|
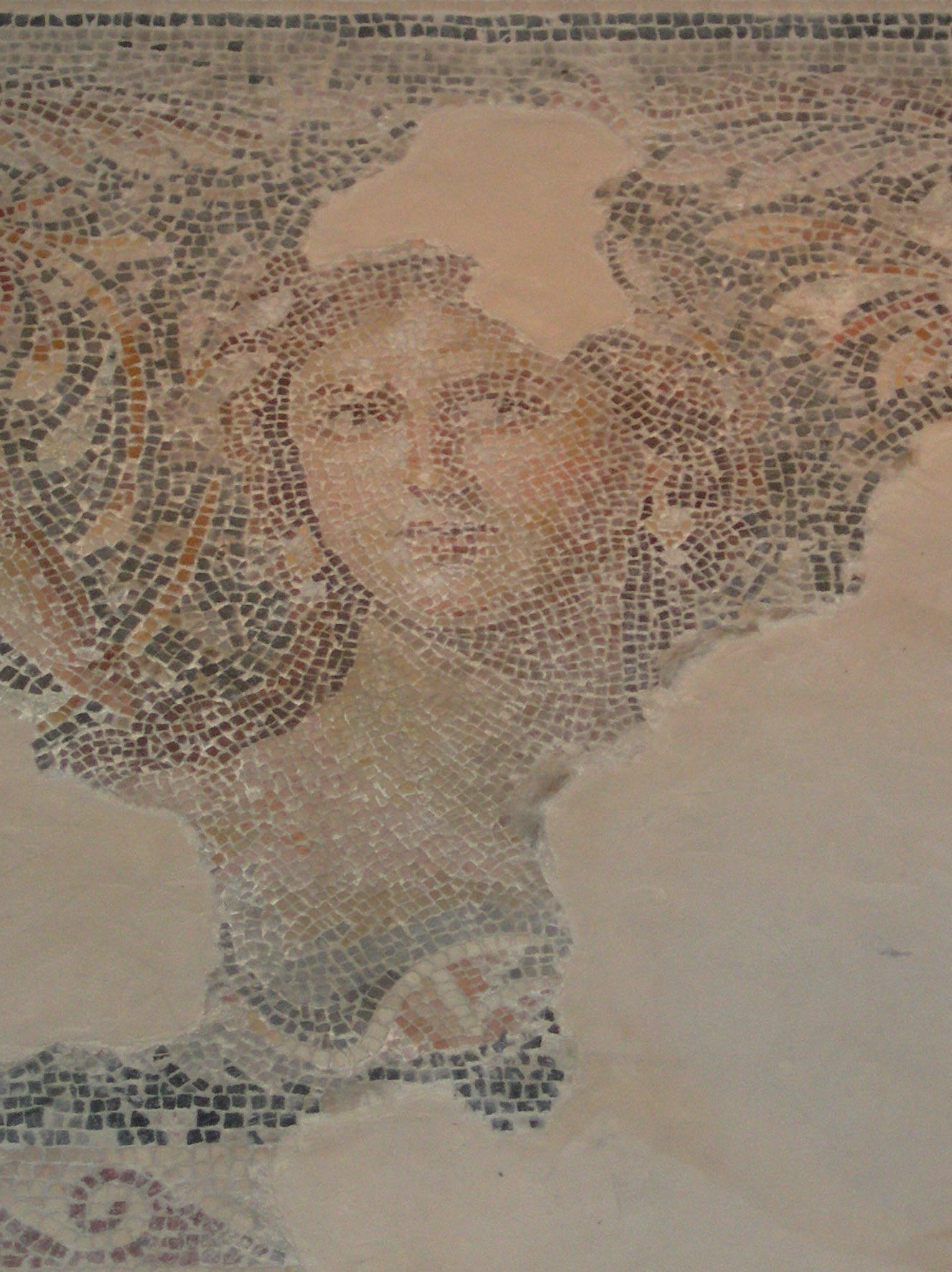
Phasa'el
Phasael or Pasiel (born in 5/4 BCE), in Greek sources Phasaelis, was a princess of Nabataean Kingdom, Nabatea, daughter of King Aretas IV Philopatris and the first wife of Herod Antipas, ruler of Galilee and Perea. Name Life Phasaelis was born to the king of the Nabataeans, Aretas IV Philopatris. The sequence in which the king's offspring is listed on an inscription found at the Obodas Chapel of Wadi Nmeir in Petra indicates that Phasaelis was the couple's fourth child, but the eldest of their daughters. Her siblings included Maliku (Malichus II), Obodat, Rabbel, Su'udat and Hagiru. Coins have been found with the profile of her father Aretas IV on the obverse, and Phasaelis' name on the reverse, which could indicate her birth to be 3-5 BC. Marriage Going by the tentative dating of the coins inscribed with her name, her marriage to Herod Antipas took place in 7 or 6 AD, when Phasaelis would have been around 11–12 years old. There is a high likelihood that the marriage w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herod Antipas
Herod Antipas (, ''Hērṓidēs Antípas''; ) was a 1st-century ruler of Galilee and Perea. He bore the title of tetrarch ("ruler of a quarter") and is referred to as both "Herod the Tetrarch" and "King Herod" in the New Testament. He was a son of Herod the Great and a grandson of Antipater the Idumaean. He is widely known today for accounts in the New Testament of his role in events that led to the executions of John the Baptist and Jesus of Nazareth (, ). Following the death of his father (4 BC in Schürer's 1890 publication, 1 BC in much of the more recent scholarship, such as Jack Finegan, W. E. Filmer, and Andrew Steinmann), Herod Antipas was recognized as tetrarch by Caesar Augustus and subsequently by his brother, the ethnarch Herod Archelaus. Antipas officially ruled Galilee and Perea as a client state of the Roman Empire.Marshall, Taylor, 2012. ''The Eternal City'', Dallas: St. John, pp. 35–65. He was responsible for building projects at Sepphoris and Betharam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
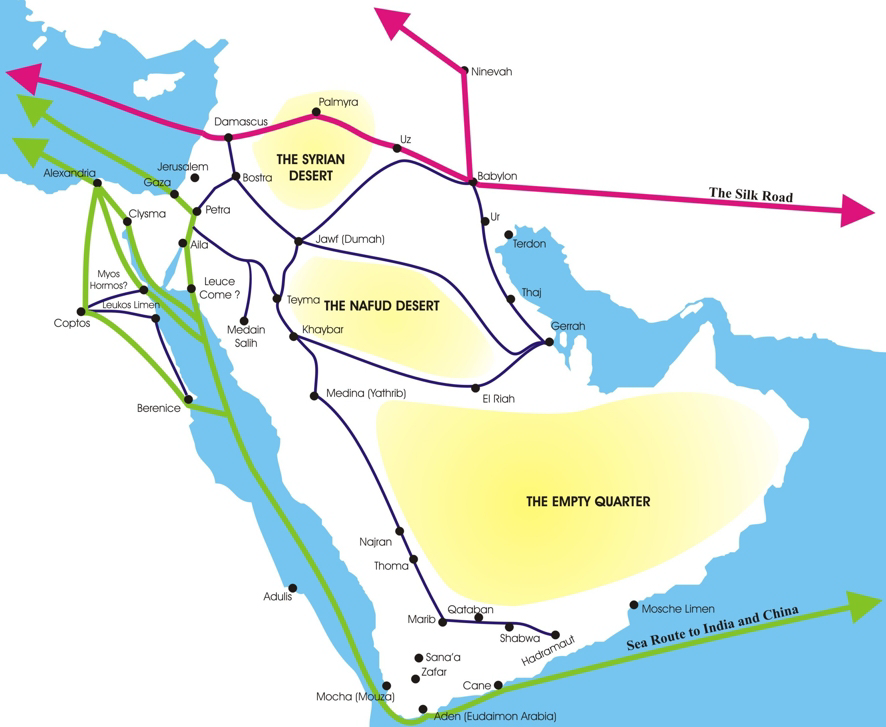
Aretas IV Philopatris
Aretas IV Philopatris (Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢊𐢛𐢞𐢞 𐢛𐢊𐢒 𐢗𐢓𐢆, ''Ḥārītaṯ Rāḥem-ʿammeh'' "Aretas, friend of his people") was the King of the Nabataeans, King of the Arab Nabataeans from roughly 9 BC to 40 AD. His daughter Phasa'el, Phasaelis was married to, and divorced from, Herod Antipas. Herod then married his stepbrother's wife, Herodias. It was opposition to this marriage that led to the beheading of John the Baptist. After he received news of the divorce, Aretas invaded the territory of Herod Antipas and defeated his army. Like his predecessors, the king's name as transcribed in Arabic is ' or ', stemming from Harith which means "the collector, provider; plowman; cultivator". Rise to power Aretas came to power after the assassination of List of Nabataean kings, Obodas III, who was apparently poisoned. Josephus says that he was originally named Aeneas, but took "Aretas" as his throne name. An inscription from Petra suggests that he may h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Book Of Longings
''The Book of Longings'' is a 2020 Christian novel by American author Sue Monk Kidd, written as a feminist reimagining of the New Testament, published by Viking. It follows a fictionalized Galilean scribe named Ana who becomes the wife of Jesus during the lost years, commenting on the silencing of women across history and literature. It received positive reviews for its respect towards the Biblical material and the characterization of its protagonists. The novel has been translated into 17 languages and a six-part miniseries adaptation was announced in 2023.Hopewell, John"'Sisi' Producer Story House Pictures to Adapt 'The Book of Longings,' About the Wife of Jesus of Nazareth" '' Variety'', 13 October 2023. Retrieved 26 August 2024. Plot Ana is the daughter of the chief scribe of Herod Antipas and the adoptive sister of Judas, a Zealot agitator. Ana learns to read and write at a young age, collecting and transcribing a personal library on Biblical women. She becomes close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herodias
Herodias (; , ''Hērōidiás''; c. 15 BC – after AD 39) was a princess of the Herodian dynasty of Judea, Judaea during the time of the Roman Empire. Christian writings connect her with the Beheading of John the Baptist, execution of John the Baptist. The daughter of Aristobulus IV and his wife Berenice (daughter of Salome), Berenice, Herodias was a full sister to Herod of Chalcis, Herod V (king of Iturea, Chalkis), Herod Agrippa (king of Judea), Aristobulus Minor, and Mariamne III (wife of Antipater (son of Herod the Great), Crown Prince Antipater). Following Antipater's execution by Herod the Great, she was possibly the first wife of Herod Archelaus, principal heir of Herod the Great and ethnarch of Judea. Marriages Herod II Herod the Great executed his sons Alexander, son of Herod, Alexander and Aristobulus IV in 7 BC, and engaged Herodias to Herod II (born ca. 27 BC; died AD 33), her half-uncle. The marriage was opposed by Antipater (son of Herod the Great), Antipater II, H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Temple Judaism
Second Temple Judaism is the Judaism, Jewish religion as it developed during the Second Temple period, which began with the construction of the Second Temple around 516 BCE and ended with the Siege of Jerusalem (70 CE), destruction of Jerusalem in 70CE. This period was marked by the emergence of multiple religious currents as well as extensive cultural, religious, and political developments among Jews. It saw the progression of the development of the Hebrew Bible canon, Hebrew Bible canon, the synagogue, and Jewish eschatology. Additionally, the Early Christianity, rise of Christianity began in the final years of the Second Temple period. According to Jewish tradition, Prophets in Judaism, authentic prophecy (, ) ceased during the early years of the Second Temple period; this left Jews without their version of divine guidance at a time when they felt most in need of support and direction. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machaerus
Machaerus (Μαχαιροῦς, from sword ; ) was a Hasmonean hilltop palace and desert fortress, rebuilt by Herod and now in ruins, located in the village of Mukawir in modern-day Jordan, southeast of the mouth of the Jordan River on the eastern side of the Dead Sea. Machaerus was built by Hasmonean king Alexander Jannaeus (r. 104–78 BCE). Destroyed later by Roman general Gabinius in 57 BCE during conflicts with Aristobulus II, it was subsequently rebuilt and expanded by Herod, who envisioned it as a potential refuge. Herod constructed a palace, cisterns, a ''mikveh'', a '' triclinium'', and a '' peristyle'' within the fortress. After the fall of Jerusalem during the First Jewish–Roman War, the fortress became a magnet for resistance against Roman rule. Following a siege by Legio X Fretensis under Bassus in 71 CE, the Jewish defenders eventually surrendered after Eleazar, a key leader, was captured. However, the Romans reneged on their agreement regarding th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dead Sea
The Dead Sea (; or ; ), also known by #Names, other names, is a landlocked salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east, the Israeli-occupied West Bank to the west and Israel to the southwest. It lies in the endorheic basin of the Jordan Rift Valley, and its main tributary is the Jordan River. As of 2025, the lake's surface is below sea level, making its shores the Lowest elevations, lowest land-based elevation on Earth. It is deep, the deepest hypersaline lake in the world. With a salinity of 342 g/kg, or 34.2% (in 2011), it is one of the List of bodies of water by salinity, world's saltiest bodies of water, 9.6 times as Seawater#Salinity, salty as the ocean—and has a density of 1.24 kg/litre, which makes swimming similar to Buoyancy, floating. This salinity makes for a harsh environment in which plants and animals cannot flourish, hence its name. The Dead Sea's main, northern basin is long and wide at its widest point. The Dead Sea has attracted visitors from around th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiquities Of The Jews
''Antiquities of the Jews'' (; , ''Ioudaikē archaiologia'') is a 20-volume historiographical work, written in Greek, by the Roman-Jewish historian Josephus in the 13th year of the reign of the Roman emperor Domitian, which was 94 CE. It contains an account of the history of the Jewish people for Josephus's gentile patrons. In the first ten volumes Josephus follows the events of the Hebrew Bible beginning with the creation of Adam and Eve. The second ten volumes continues the history of the Jewish people beyond the biblical text and up to the First Jewish–Roman War (66–73 CE). This work, along with Josephus's other major work, '' The Jewish War'' (''De Bello Iudaico''), provides valuable background material for historians wishing to understand 1st-century CE Judaism and the early Christian period. Stephen L. Harris, ''Understanding the Bible'', (Palo Alto: Mayfield, 1985). Content Josephus' ''Antiquities of the Jews'' is a vital source for the history of the intertes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbridge Streeter Brooks
Elbridge Streeter Brooks (April 14, 1846 – January 7, 1902) was an American author, editor, and critic. He is chiefly remembered as an author of numerous works of fiction and nonfiction for children, much of it on historical or patriotic subjects. His byline for most of his writing was Elbridge S. Brooks. Life and family Brooks was born on April 14, 1846, in Lowell, Massachusetts, the son of Universalist minister Elbridge Gerry Brooks and Martha Fowle (Monroe) Brooks. He was raised in Bath, Maine, Lynn, Massachusetts and New York City, where his father served in various churches. He was educated in the public schools of Lynn and New York and entered the Free Academy (later the College of the City of New York) in 1861, which he left during his junior year to seek work. Later, in 1887, he received an A.M. degree from Tufts College. As an adult he lived in Philadelphia and New York City until removing to Somerville, Massachusetts, his mother's home town, in 1887. He married, in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataean Kingdom
The Nabataean Kingdom (Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢕𐢃𐢋𐢈 ''Nabāṭū''), also named Nabatea () was a political state of the Nabataeans during classical antiquity. The Nabataean Kingdom controlled many of the trade routes of the region, amassing large wealth and drawing the envy of its neighbors. It stretched south along the Tihamah into the Hejaz, up as far north as Damascus, which it controlled for a short period (85–71 BC). Nabataea remained an independent political entity from the mid-3rd century BC until it was annexed in AD 106 by the Roman Empire, which renamed it to Arabia Petraea. History Nabataeans The Nabataeans were one among several formerly Bedouin, nomadic Arab tribes that roamed (later settled) the Arabian Desert and moved with their herds to wherever they could find pasture and water. They became familiar with their area as seasons passed, and they struggled to survive during bad years when seasonal rainfall diminished. The origin of the specific tribe of Arab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talmud
The Talmud (; ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of Haskalah#Effects, modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish culture, Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews. The Talmud includes the teachings and opinions of thousands of rabbis on a variety of subjects, including halakha, Jewish ethics, Jewish philosophy, philosophy, Jewish customs, customs, Jewish history, history, and Jewish folklore, folklore, and many other topics. The Talmud is a commentary on the Mishnah. This text is made up of 63 Masekhet, tractates, each covering one subject area. The language of the Talmud is Jewish Babylonian Aramaic. Talmudic tradition emerged and was compiled between the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE and the Arab conquest in the early seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Big Fisherman
''The Big Fisherman'' is a 1959 American historical drama film directed by Frank Borzage about the life of Simon Peter, one of the disciples of Jesus. Starring Howard Keel, Susan Kohner and John Saxon, the production is adapted from the 1948 novel of the same name by Lloyd C. Douglas. The film was shot at Universal-International studios but released by Buena Vista, the film releasing company of Walt Disney Productions. '' The Robe'' ends with "the Big Fisherman" as a nickname for Peter; Jesus called him "the fisher of men" and "the Rock". Plot The story traces Peter's journey from self-sufficient fisherman to his dependency on a risen Christ. It also presents another story of redemption and forgiveness, as he takes in a young Arab/Jewish girl, Fara. As they both learn of Jesus, it changes their lives. The young Fara discovers that she is the daughter of Herod Antipas who married and shortly discarded her Arab mother Arnon in favor of Herodias. Disguised as a boy, Fara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |