|
Pharmahuasca
Pharmahuasca is a pharmaceutical version of the entheogenic brew ayahuasca. Traditional ayahuasca is made by brewing the MAOI-containing Banisteriopsis caapi vine with a DMT-containing plant, such as Psychotria viridis. Pharmahuasca refers to a similar combination that uses a pharmaceutical MAOI instead of a plant. For pharmahuasca, 50 mg N,N-DMT and 100 mg harmaline is usually the recommended dosage per person. However, combinations of 50 mg harmaline, 50 mg harmine, and 50 mg, N,N-DMT have been tested with success. As a rule, the fewer the β-carbolines, the less nausea; the more DMT, the more spectacular the visions. The constituents are put into separate gelatin capsules. The capsules with harmaline/harmine are swallowed first and the capsules containing DMT are taken 15 to 20 minutes later. Purely synthetic MAO inhibitors can be used in place of harmaline and harmine, although caution must be taken when choosing an MAOI. The use of Moclobemide, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayahuasca
AyahuascaPronounced as in the UK and in the US. Also occasionally known in English as ''ayaguasca'' ( Spanish-derived), ''aioasca'' (Brazilian Portuguese-derived), or as ''yagé'', pronounced or . Etymologically, all forms but ''yagé'' descend from the compound Quechua word ''ayawaska'', from ''aya'' () and ''waska'' (). For more names for ayahuasca, see § Nomenclature. is a South AmericanGoldin D., Salani D. "Ayahuasca: What Healthcare Providers Need to Know". ''J. Addict. Nurs..'' 2021;32(2):167-173. . psychoactive and entheogenic brewed drink traditionally used both socially and as a ceremonial or shamanic spiritual medicine among the indigenous peoples of the Amazon basin, and more recently in Western society. The tea causes altered states of consciousness often known as " psychedelic experiences" which include visual hallucinations and altered perceptions of reality. Ayahuasca is commonly made from the '' Banisteriopsis caapi'' vine, the '' Psychotria viridis'' shrub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyltryptamine
''N'',''N''-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT or ''N'',''N''-DMT, SPL026) is a substituted tryptamine that occurs in many plants and animals, including human beings, and which is both a derivative and a structural analog of tryptamine. It is used as a psychedelic drug and prepared by various cultures for ritual purposes as an entheogen. DMT has a rapid onset, intense effects, and a relatively short duration of action. For those reasons, DMT was known as the "business trip" during the 1960s in the United States, as a user could access the full depth of a psychedelic experience in considerably less time than with other substances such as LSD or psilocybin mushrooms. DMT can be inhaled, ingested, or injected and its effects depend on the dose, as well as the mode of administration. When inhaled or injected, the effects last a short period of time: about five to 15 minutes. Effects can last three hours or more when orally ingested along with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmaceutical
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and relies on the science of pharmacology for continual advancement and on pharmacy for appropriate management. Drugs are classified in multiple ways. One of the key divisions is by level of control, which distinguishes prescription drugs (those that a pharmacist dispenses only on the order of a physician, physician assistant, or qualified nurse) from over-the-counter drugs (those that consumers can order for themselves). Another key distinction is between traditional small molecule drugs, usually derived from chemical synthesis, and biopharmaceuticals, which include recombinant proteins, vaccines, blood products used therapeutically (such as IVIG), gene therapy, monoclonal antibodies and cell therapy (for instance, stem cell thera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reversible Inhibitor Of Monoamine Oxidase A
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that selectively and reversibly inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the treatment of depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in the United States. Medical uses MAOIs have been found to be effective in the treatment of panic disorder with agoraphobia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysubstance Combinations
Polysubstance was used in the American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders (DSM-IV 1994) to refer to three or more drugs (including alcohol) to which an individual has become dependent (i.e., meets the diagnostic criteria for substance dependence). The criteria were changed in the DSM-5. In the DSM-IV nosology, polysubstance dependence (diagnostic code 304.80) indicated that the use of any one of the substances did not meet the diagnostic criteria for substance dependence Substance dependence, also known as drug dependence, is a biopsychological situation whereby an individual's functionality is dependent on the necessitated re-consumption of a psychoactive substance because of an adaptive state that has develope ... while the combined use of the drugs did meet substance dependence diagnostic criteria. Two research studiesMartinotti G; Carli V; Tedeschi D; Di Giannantonio M; Roy A; Janiri L; Sarchiapone, M. (2009). Mono- and polysubs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entheogen
Entheogens are psychoactive substances that induce alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition, or behavior for the purposes of engendering spiritual development or otherwiseRätsch, Christian, ''The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Plants: Ethnopharmacology and Its Applications'' pub. Park Street Press 2005 in sacred contexts. Anthropological study has established that entheogens are used for religious, magical, shamanic, or spiritual purposes in many parts of the world. Entheogens have traditionally been used to supplement many diverse practices geared towards achieving transcendence, including divination, meditation, yoga, sensory deprivation, healings, asceticism, prayer, trance, rituals, chanting, imitation of sounds, hymns like peyote songs, drumming, and ecstatic dance. The psychedelic experience is often compared to non-ordinary forms of consciousness such as those experienced in meditation, near-death experiences, and mystical experiences. Ego d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College ..., natural product, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.Chemical Encyclopedia: alkaloids xumuk.ru Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marplan
Isocarboxazid (Marplan, Marplon, Enerzer) is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class used as an antidepressant. Along with phenelzine and tranylcypromine, it is one of only three classical MAOIs still available for clinical use in the treatment of psychiatric disorders in the United States, though it is not as commonly employed in comparison to the others. Isocarboxazid is primarily used to treat mood and anxiety disorders. It has also been investigated in the treatment of schizophrenia, Parkinson's disease and other dementia-related disorders. Isocarboxazid, as well as other MAOIs, increase the levels of the monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, melatonin, phenethylamine in the brain.Volz, Hanz-Peter. (November 1998) “Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors A Perspective on Their Use in The Elderly” ''Biochemical Pharmacology'' (5) 341-352. Classical MAOIs, including isocarboxazid, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAOI
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that selectively and reversibly inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the treatment of depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in the United States. Medical uses MAOIs have been found to be effective in the treatment of panic disorder with agoraphobia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
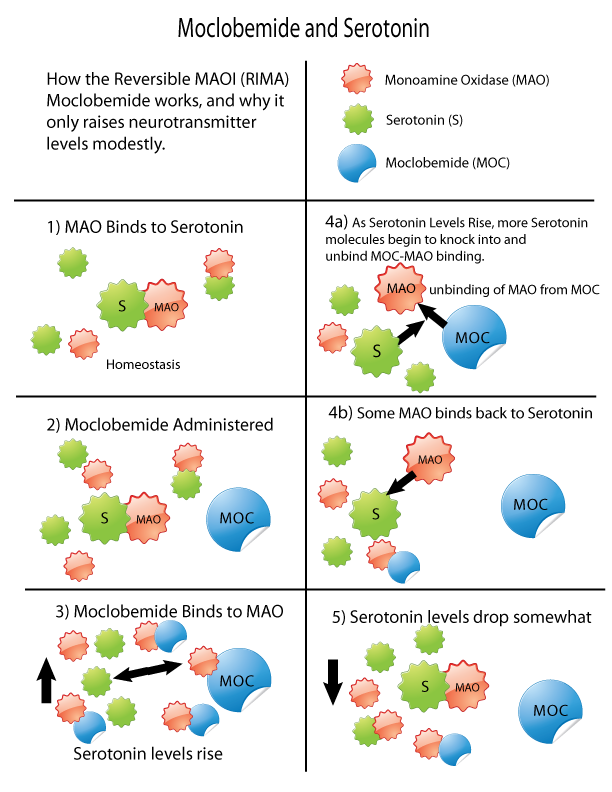
Moclobemide
Moclobemide, sold under the brand names Amira, Aurorix, Clobemix, Depnil and Manerix among others, is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) drug primarily used to treat depression and social anxiety. It is not approved for use in the United States, but is approved in other Western countries such as Canada, the UK and Australia ( TGA approved in December 2000). It is produced by affiliates of the Hoffmann–La Roche pharmaceutical company. Initially, Aurorix was also marketed by Roche in South Africa, but was withdrawn after its patent rights expired and Cipla Medpro's Depnil and Pharma Dynamic's Clorix became available at half the cost. No significant rise in blood pressure occurs when moclobemide is combined with amines such as tyramine-containing foods or pressor amine drugs, unlike with the older irreversible and non-selective monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), which cause a severe rise in blood pressure with such combination. Due to the lack of anticholine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entheogen
Entheogens are psychoactive substances that induce alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition, or behavior for the purposes of engendering spiritual development or otherwiseRätsch, Christian, ''The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Plants: Ethnopharmacology and Its Applications'' pub. Park Street Press 2005 in sacred contexts. Anthropological study has established that entheogens are used for religious, magical, shamanic, or spiritual purposes in many parts of the world. Entheogens have traditionally been used to supplement many diverse practices geared towards achieving transcendence, including divination, meditation, yoga, sensory deprivation, healings, asceticism, prayer, trance, rituals, chanting, imitation of sounds, hymns like peyote songs, drumming, and ecstatic dance. The psychedelic experience is often compared to non-ordinary forms of consciousness such as those experienced in meditation, near-death experiences, and mystical experiences. Ego d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |