common; therefore, differential equations play a prominent role in many disciplines including engineering, physics, economics, and biology. Mainly the study of differential equations consists of the study of their solutions (the set of functions that satisfy each equation), and of the properties of their solutions. Only the simplest differential equations are solvable by explicit formulas; however, many properties of solutions of a given differential equation may be determined without computing them exactly. Often when a closed-form expression for the solutions is not available, solutions may be approximated numerically using computers. The theory of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Space
In dynamical system theory, a phase space is a space in which all possible states of a system are represented, with each possible state corresponding to one unique point in the phase space. For mechanical systems, the phase space usually consists of all possible values of position and momentum variables. It is the outer product of direct space and reciprocal space. The concept of phase space was developed in the late 19th century by Ludwig Boltzmann, Henri Poincaré, and Josiah Willard Gibbs. Introduction In a phase space, every degree of freedom or parameter of the system is represented as an axis of a multidimensional space; a one-dimensional system is called a phase line, while a two-dimensional system is called a phase plane. For every possible state of the system or allowed combination of values of the system's parameters, a point is included in the multidimensional space. The system's evolving state over time traces a path (a phase-space trajectory for the system) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curve
In mathematics, a curve (also called a curved line in older texts) is an object similar to a line (geometry), line, but that does not have to be Linearity, straight. Intuitively, a curve may be thought of as the trace left by a moving point (geometry), point. This is the definition that appeared more than 2000 years ago in Euclid's Elements, Euclid's ''Elements'': "The [curved] line is […] the first species of quantity, which has only one dimension, namely length, without any width nor depth, and is nothing else than the flow or run of the point which […] will leave from its imaginary moving some vestige in length, exempt of any width." This definition of a curve has been formalized in modern mathematics as: ''A curve is the image (mathematics), image of an interval (mathematics), interval to a topological space by a continuous function''. In some contexts, the function that defines the curve is called a ''parametrization'', and the curve is a parametric curve. In this artic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trajectory
A trajectory or flight path is the path that an object with mass in motion follows through space as a function of time. In classical mechanics, a trajectory is defined by Hamiltonian mechanics via canonical coordinates; hence, a complete trajectory is defined by position and momentum, simultaneously. The mass might be a projectile or a satellite. For example, it can be an orbit — the path of a planet, asteroid, or comet as it travels around a central mass. In control theory, a trajectory is a time-ordered set of states of a dynamical system (see e.g. Poincaré map). In discrete mathematics, a trajectory is a sequence (f^k(x))_ of values calculated by the iterated application of a mapping f to an element x of its source. Physics of trajectories A familiar example of a trajectory is the path of a projectile, such as a thrown ball or rock. In a significantly simplified model, the object moves only under the influence of a uniform gravitational force field. This can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbit (dynamics)
In mathematics, specifically in the study of dynamical systems, an orbit is a collection of points related by the evolution function of the dynamical system. It can be understood as the subset of phase space covered by the trajectory of the dynamical system under a particular set of initial conditions, as the system evolves. As a phase space trajectory is uniquely determined for any given set of phase space coordinates, it is not possible for different orbits to intersect in phase space, therefore the set of all orbits of a dynamical system is a partition of the phase space. Understanding the properties of orbits by using topological methods is one of the objectives of the modern theory of dynamical systems. For discrete-time dynamical systems, the orbits are sequences; for real dynamical systems, the orbits are curves; and for holomorphic dynamical systems, the orbits are Riemann surfaces. Definition Given a dynamical system (''T'', ''M'', Φ) with ''T'' a group, ''M'' a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traveling Wave
In physics, mathematics, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from equilibrium) of one or more quantities. Waves can be periodic, in which case those quantities oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium (resting) value at some frequency. When the entire waveform moves in one direction, it is said to be a ''traveling wave''; by contrast, a pair of superimposed periodic waves traveling in opposite directions makes a ''standing wave''. In a standing wave, the amplitude of vibration has nulls at some positions where the wave amplitude appears smaller or even zero. Waves are often described by a ''wave equation'' (standing wave field of two opposite waves) or a one-way wave equation for single wave propagation in a defined direction. Two types of waves are most commonly studied in classical physics. In a ''mechanical wave'', stress and strain fields oscillate about a mechanical equilibrium. A mechanical wave is a local deformation (strain) in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction–diffusion System
Reaction–diffusion systems are mathematical models which correspond to several physical phenomena. The most common is the change in space and time of the concentration of one or more chemical substances: local chemical reactions in which the substances are transformed into each other, and diffusion which causes the substances to spread out over a surface in space. Reaction–diffusion systems are naturally applied in chemistry. However, the system can also describe dynamical processes of non-chemical nature. Examples are found in biology, geology and physics (neutron diffusion theory) and ecology. Mathematically, reaction–diffusion systems take the form of semi-linear parabolic partial differential equations. They can be represented in the general form :\partial_t \boldsymbol = \underline \,\nabla^2 \boldsymbol + \boldsymbol(\boldsymbol), where represents the unknown vector function, is a diagonal matrix of diffusion coefficients, and accounts for all local reactions. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction–diffusion System
Reaction–diffusion systems are mathematical models which correspond to several physical phenomena. The most common is the change in space and time of the concentration of one or more chemical substances: local chemical reactions in which the substances are transformed into each other, and diffusion which causes the substances to spread out over a surface in space. Reaction–diffusion systems are naturally applied in chemistry. However, the system can also describe dynamical processes of non-chemical nature. Examples are found in biology, geology and physics (neutron diffusion theory) and ecology. Mathematically, reaction–diffusion systems take the form of semi-linear parabolic partial differential equations. They can be represented in the general form :\partial_t \boldsymbol = \underline \,\nabla^2 \boldsymbol + \boldsymbol(\boldsymbol), where represents the unknown vector function, is a diagonal matrix of diffusion coefficients, and accounts for all local reactions. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
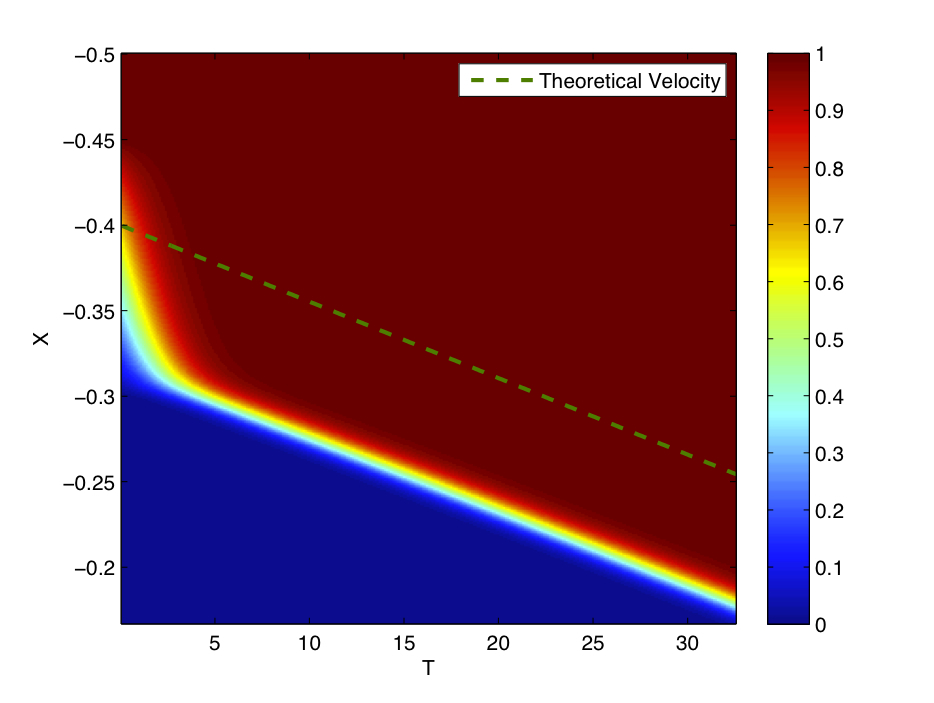
Fisher's Equation
In mathematics, Fisher's equation (named after statistician and biologist Ronald Fisher) also known as the Kolmogorov–Petrovsky–Piskunov equation (named after Andrey Kolmogorov, Ivan Petrovsky, and Nikolai Piskunov), KPP equation or Fisher–KPP equation is the partial differential equation: : \frac - D \frac = r u(1-u).\, It is a kind of reaction–diffusion system that can be used to model population growth and wave propagation. Details Fisher's equation belongs to the class of reaction–diffusion equation: in fact, it is one of the simplest semilinear reaction-diffusion equations, the one which has the inhomogeneous term : f(u,x,t) = r u (1-u),\, which can exhibit traveling wave solutions that switch between equilibrium states given by f(u) = 0. Such equations occur, e.g., in ecology, physiology, combustion, crystallization, plasma physics, and in general phase transition problems. Fisher proposed this equation in his 1937 paper ''The wave of advance of advanta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |