|
Phaeocystida
Phaeocystida, also known as Phaeocystina, is a group of cercozoans in the class Phaeodarea. It was first described by Ernst Haeckel in 1887 and treated traditionally as a suborder, but later was raised to order level until Cavalier-Smith Thomas (Tom) Cavalier-Smith, FRS, FRSC, NERC Professorial Fellow (21 October 1942 – 19 March 2021), was a professor of evolutionary biology in the Department of Zoology, at the University of Oxford. His research has led to disc ...'s classification lowered it again to suborder level. It belongs to the order Eodarida, characterised by simpler silica skeletons or a lack thereof. References * Report on the Radiolaria. E Haeckel, 1887 * Report on the scientific results of the voyage of the HMS Challenger during the years 1873–1876. E Haeckel, Zoology series, 1887 External links * Phaeocystidaat the World Register of Marine Spacies (WoRMS) Phaeodaria Cercozoa orders {{Cercozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eodarida
Phaeodarea, or Phaeodaria, is a group of amoeboid cercozoan organisms. They are traditionally considered radiolarians, but in molecular trees do not appear to be close relatives of the other groups, and are instead placed among the Cercozoa. They are distinguished by the structure of their central capsule and by the presence of a phaeodium, an aggregate of waste particles within the cell. The term "Radiozoa" has been used to refer to radiolaria when Phaeodarea is explicitly excluded. Phaeodarea produce hollow skeletons composed of amorphous silica and organic material, which rarely fossilize. The endoplasm is divided by a cape with three openings, of which one gives rise to feeding pseudopods, and the others let through bundles of microtubules that support the axopods. Unlike true radiolarians, there are no cross-bridges between them. They also lack symbiotic algae, generally living below the photic zone, and do not produce any Celestine (mineral), strontium sulphate. Taxonomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaeodarea
Phaeodarea, or Phaeodaria, is a group of amoeboid cercozoan organisms. They are traditionally considered radiolarians, but in molecular trees do not appear to be close relatives of the other groups, and are instead placed among the Cercozoa. They are distinguished by the structure of their central capsule and by the presence of a phaeodium, an aggregate of waste particles within the cell. The term "Radiozoa" has been used to refer to radiolaria when Phaeodarea is explicitly excluded. Phaeodarea produce hollow skeletons composed of amorphous silica and organic material, which rarely fossilize. The endoplasm is divided by a cape with three openings, of which one gives rise to feeding pseudopods, and the others let through bundles of microtubules that support the axopods. Unlike true radiolarians, there are no cross-bridges between them. They also lack symbiotic algae, generally living below the photic zone, and do not produce any strontium sulphate. Taxonomy Phylogeny Through p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaeodaria
Phaeodarea, or Phaeodaria, is a group of amoeboid cercozoan organisms. They are traditionally considered radiolarians, but in molecular trees do not appear to be close relatives of the other groups, and are instead placed among the Cercozoa. They are distinguished by the structure of their central capsule and by the presence of a phaeodium, an aggregate of waste particles within the cell. The term "Radiozoa" has been used to refer to radiolaria when Phaeodarea is explicitly excluded. Phaeodarea produce hollow skeletons composed of amorphous silica and organic material, which rarely fossilize. The endoplasm is divided by a cape with three openings, of which one gives rise to feeding pseudopods, and the others let through bundles of microtubules that support the axopods. Unlike true radiolarians, there are no cross-bridges between them. They also lack symbiotic algae, generally living below the photic zone, and do not produce any strontium sulphate. Taxonomy Phylogeny Through p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aulacanthidae
Aulacanthidae is a family of cercozoans in the order Phaeocystida Phaeocystida, also known as Phaeocystina, is a group of cercozoans in the class Phaeodarea. It was first described by Ernst Haeckel in 1887 and treated traditionally as a suborder, but later was raised to order level until Cavalier-Smith Th .... References * Report on the Radiolaria. E Haeckel, 1887 * Report on the scientific results of the voyage of the HMS Challenger during the years 1873–1876. E Haeckel, Zoology series, 1887 External links * Aulacanthidaeat the World Register of Marine Spacies (WoRMS) Phaeodaria Cercozoa families {{Cercozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Haeckel
Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel (; 16 February 1834 – 9 August 1919) was a German zoologist, naturalist, eugenicist, philosopher, physician, professor, marine biologist and artist. He discovered, described and named thousands of new species, mapped a genealogical tree relating all life forms and coined many terms in biology, including ''ecology'', '' phylum'', ''phylogeny'', and ''Protista.'' Haeckel promoted and popularised Charles Darwin's work in Germany and developed the influential but no longer widely held recapitulation theory ("ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny") claiming that an individual organism's biological development, or ontogeny, parallels and summarises its species' evolutionary development, or phylogeny. The published artwork of Haeckel includes over 100 detailed, multi-colour illustrations of animals and sea creatures, collected in his ''Kunstformen der Natur'' ("Art Forms of Nature"), a book which would go on to influence the Art Nouveau artistic mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astracanthidae
''Astracantha'' is a genus of phaeodaria containing the sole species of plankton ''A. heteracantha''. It was first described by the zoologist Valentin Haecker in 1908. It is the only member of the family Astracanthidae, described by Ernst Haeckel in 1887. This genus is characterized by a skeleton or theca In biology, a theca (plural thecae) is a sheath or a covering. Botany In botany, the theca is related to plant's flower anatomy. The theca of an angiosperm consists of a pair of microsporangia that are adjacent to each other and share a commo ... comprised by 30 to 40 hollow spines radiating from the central focal point. Midway along each spine there are numerous short, irregularly spaced, outwardly curved branches that bear terminal thorns proximally (i.e. closer to the cell), but become terminally (i.e. further from the cell) smooth-pointed and slightly thicker. The length of their radial tubes is around 1.8 millimeters. References Phaeodaria {{Cercozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cercozoan
Cercozoa is a phylum of diverse single-celled eukaryotes. They lack shared morphological characteristics at the microscopic level, and are instead defined by molecular phylogenies of rRNA and actin or polyubiquitin. They were the first major eukaryotic group to be recognized mainly through molecular phylogenies. They are the natural predators of many species of microbacteria and Archea. They are closely related to the phylum Retaria, comprising amoeboids that usually have complex shells, and together form a supergroup called Rhizaria. Characteristics The group includes most amoeboids and flagellates that feed by means of filose pseudopods. These may be restricted to part of the cell surface, but there is never a true cytostome or mouth as found in many other protozoa. They show a variety of forms and have proven difficult to define in terms of structural characteristics, although their unity is strongly supported by phylogenetic studies. Diversity Some cercozoans are grouped by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
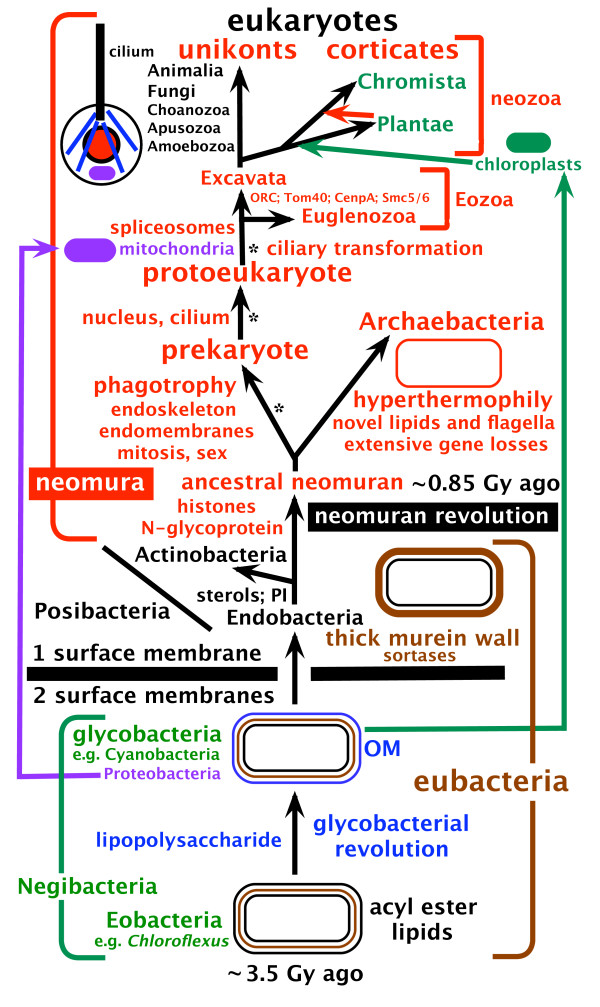
Cavalier-Smith
Thomas (Tom) Cavalier-Smith, FRS, FRSC, NERC Professorial Fellow (21 October 1942 – 19 March 2021), was a professor of evolutionary biology in the Department of Zoology, at the University of Oxford. His research has led to discovery of a number of unicellular organisms (protists) and advocated for a variety of major taxonomic groups, such as the Chromista, Chromalveolata, Opisthokonta, Rhizaria, and Excavata. He was known for his systems of classification of all organisms. Life and career Cavalier-Smith was born on 21 October 1942 in London. His parents were Mary Maude (née Bratt) and Alan Hailes Spencer Cavalier Smith. He was educated at Norwich School, Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge (MA) and King's College London (PhD). He was under the supervision of Sir John Randall for his PhD thesis between 1964 and 1967; his thesis was entitled "''Organelle Development in'' Chlamydomonas reinhardii". From 1967 to 1969, Cavalier-Smith was a guest investigato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |