|
Pharmacodynamic Genes And Drugs
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or combinations of organisms (for example, infection). Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics are the main branches of pharmacology, being itself a topic of biology interested in the study of the interactions between both endogenous and exogenous chemical substances with living organisms. In particular, pharmacodynamics is the study of how a drug affects an organism, whereas pharmacokinetics is the study of how the organism affects the drug. Both together influence dosing, benefit, and adverse effects. Pharmacodynamics is sometimes abbreviated as PD and pharmacokinetics as PK, especially in combined reference (for example, when speaking of PK/PD models). Pharmacodynamics places particular emphasis on dose–response relationships, that is, the relationships between drug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or combinations of organisms (for example, infection). Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics are the main branches of pharmacology, being itself a topic of biology interested in the study of the interactions between both endogenous and exogenous chemical substances with living organisms. In particular, pharmacodynamics is the study of how a drug affects an organism, whereas pharmacokinetics is the study of how the organism affects the drug. Both together influence dosing, benefit, and adverse effects. Pharmacodynamics is sometimes abbreviated as PD and pharmacokinetics as PK, especially in combined reference (for example, when speaking of PK/PD models). Pharmacodynamics places particular emphasis on dose–response relationships, that is, the relationships between d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Dynamics
Reaction dynamics is a field within physical chemistry, studying why chemical reactions occur, how to predict their behavior, and how to control them. It is closely related to chemical kinetics, but is concerned with individual chemical events on atomic length scales and over very brief time periods. It considers ''state-to-state kinetics'' between reactant and product molecules in specific quantum states, and how energy is distributed between translational, vibrational, rotational, and electronic modes. Laidler, K.J. ''Chemical Kinetics'' (3rd ed., Harper & Row 1987), Chap.12 Experimental methods of reaction dynamics probe the chemical physics associated with molecular collisions. They include crossed molecular beam and infrared chemiluminescence experiments, both recognized by the 1986 Nobel Prize in Chemistry awarded to Dudley Herschbach, Yuan T. Lee, and John C. Polanyi "for their contributions concerning the dynamics of chemical elementary processes", In the crossed beam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catecholamine
A catecholamine (; abbreviated CA) is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic compound that has a catechol (benzene with two hydroxyl side groups next to each other) and a side-chain amine. Catechol can be either a free molecule or a substituent of a larger molecule, where it represents a 1,2-dihydroxybenzene group. Catecholamines are derived from the amino acid tyrosine, which is derived from dietary sources as well as synthesis from phenylalanine. Catecholamines are water-soluble and are 50% bound to plasma proteins in circulation. Included among catecholamines are epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and dopamine. Release of the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine from the adrenal medulla of the adrenal glands is part of the fight-or-flight response. Tyrosine is created from phenylalanine by hydroxylation by the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase. Tyrosine is also ingested directly from dietary protein. Catecholamine-secreting cells use sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricyclic Antidepressant
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are a class of medications that are used primarily as antidepressants, which is important for the management of depression. They are second-line drugs next to SSRIs. TCAs were discovered in the early 1950s and were marketed later in the decade. They are named after their chemical structure, which contains three rings of atoms. Tetracyclic antidepressants (TeCAs), which contain four rings of atoms, are a closely related group of antidepressant compounds. Although TCAs are sometimes prescribed for depressive disorders, they have been largely replaced in clinical use in most parts of the world by newer antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (NRIs). Adverse effects have been found to be of a similar level between TCAs and SSRIs. Another class of antidepressants, tetracyclic antidepressants, are also used around the world, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Transport
Reverse transport, or transporter reversal, is a phenomenon in which the substrates of a membrane transport protein are moved in the opposite direction to that of their typical movement by the transporter. Transporter reversal typically occurs when a membrane transport protein is phosphorylated by a particular protein kinase, which is an enzyme that adds a phosphate group to proteins. The primary function of most neurotransmitter transporters is to facilitate neurotransmitter reuptake (i.e., the reabsorption of neurotransmitters by the cell which released them). During neurotransmitter reuptake, neurotransmitter transporters will move specific types of neurotransmitters from the extracellular space into the cytosol of a neuron or glial cell. When these transporters operate in reverse, they produce neurotransmitter efflux (i.e., the movement of neurotransmitters from the cytosol to the extracellular space via transporter-mediated release, as opposed to exocytotic release). In neuron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reuptake
Reuptake is the reabsorption of a neurotransmitter by a neurotransmitter transporter located along the plasma membrane of an axon terminal (i.e., the pre-synaptic neuron at a synapse) or glial cell after it has performed its function of transmitting a neural impulse. Reuptake is necessary for normal synaptic physiology because it allows for the recycling of neurotransmitters and regulates the level of neurotransmitter present in the synapse, thereby controlling how long a signal resulting from neurotransmitter release lasts. Because neurotransmitters are too large and hydrophilic to diffuse through the membrane, specific transport proteins are necessary for the reabsorption of neurotransmitters. Much research, both biochemical and structural, has been performed to obtain clues about the mechanism of reuptake. Protein structure The first primary sequence of a reuptake protein was published in 1990. The technique for protein sequence determination relied upon the purification, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Activator
Enzyme activators are molecules that bind to enzymes and increase their activity. They are the opposite of enzyme inhibitors. These molecules are often involved in the allosteric regulation of enzymes in the control of metabolism. An example of an enzyme activator working in this way is fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, which activates phosphofructokinase 1 and increases the rate of glycolysis in response to the hormone glucagon. In some cases, when a substrate binds to one catalytic subunit of an enzyme, this can trigger an increase in the substrate affinity as well as catalytic activity in the enzyme's other subunits, and thus the substrate acts as an activator. Examples Hexokinase-I Hexokinase-I (HK-I) is an enzyme activator because it draws glucose into the glycolysis pathway. Its function is to phosphorylate glucose releasing glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) as the product. HK-I not only signals the activation of glucose into glycolysis but also maintains a low glucose concentration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Inducer
An enzyme inducer is a type of drug that increases the metabolic activity of an enzyme either by binding to the enzyme and activating it, or by increasing the expression of the gene coding for the enzyme. It is the opposite of an enzyme repressor. See also * Enzyme activator * Enzyme inhibitor * Regulation of gene expression Regulation of gene expression, or gene regulation, includes a wide range of mechanisms that are used by cells to increase or decrease the production of specific gene products (protein or RNA). Sophisticated programs of gene expression are wide ... References External links Hepatic enzyme inducersHepatic enzyme inhibitors Medicinal chemistry Enzymes Metabolism {{medicinal-chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Inhibitor
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life, in which substrate molecules are converted into products. An enzyme facilitates a specific chemical reaction by binding the substrate to its active site, a specialized area on the enzyme that accelerates the most difficult step of the reaction. An enzyme inhibitor stops ("inhibits") this process, either by binding to the enzyme's active site (thus preventing the substrate itself from binding) or by binding to another site on the enzyme such that the enzyme's catalysis of the reaction is blocked. Enzyme inhibitors may bind reversibly or irreversibly. Irreversible inhibitors form a chemical bond with the enzyme such that the enzyme is inhibited until the chemical bond is broken. By contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and may spontaneously leave the enzyme, allowing the enzyme to resume its function. Reve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
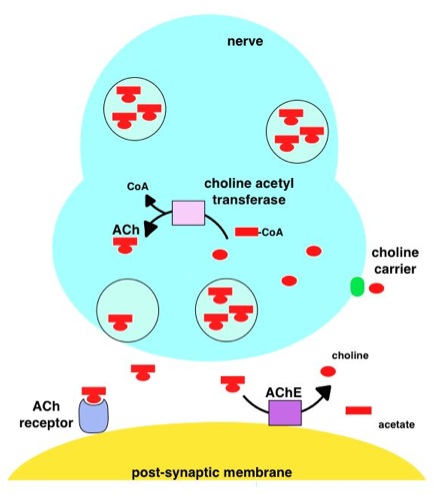
Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase (HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ... that catalysis, catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine and some other choline esters that function as neurotransmitters: : acetylcholine + H2O = choline + acetate It is found at mainly neuromuscular junctions and in chemical synapses of the cholinergic type, where its activity serves to terminate neurotransmission, synaptic transmission. It belongs to the carboxylesterase family of enzymes. It is the primary target of inhibition by organophosphorus compounds such as nerve agents and pesticides. Enzyme structure and mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neostigmine
Neostigmine, sold under the brand name Bloxiverz, among others, is a medication used to treat myasthenia gravis, Ogilvie syndrome, and urinary retention without the presence of a blockage. It is also used in anaesthesia to end the effects of non-depolarising neuromuscular blocking medication. It is given by injection either into a vein, muscle, or under the skin. After injection effects are generally greatest within 30 minutes and last up to 4 hours. Common side effects include nausea, increased saliva, crampy abdominal pain, and slow heart rate. More severe side effects include low blood pressure, weakness, and allergic reactions. It is unclear if use in pregnancy is safe for the baby. Neostigmine is in the cholinergic family of medications. It works by blocking the action of acetylcholinesterase and therefore increases the levels of acetylcholine. Neostigmine was patented in 1931. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. The term is from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |