|
Pharyngeal Pouch (embryology)
In the embryonic development of vertebrates, pharyngeal pouches form on the endodermal side between the pharyngeal arches. The pharyngeal grooves (or clefts) form the lateral ectodermal surface of the neck region to separate the arches. Specific pouches First pouch The endoderm lines the future auditory tube (pharyngotympanic Eustachian tube), middle ear, mastoid antrum, and inner layer of the tympanic membrane. Derivatives of this pouch are supplied by Mandibular nerve. Second pouch * Contributes the middle ear, palatine tonsils, supplied by the facial nerve. Third pouch * The third pouch possesses dorsal and ventral wings. Derivatives of the dorsal wings include the inferior parathyroid glands, while the ventral wings fuse to form the cytoreticular cells of the thymus. The main nerve supply to the derivatives of this pouch is cranial nerve IX, glossopharyngeal nerve. Fourth pouch Derivatives include: * superior parathyroid glands and ultimobranchial body which forms the paraf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryonic Development
In developmental biology, animal embryonic development, also known as animal embryogenesis, is the developmental stage of an animal embryo. Embryonic development starts with the fertilization of an egg cell (ovum) by a sperm, sperm cell (spermatozoon). Once fertilized, the ovum becomes a single diploid cell known as a zygote. The zygote undergoes mitosis, mitotic cell division, divisions with no significant growth (a process known as cleavage (embryo), cleavage) and cellular differentiation, leading to development of a multicellular embryo after passing through an organizational checkpoint during mid-embryogenesis. In mammals, the term refers chiefly to the early stages of prenatal development, whereas the terms fetus and fetal development describe later stages. The main stages of animal embryonic development are as follows: * The zygote undergoes a series of cell divisions (called cleavage) to form a structure called a morula. * The morula develops into a structure called a bla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve (), also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper Medulla oblongata, medulla, just anterior (closer to the nose) to the vagus nerve. Being a mixed nerve (sensorimotor), it carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the Basal plate (neural tube), basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, whereas the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest. Structure From the anterior portion of the medulla oblongata, the glossopharyngeal nerve passes laterally across or below the Flocculus (cerebellar), flocculus, and leaves the skull through the central part of the jugular foramen. From the superior and inferior ganglia in jugular foramen, it has its own sheath of dura mater. The inferior ganglion on the inferior surface of petrous part of temporal is related with a tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Developmental Biology
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology, and the study of animal behaviour is known as ethology. The animal kingdom is divided into five major clades, namely Porifera, Ctenophora, Placozo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Human Cell Types Derived From The Germ Layers
This is a list of Cell (biology), cells in humans derived from the three embryonic germ layers – ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. Cells derived from ectoderm Surface ectoderm Skin * Trichocyte (human), Trichocyte * Keratinocyte Anterior pituitary * Gonadotropic cell, Gonadotrope * Corticotropic cell, Corticotrope * Thyrotropic cell, Thyrotrope * Somatotropic cell, Somatotrope * Prolactin cell, Lactotroph Tooth enamel * Ameloblast Neural crest Peripheral nervous system * Neuron * Neuroglia, Glia ** Schwann cell ** Satellite glial cell Neuroendocrine system * Chromaffin cell * Glomus cell Skin * Melanocyte ** Nevus cell * Merkel cell Teeth * Odontoblast * Cementoblast Eyes * Corneal keratocyte Smooth muscle Neural tube Central nervous system * Neuron * Glia ** Astrocyte ** Ependyma, Ependymocytes ** Müller glia (retina) ** Oligodendrocyte ** Oligodendrocyte progenitor cell ** Pituicyte (posterior pituitary) Pineal gland * Pinealocyte Cells derived from mesoderm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branchio-oto-renal Syndrome
Branchio-oto-renal syndrome (BOR) is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder involving the kidneys, ears, and neck. It is also known as Melnick-Fraser syndrome. Signs and symptoms The signs and symptoms of branchio-oto-renal syndrome are consistent with underdeveloped (hypoplastic) or absent kidneys with resultant chronic kidney disease or kidney failure. Ear anomalies include extra openings in front of the ears, extra pieces of skin in front of the ears (preauricular tags), or further malformation or absence of the outer ear ( pinna). Malformation or absence of the middle ear is also possible, individuals can have mild to profound hearing loss. People with BOR may also have cysts or fistulae along the sides of their neck. In some individuals and families, renal features are completely absent. The disease may then be termed "branchio-oto syndrome" (BO syndrome)., updated, 2015, Cause The cause of branchio-oto-renal syndrome are mutations in genes, EYA1, SIX1, and SIX5 (approxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DiGeorge Syndrome
DiGeorge syndrome, also known as 22q11.2 deletion syndrome, is a syndrome caused by a microdeletion on the long arm of chromosome 22. While the symptoms can vary, they often include congenital heart problems, specific facial features, frequent infections, developmental disability, intellectual disability and cleft palate. Associated conditions include kidney problems, schizophrenia, hearing loss and autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis or Graves' disease. DiGeorge syndrome is typically due to the deletion of 30 to 40 genes in the middle of chromosome 22 at a location known as ''22q11.2''. About 90% of cases occur due to a new mutation during early development, while 10% are inherited. It is autosomal dominant, meaning that only one affected chromosome is needed for the condition to occur. Diagnosis is suspected based on the symptoms and confirmed by genetic testing. Although there is no cure, treatment can improve symptoms. This often includes a multidisci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinus Cervicalis
The cervical sinus is a structure formed during embryonic development. It is a deep depression found on each side of the neck. It is formed as the second pharyngeal arch (hyoid arch) grows faster than the other pharyngeal arches, so they become covered. The first pharyngeal arch (mandibular arch) also grows slightly faster. It may fail to obliterate, forming a branchial cleft cyst or fistula, which is prone to infection. Structure The cervical sinus is bounded in front by the second pharyngeal arch (hyoid arch), and behind by the thoracic wall. The second pharyngeal arch (hyoid arch) grows faster than the other pharyngeal arches, so they become covered. It is ultimately obliterated by the fusion of its walls by the 7th week of gestation. Clinical significance Sometimes, the cervical sinus can fail to obliterate and thus remains as a branchial cleft cyst. The second pharyngeal arch may also not grow over the lower pharyngeal arches. This may be found anterior to the ster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
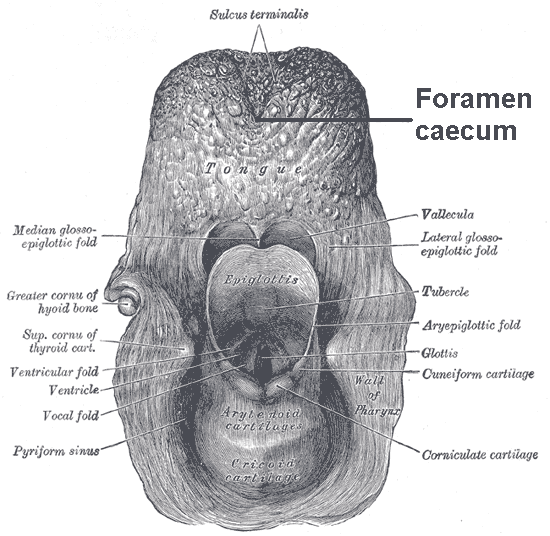
Ductus Thyreoglossus
The thyroglossal duct is an embryological anatomical structure forming an open connection between the initial area of development of the thyroid gland and its final position. It is located exactly mid-line, between the anterior 2/3 and posterior 1/3 of the tongue. The thyroid gland starts developing in the oropharynx in the fetus and descends to its final position taking a path through the tongue, hyoid bone and neck muscles. The connection between its original position and its final position is the thyroglossal duct. This duct normally atrophies and closes off as the foramen cecum before birth Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the f ... but can remain open in some people. Clinical significance A thyroglossal duct that fails to atrophy is called a persistent thyroglossal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongue
The tongue is a Muscle, muscular organ (anatomy), organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for chewing and swallowing as part of the digestive system, digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is to enable speech in humans and animal communication, vocalization in other animals. The human tongue is divided into two parts, an oral cavity, oral part at the front and a pharynx, pharyngeal part at the back. The left and right sides are also separated along most of its length by a vertical section of connective tissue, fibrous tissue (the lingual septum) that results in a groove, the median sulcus, on the tongue's surface. There are two groups of glossal muscles. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculum Impar
The median tongue bud (also tuberculum impar) marks the beginning of the development of the tongue. It appears as a midline swelling from the first pharyngeal arch late in the fourth week of embryogenesis. In the fifth week, a pair of lateral lingual swelling The tongue is a Muscle, muscular organ (anatomy), organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for chewing and swallowing as part of the digestive system, digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper s ...s (or ''distal tongue buds'') develop above and in line with the median tongue bud. These swellings grow downwards towards each other, quickly overgrowing the median tongue bud. The line of the fusion of the distal tongue buds is marked by the median sulcus. References External links * Embryology {{Portal bar, Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculum Laterale
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for chewing and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is to enable speech in humans and vocalization in other animals. The human tongue is divided into two parts, an oral part at the front and a pharyngeal part at the back. The left and right sides are also separated along most of its length by a vertical section of fibrous tissue (the lingual septum) that results in a groove, the median sulcus, on the tongue's surface. There are two groups of glossal muscles. The four intrinsic muscles alter the shape of the tongue and are not attached to bone. The four paired ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharyngeal Grooves
A pharyngeal groove (or branchial groove, or pharyngeal cleft) is made up of ectoderm unlike its counterpart the pharyngeal pouch on the endodermal side. The first pharyngeal groove produces the external auditory meatus The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the auricle to the eardrum and is about in length and in diameter. Str ... (ear canal). The rest (2, 3, and 4) are overlapped by the growing second pharyngeal arch, and form the floor of the depression termed the cervical sinus, which opens ventrally, and is finally obliterated. See also * Branchial cleft cyst * Collaural fistula References Animal developmental biology Pharyngeal arches {{developmental-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |