|
Pharmacomicrobiomics Venn Diagram
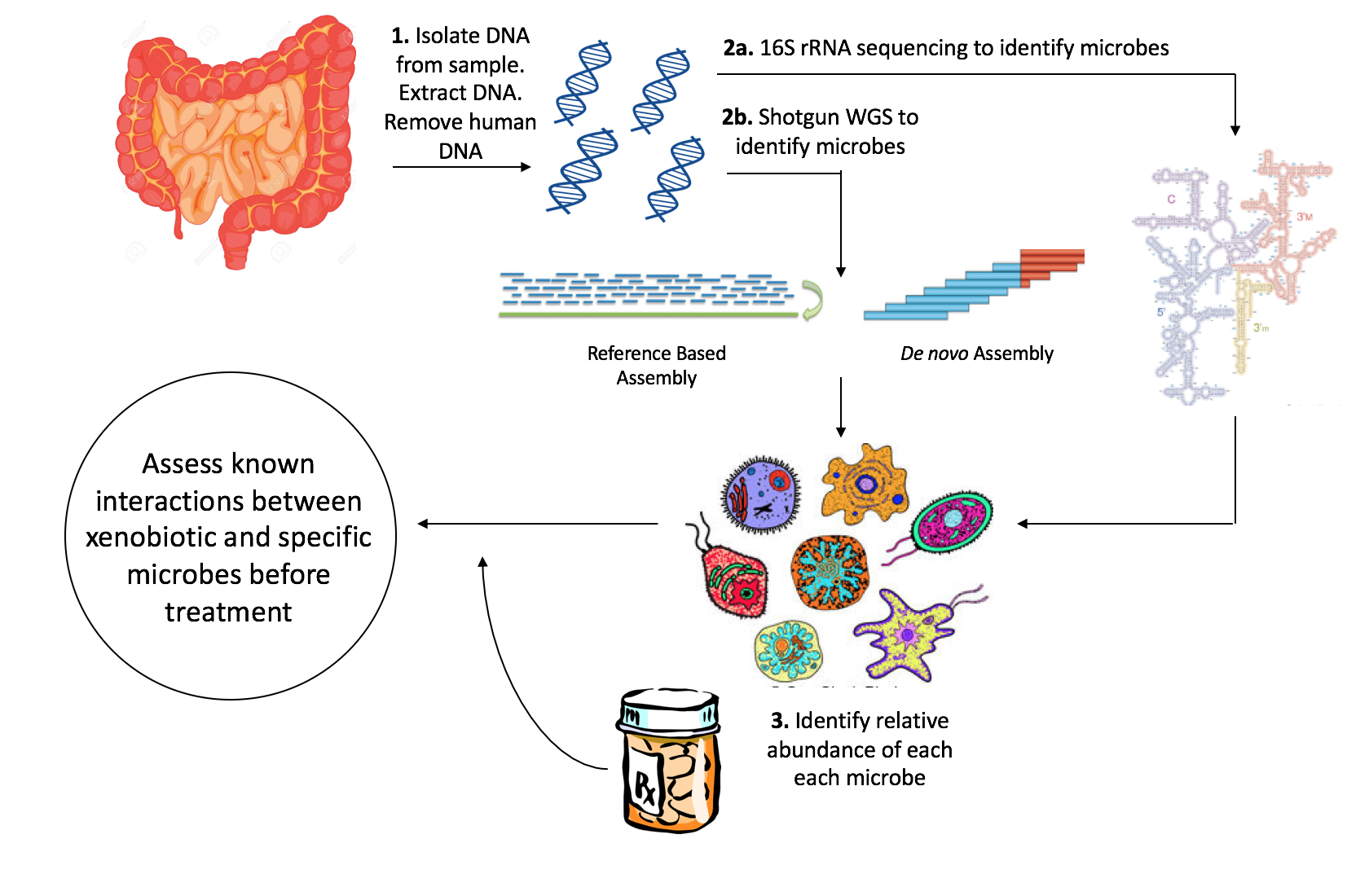
Pharmacomicrobiomics, first proposed by Prof. Marco Candela for the ERC-2009-StG project call (proposal n. 242860, titled "PharmacoMICROBIOMICS, study of the microbiome determinants of the different drug responses between individuals") and later publicly used in 2010, is defined as the effect of microbiome variations on drug disposition, action, and toxicity. Pharmacomicrobiomics is concerned with the interaction between xenobiotics, or foreign compounds, and the gut microbiome. It is estimated that over 100 trillion prokaryotes representing more than 1000 species reside in the gut. Within the gut, microbes help modulate developmental, immunological and nutrition host functions. The aggregate genome of microbes extends the metabolic capabilities of humans, allowing them to capture nutrients from diverse sources. Namely, through the secretion of enzymes that assist in the metabolism of chemicals foreign to the body, modification of liver and intestinal enzymes, and modulation of the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacomicrobiomics Venn Diagram
Pharmacomicrobiomics, first proposed by Prof. Marco Candela for the ERC-2009-StG project call (proposal n. 242860, titled "PharmacoMICROBIOMICS, study of the microbiome determinants of the different drug responses between individuals") and later publicly used in 2010, is defined as the effect of microbiome variations on drug disposition, action, and toxicity. Pharmacomicrobiomics is concerned with the interaction between xenobiotics, or foreign compounds, and the gut microbiome. It is estimated that over 100 trillion prokaryotes representing more than 1000 species reside in the gut. Within the gut, microbes help modulate developmental, immunological and nutrition host functions. The aggregate genome of microbes extends the metabolic capabilities of humans, allowing them to capture nutrients from diverse sources. Namely, through the secretion of enzymes that assist in the metabolism of chemicals foreign to the body, modification of liver and intestinal enzymes, and modulation of the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It is typically used to induce cooperation with a medical procedure. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in some instances eliminate, sensation, although analgesia and anesthesia are neurophysiologically overlapping and thus various drugs have both analgesic and anesthetic effects. Analgesic choice is also determined by the type of pain: For neuropathic pain, traditional analgesics are less effective, and there is often benefit from classes of drugs that are not normally considered analgesics, such as tricyclic antidepressants and anticonvulsants. Various analgesics, such as many NSAIDs, are available over the counter in most countries, whereas various others are prescription drugs owing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between Unicellular organism, unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the evolution of many organisms. HGT is influencing scientific understanding of higher order evolution while more significantly shifting perspectives on bacterial evolution. Horizontal gene transfer is the primary mechanism for the spread of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, and plays an important role in the evolution of bacteria that can degrade novel compounds such as human-created Bactericide, pesticides and in the evolution, maintenance, and transmission of virulence. It often involves Temperateness (virology), temperate bacteriophages and plasmids. Genes responsible for antibiotic resistance in one species of bacteria can be transferred to another species of bacteria through various m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of use, but largely include an increased risk of gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeds, heart attack, and kidney disease. The term ''non-steroidal'', common from around 1960, distinguishes these drugs from corticosteroids, which during the 1950s had acquired a bad reputation due to overuse and side-effect problems after their initial introduction in 1948. NSAIDs work by inhibiting the activity of cyclooxygenase enzymes (the COX-1 and COX-2 isoenzymes). In cells, these enzymes are involved in the synthesis of key biological mediators, namely prostaglandins, which are involved in inflammation, and thromboxanes, which are involved in blood clotting. There are two general types of NSAIDs available: non-selective, and COX-2 selective. Most N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulindac
Sulindac is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the arylalkanoic acid class that is marketed as Clinoril. Imbaral (not to be confused with mebaral) is another name for this drug. Its name is derived from sul(finyl)+ ind(ene)+ ac(etic acid) It was patented in 1969 and approved for medical use in 1976. Medical uses Like other NSAIDs, it is useful in the treatment of acute or chronic inflammatory conditions. Sulindac is a prodrug, derived from sulfinylindene, that is converted in the body to the active NSAID. More specifically, the agent is converted by liver enzymes to a sulfide that is excreted in the bile and then reabsorbed from the intestine. This is thought to help maintain constant blood levels with reduced gastrointestinal side effects. Some studies have shown sulindac to be relatively less irritating to the stomach than other NSAIDs except for drugs of the COX-2 inhibitor class . The exact mechanism of its NSAID properties is unknown, but it is thought to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfinpyrazone
Sulfinpyrazone is a uricosuric medication used to treat gout. It also sometimes is used to reduce platelet aggregation by inhibiting degranulation of platelets which reduces the release of ADP and thromboxane. Like other uricosurics, sulfinpyrazone works by competitively inhibiting uric acid reabsorption in the proximal tubule of the kidney. Contraindications Sulfinpyrazone must not be used in persons with renal impairment or a history of uric acid kidney stones. Research Trial have found that, Sulfinpyrazone taken in specific daily dose immediately following a patient having suffered from a myocardial infarction A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may ... seem to drastically reduce the incidence of sudden death by as much as 43% and cardiac mortality by 32% in the 24 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metronidazole
Metronidazole, sold under the brand name Flagyl among others, is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication. It is used either alone or with other antibiotics to treat pelvic inflammatory disease, endocarditis, and bacterial vaginosis. It is effective for dracunculiasis, giardiasis, trichomoniasis, and amebiasis. It is an option for a first episode of mild-to-moderate ''Clostridium difficile'' colitis if vancomycin or fidaxomicin is unavailable. Metronidazole is available by mouth, as a cream, and by injection into a vein. Common side effects include nausea, a metallic taste, loss of appetite, and headaches. Occasionally seizures or allergies to the medication may occur. Some state that metronidazole should not be used in early pregnancy, while others state doses for trichomoniasis are safe. Metronidazole is generally considered compatible with breastfeeding. Metronidazole began to be commercially used in 1960 in France. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Esse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antifungal
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryptococcal meningitis, and others. Such drugs are usually yes obtained by a doctor's prescription, but a few are available over the counter (OTC). Types of antifungal There are two types of antifungals: local and systemic. Local antifungals are usually administered topically or vaginally, depending on the condition being treated. Systemic antifungals are administered orally or intravenously. Of the clinically employed azole antifungals, only a handful are used systemically. These include ketoconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole, fosfluconazole, voriconazole, posaconazole, and isavuconazole. Examples of non-azole systemic antifungals include griseofulvin and terbinafine. Classes Polyenes A polyene is a molecule with multiple conjugated do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flucytosine
Flucytosine, also known as 5-fluorocytosine (5-FC), is an antifungal medication. It is specifically used, together with amphotericin B, for serious ''Candida'' infections and cryptococcosis. It may be used by itself or with other antifungals for chromomycosis. Flucytosine is used by mouth and by injection into a vein. Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, loss of appetite, diarrhea, vomiting, and psychosis. Anaphylaxis and other allergic reactions occasionally occur. It is unclear if use in pregnancy is safe for the baby. Flucytosine is in the fluorinated pyrimidine analogue family of medications. It works by being converted into fluorouracil inside the fungus, which impairs its ability to make protein. Flucytosine was first made in 1957. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. As of 2016, in the United States the medication cost about US$2,000 per day while in the United Kingdom it is about US$22 per day. It is not available in mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiotonic
A cardiac stimulant is a substance which acts as a stimulant of the heart – e.g., via positive chronotropic or inotropic action. Examples of cardiac stimulant drugs are cocaine and methamphetamine Methamphetamine (contracted from ) is a potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is mainly used as a recreational drug and less commonly as a second-line treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and obesity. Methamph .... References External links * {{cardiovascular-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digoxin
Digoxin (better known as Digitalis), sold under the brand name Lanoxin among others, is a medication used to treat various heart conditions. Most frequently it is used for atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and heart failure. Digoxin is one of the oldest medications used in the field of cardiology. It works by increasing myocardial contractility, increasing stroke volume and blood pressure, reducing heart rate, and somewhat extending the time frame of the contraction. Digoxin is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein. Digoxin has a half life of approximately 36 hours given at average doses in patients with normal renal function. It is excreted mostly unchanged in the urine. Common side effects include breast enlargement with other side effects generally due to an excessive dose. These side effects may include loss of appetite, nausea, trouble seeing, confusion, and an irregular heartbeat. Greater care is required in older people and those with poor kidney function. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes use as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis. By mouth or by injection into a vein, it is used to treat meningitis, plague, cholera, and typhoid fever. Its use by mouth or by injection is only recommended when safer antibiotics cannot be used. Monitoring both blood levels of the medication and blood cell levels every two days is recommended during treatment. Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, nausea, and diarrhea. The bone marrow suppression may result in death. To reduce the risk of side effects treatment duration should be as short as possible. People with liver or kidney problems may need lower doses. In young children a condition known as gray baby syndrome may occur which results in a swollen stomach and low blood pressure. Its use near the end of pregnancy and during breastfeeding is typically not recommended. Chloramphenicol is a broad-spectrum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |